9.3 Simulated Annealing
Branch-and-Bound
- Find the probable solution first
- If we find a solution, go to the next probable "state" a partial solution
항상 부분해들을 체계적으로 탐색하고 bound를 pruning하여 정확한 최적해를 보장한다.
Simulated Annealing
- Find a complete candidate solution
- If it is not good enough, change some components to go the another "state"
- Assumption: current solution with a minor change its quality so much
항상 완전한 해 하나를 들고 다니면서, 조금씩 변형해 가며 좋은 해를 찾는 확률적 최적화 기법이다.
Search solutions near currently observed good solutions

Branch-and-Bound quality가 나쁜 상태는 중간 단계에서 pruning하고 다시는 탐색하지 않는다. 반대로 SA는 해를 완전히 제거하지 않고 현재 해를 조금씩 변경하면서 주변 해 공간을 계속 탐색한다.
- If quality is bad large change
- If quality is good small change
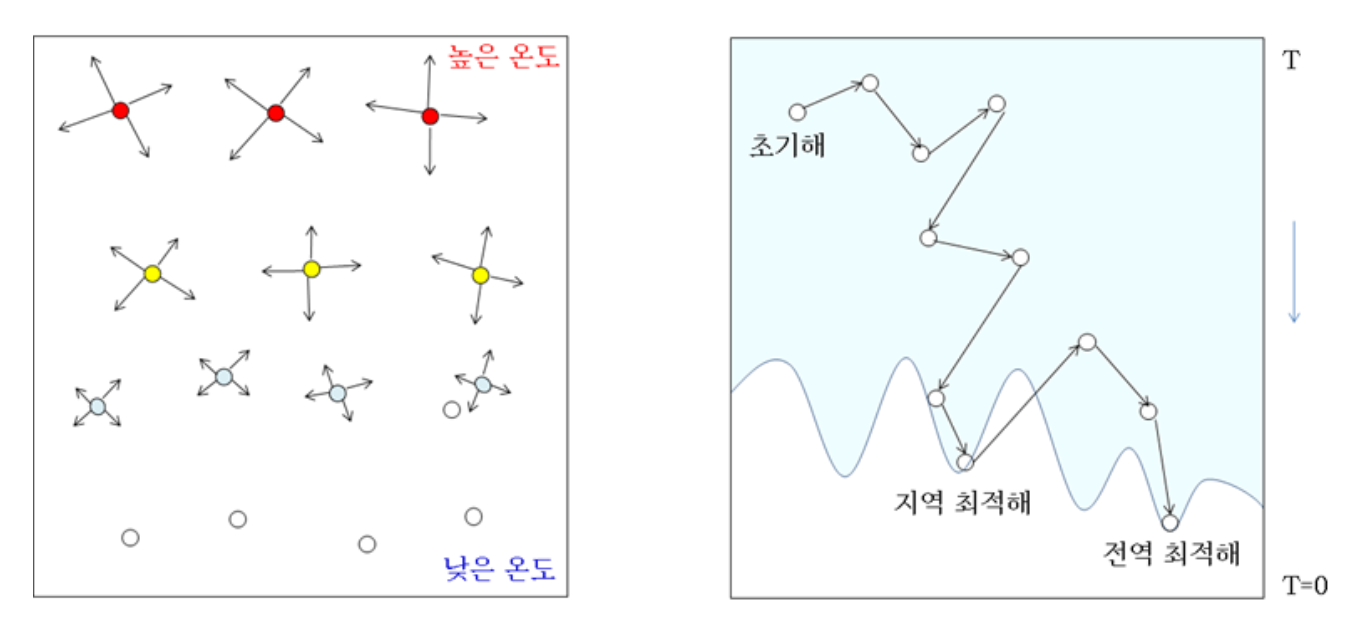
온도 T가 높을 때는 큰 변화도 자주 허용하므로 해가 크게 요동치며 전역 탐색을 시도한다.
- Criterion
- How much change is required for how good solutions?
- Unclear
- An approach
- Control by temperature
9.3.1 SimulatedAnnealing()
- S: 모든 정점을 한 번씩 방문해 이루어진 하나의 cycle
- T: 온도

d가 0 이상(같거나 더 나쁜 해)일 때도, 난수 와 비교해 q < p이면 그 해로 이동하도록 하여 나쁜 해를 확률적으로 가끔 받아들인다.
- Cooling rate
- , 온도가 감소하는 속도 결정
- 가 1에 가까울수록 온도가 천천히 줄어들어 이웃으로의 이동 오래 유지되고 탐색 강해짐
- 작을수록 온도가 빨리 식어 이웃 이동이 빨리 제한되고, 탐색 범위가 좁아짐
- Make movement to a neighbor slow
- Affect exploration strength
- Probability of selecting a randomly generated neighbor p
-
- 초기에는 가 커서 가 크므로 나쁜 해도 비교적 자유롭게 받아들여 다양한 를 탐색할 수 있다.
- 가 클수록(해가 많이 나빠질수록) 는 작아지지만, 0이 되지는 않으므로 지역 최적해에 갇혀도 탈출 가능성이 존재한다.
