PostgreSQL
- Relational Database Management System
- Post-gress라고 발음. (QL은 생략)
- ANSI-SQL:2008 compatible (가장 Oracle-compatible)
DBA creates Users and Databases
bard@mac: ~$ psql
psql (14.7 ...)
postgres=#새로운 유저 생성
postgres=> CREATE USER bard with encrypted password 'changethis';DB 생성 및 권한 부여
postgres=> CREATE DATABASE bard;
postgres=> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES on database bard TO bard;유저 로그인
bard@mac: ~$ psql -h localhost -U bard
Password for user bard: changethis
psql (14.7 (…))
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, …)
Type "help" for help.
bard=>psql Command Line options
-d name,--dbname name: 데이터베이스 이름-c sql,--command sql: sql 명령 실행- 등등 있음..
psql Meta commands
\l: 존재하는 데이터베이스 리스트\c db_name: 해당 db에 연결\d: 모든 테이블 보여줌\d table: 그 테이블에 대한 정보 보여줌\i file_name: 해당 파일을 읽어서 query