- Large T high probability to accept a neighbor
- Small T low probability to accept a neighbor
9.3.2 Pre-defined operators for TSP
- How to generate a neighbor?
- Use pre-defined operators (for TSP)
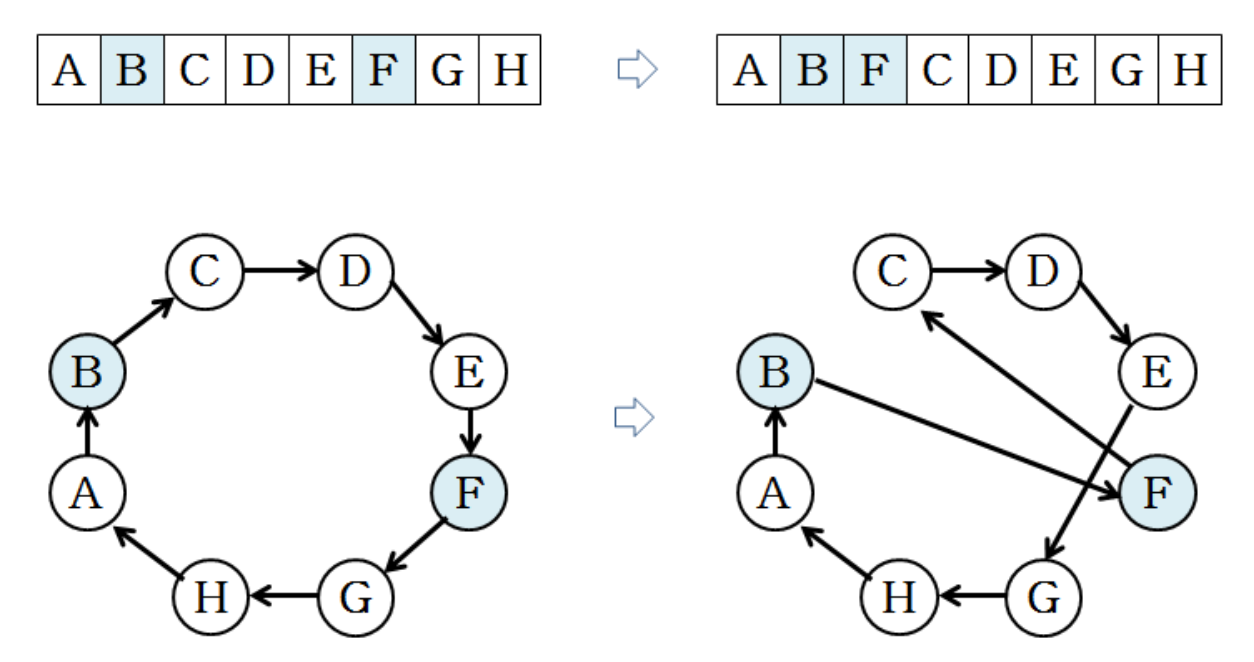
- Insertion
- Switching
- Inversion
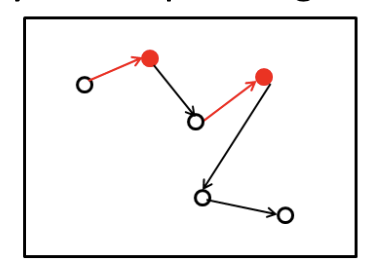
1. Insertion
2. Switching
- 2번의 insertion과 같지만 insertion보다 많은 path의 변화를 일으킨다.
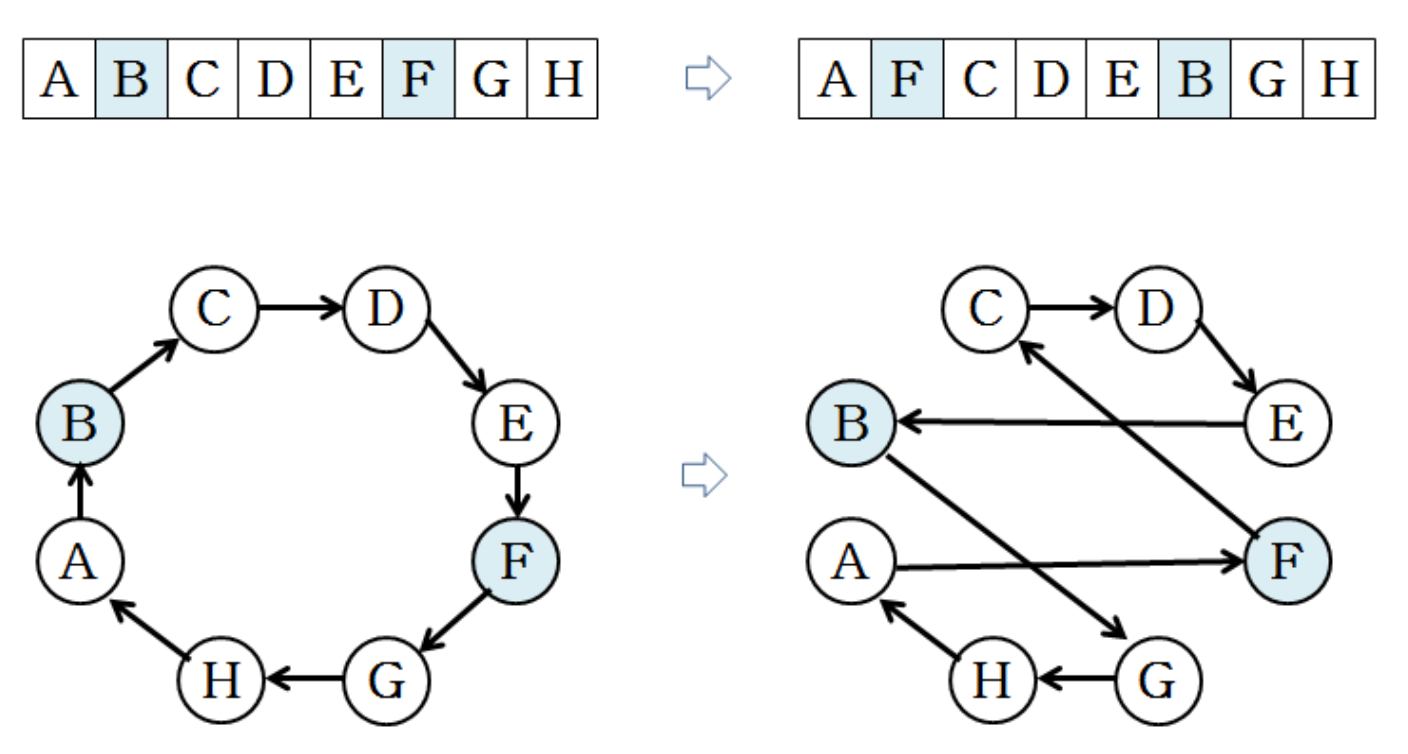
3. Inversion
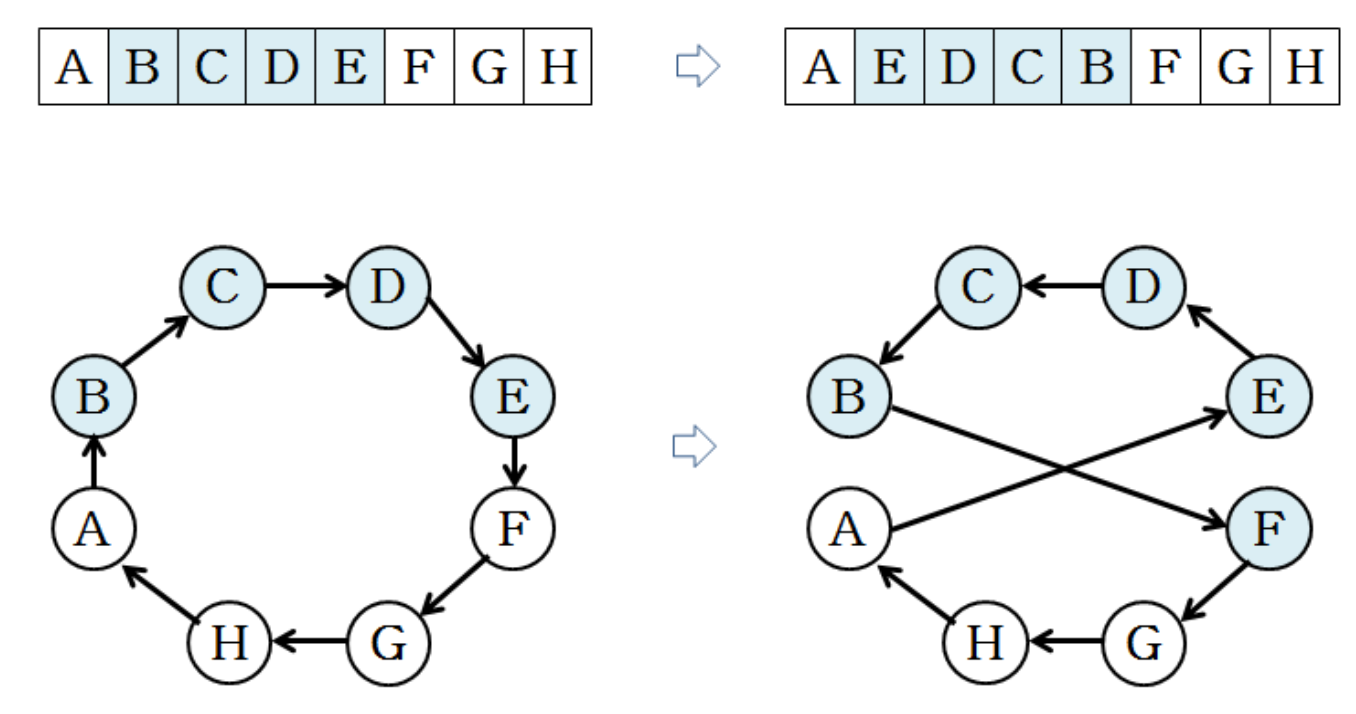
9.4 Genetic Algorithm
Simulated Annealing
- Improve an observed solution
- Determine the next search subspace by the best in the observed samples
좋은 해 하나를 계속 변형하며 탐색하는 알고리즘
Idea of Genetic Algorithm
- Why not improve many samples?
- They may have a good combination for optimal solutions (building block)
- If we can re-combinate the building blocks an optimal solution
좋은 부분 구조를 가진 해들을 여러 개 유지하고, 그 사이에서 교차와 돌연변이 같은 연산으로 모의 담금질처럼 변형을 주되 집단 전체를 진화시키는 방법
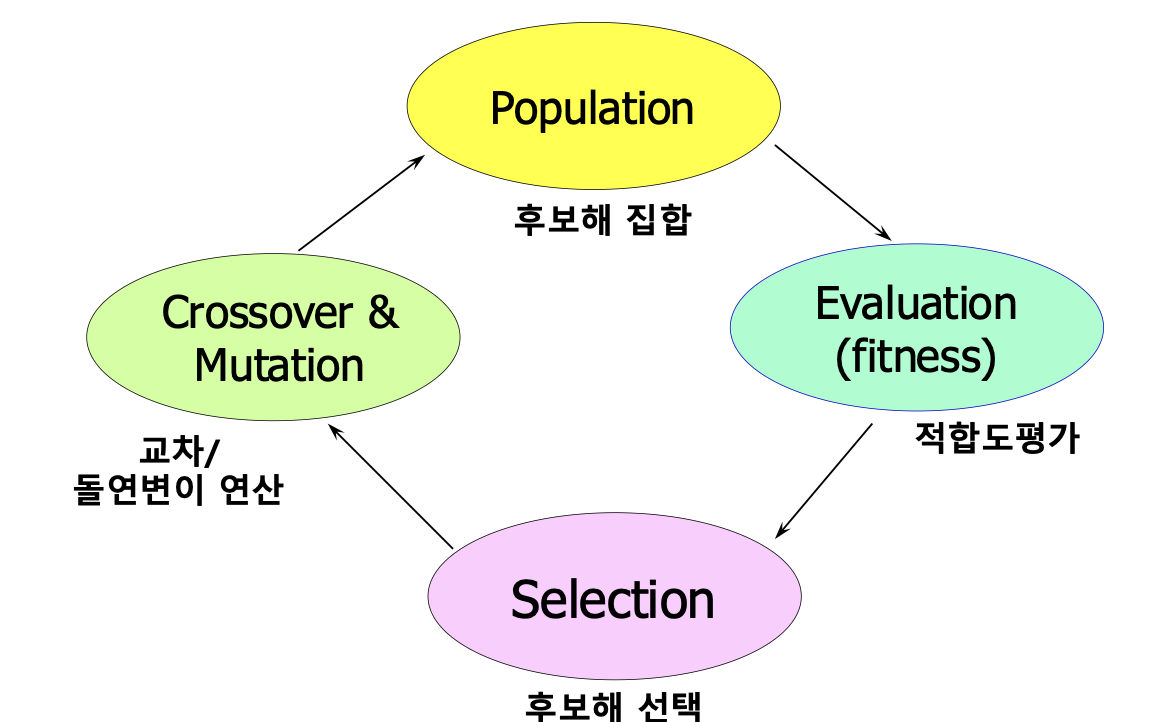
9.4.1 Genetic()
- The simplest from of GA
- G: 세대 t에서의 population
- 개체: population 안에 들어있는 한 개의 해

- Evaluate individuals in
- 각 개체의 fitness를 계산해 평가
- 이 값을 기준으로 좋은 해/나쁜 해를 구분하고 선택, 교차 확률 등에 사용한다.
E.g.,
- TSP: G = {A, B, C, D, E}, stating node = A
- Examples of candidate solutions: ABCDEA, ACDEBA, AECDBA, ...
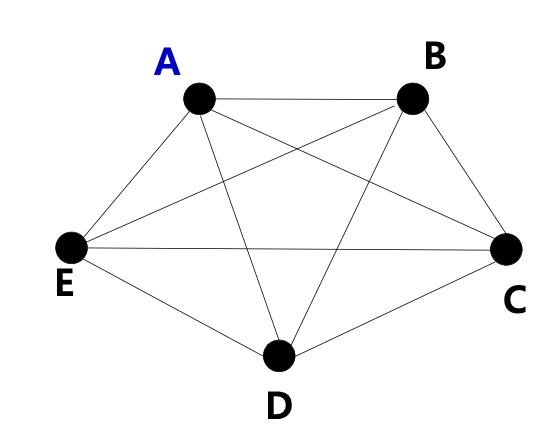
Search Space
- Permutation of 5 nodes = 5! = 120
- (n-1)! for n vertices = (5-1)! = 4! = 24

9.4.2 Fitness Definition
- Fitness = Target objective to optimize
- TSP: minimum weight sum
- Fitness Function(a candidate solution) = weight sum of used edges
- f(ABCDEA) = 5 + 2 + 1 + 3 + 9 = 20

Basic Operator
- Selection
- Crossover
- Mutation
- .. many other operators exist
1. Selection
- Determines which individuals will be "selected" for the next generation
- Issues
- How many individuals?
- How good individuals?
- How diverse individuals?
- Elitism
Roulette Wheel Selection
- The simplest selection method
- Probability is assigned by fitness
- Probability of selecting sample A
- f(A) / sum(f(i) for all i)
- Issues
- Relative ratio
- Absolute ratio
- Adaptive ratio
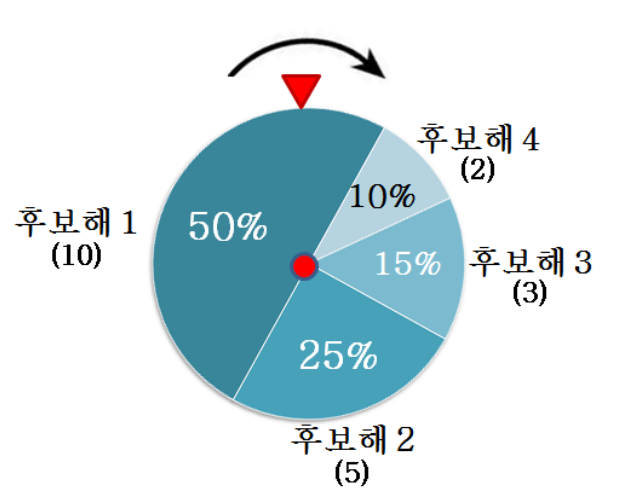
- Evaluate a multinomial distribution
- Repeat sampling
- Issue
- Duplicated sampling
- Others: Tournament Selection, ...
2. Crossover
- A process to compose building blocks
- One-point crossover
- two-point crossover

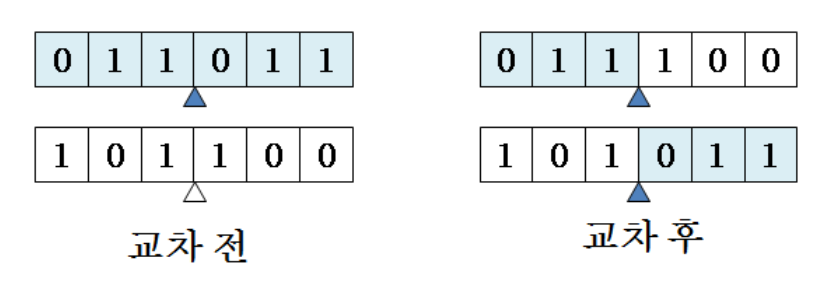
- Probability controls the probability of searching better solutions
- 101011 is the optimal solution
- The probability of applying crossover: p
- The probability of selecting crossover point: 1/5
- p/5: the probability of finding the optimal solution from the above two parents
3. Mutation 돌연변이
- Introduce a mutation to a candidate solution
- Small change
- Probability of applying mutation in a solution: p
- Issue
- How large probability with respect to population size, individual length
어떤 위치의 bit 하나를 filp하는 것을 의미한다.
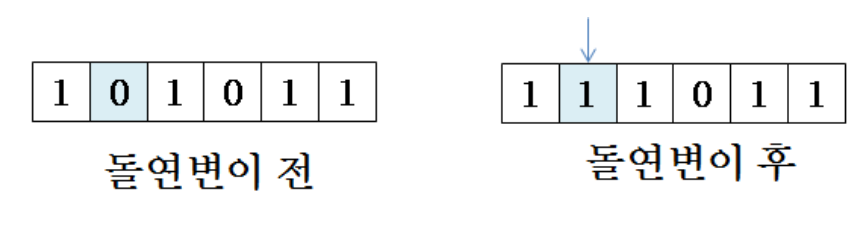
- Break found building blocks
- Used for increasing diversity
- Expect a small probability to observe
- 돌연변이 확률은 작게 잡지만, 그 작은 확률 덕분에 완전히 새로운 building block이 가끔 등장하길 기대한다.
- If composin building blocks do nt increase fitness monotonically, the mutation is more effective
very strong dependency between elemetns - Mutation Rate: (1/PopSize) ~ (1/Length)
염색체 내 요소들 사이 상호 의존성이 강해서 부분 최적 구조의 단순 조합으로는 전역 최적해를 만들기 어려운 경우, 기존 building block을 깨고 완전히 다른 조합을 만드는 돌연변이가 오히려 더 효과적일 수 있다.
돌연변이 연산 역할
돌연변이 연산 후
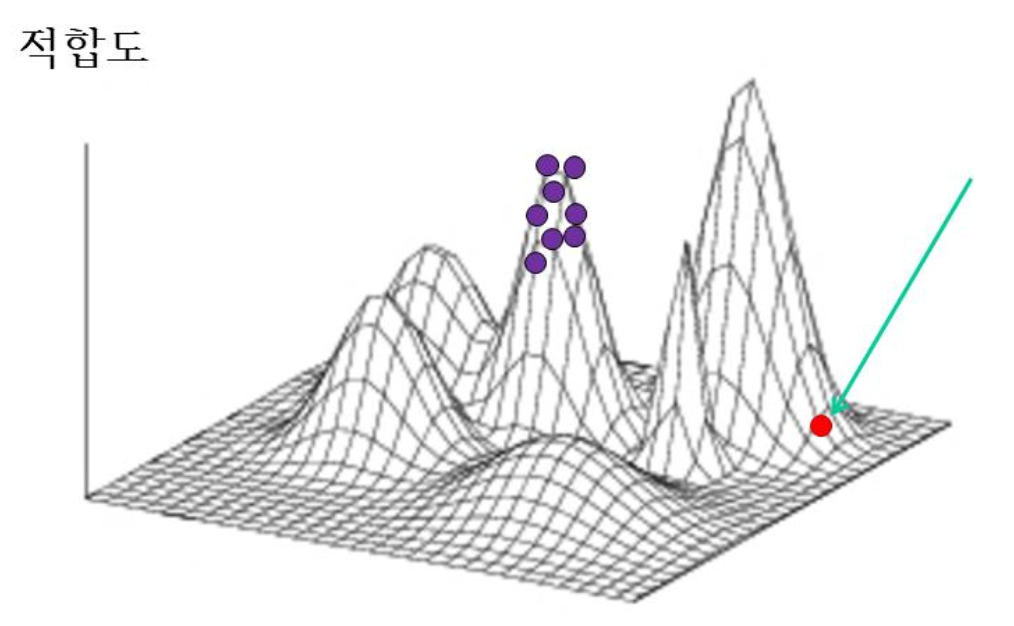
여러 세대가 지난 후
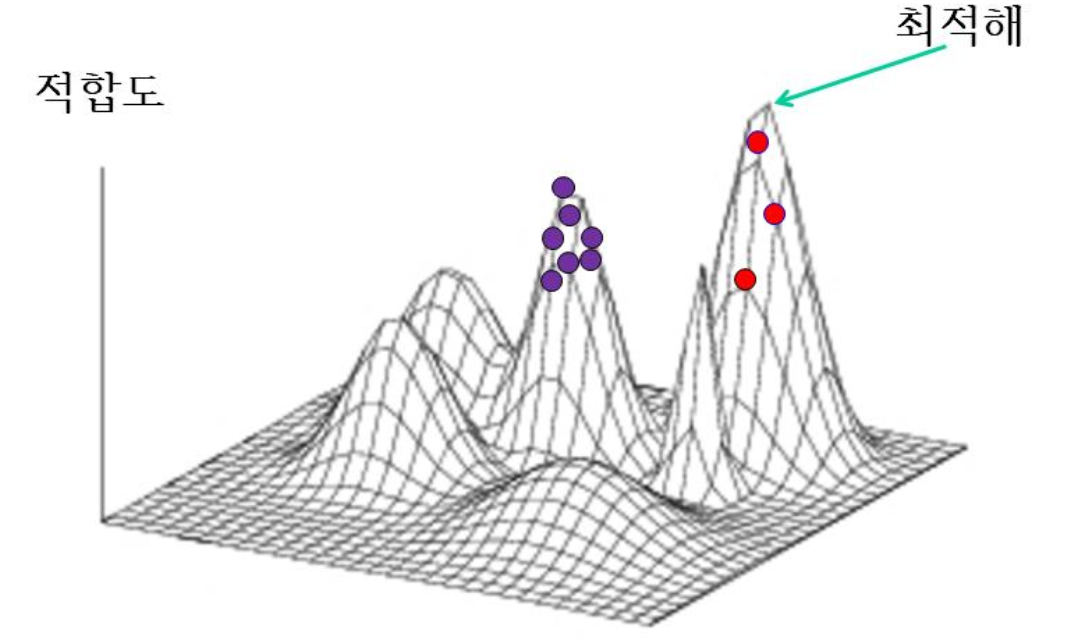
Terminating Condition
- Not constant
- No guarantee that the genetic algorithm will always find an optimal solution
- In general, the algorithm is terminated when no more good solutions emerge during the execution of the algorithm threshold
9.4.3 Example of Running GA
- Find an to maximize in the range
- Population size: 4
- Selection at the first generation: 1, 29, 3, 10 (assume)
- Fitness of the selected individuals
- f(1) = 117
- f(29) = 341
- f(3) = 185
- f(10) = 360
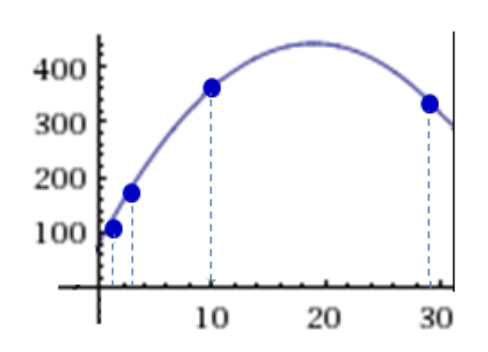
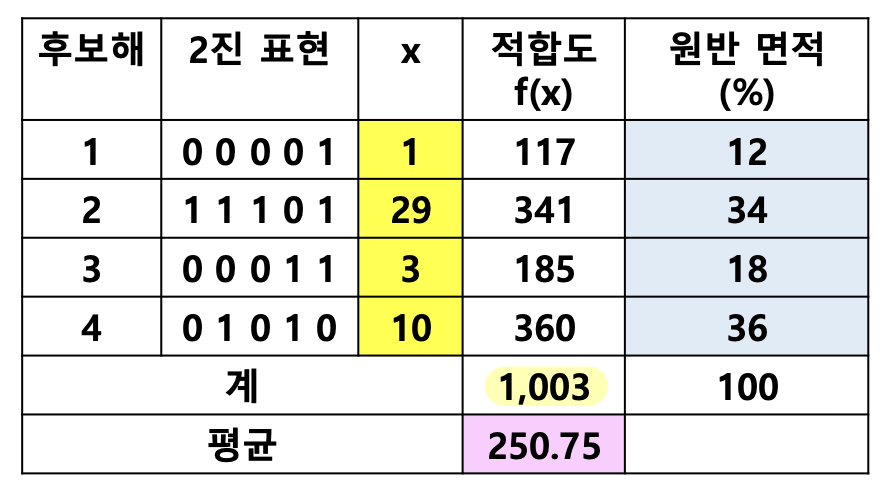
- Roulette-Wheel Selection
- Average fitness in the population: 250.75
Selection
- Non-deterministic, assumption
- 2 x id4, 1 x id2, 1 x id3, 0 x id1
Crossover
- Non-deterministic, assumption
- id2 + id4, id3 + id4
- One point crossover
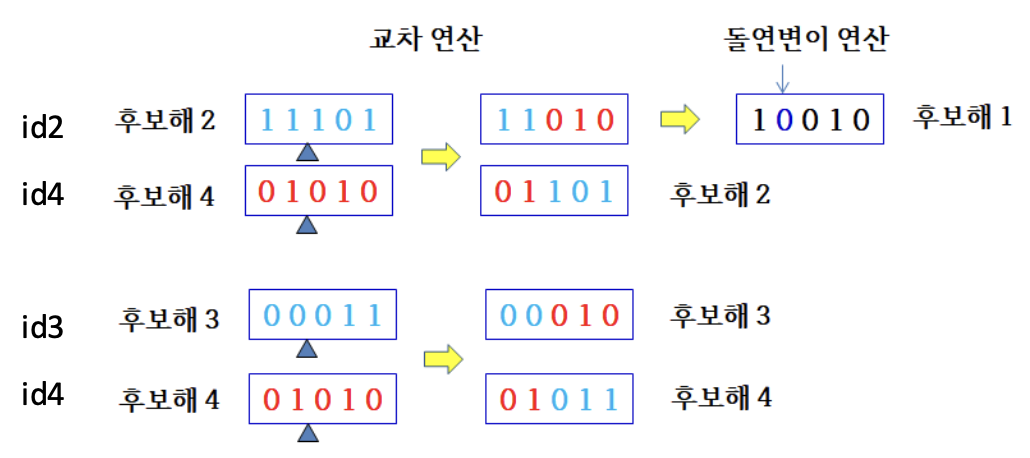
Mutation
- Non-deterministic, assumption
- Generated samples by crossover are mutated
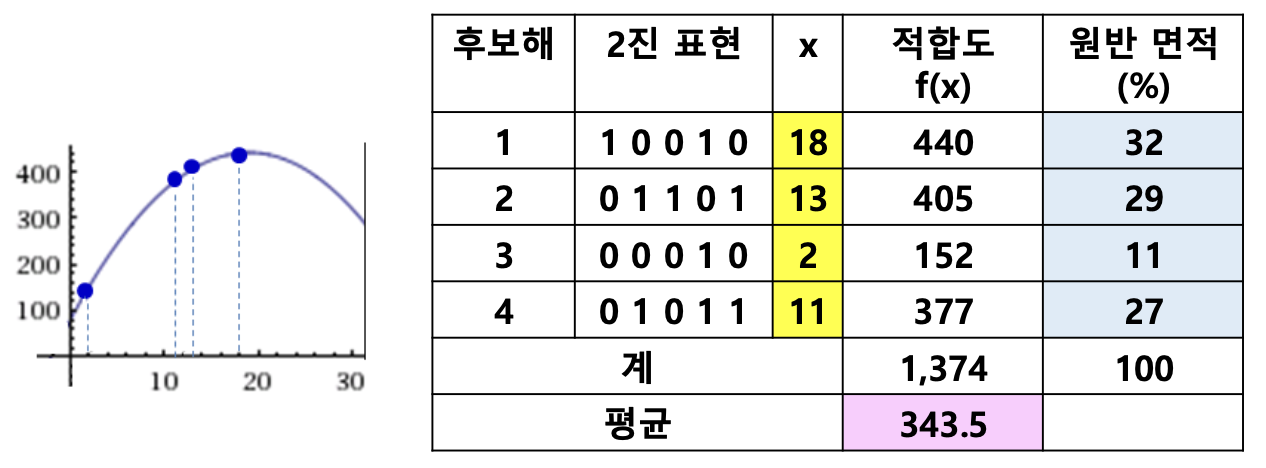
- Average fitness of population at the second generation: 343.5
- Repeat until, the best solution is not improved anymore
9.4.4 Genetic Algorithm for TSP
- Various crossover operators
1. Two-point crossover
- Select two points
- Can represent more expressive building blocks
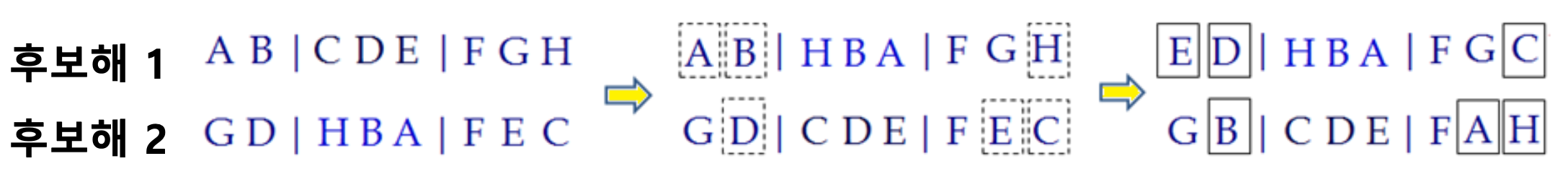
교차 구간은 고정이다.
2. Cycle crossover
- One-point exchange
- Repeat until two solutions make complete solutions
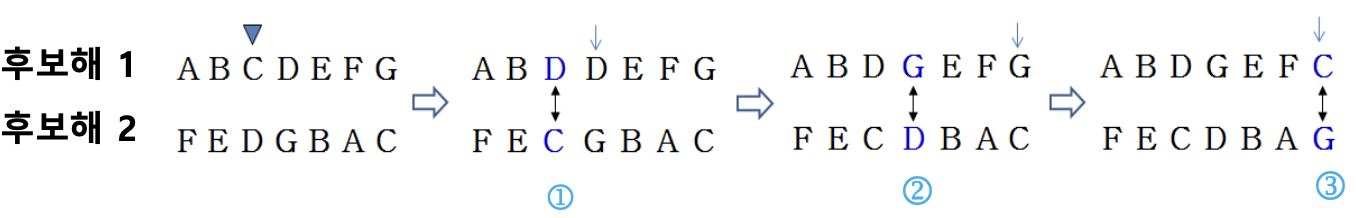
System parameters to empirically tune
- Population size
- Selection operator
- Crossover rate
- Mutation rate
- Terminating condition
To improve performance
- Chromosome representation
- Operator bias in selecting next subspace for search
- Exploration and exploitation control
- Elitism
9.4.5 Advanced Algorithms
- Control of selecting the next search space
- Probabilistic Model(Estimation of distribution algorithm, CMA-ES)
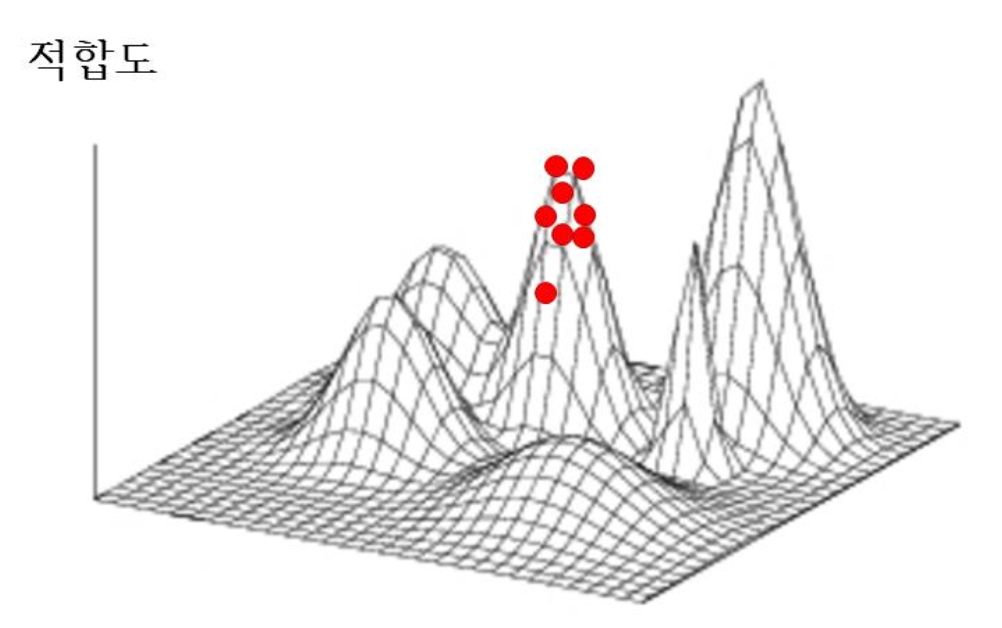
- Multimodal optimization
- Find k-best solutions independently (particle swarm optimization)
- Bi-population
- Optimize many objectives (not a single objective form of many objectives) (multi-objective optimization)
- Searching best model (not a single solution for a model)
- Genetic programming
- Many and many algorithms ...
9.4.6 Applications
- Very good performance for complex problems in general
- Bin-packing
- Task-scheduling
- TSP
- Knapsack problem
Practical Applications
- Robotics
- Signal processing
- Circuit design
- Flight design
- Communication optimization
- Any problem can be solved by GA
- Area: machine learning, pattern recognition, evolutionary computation
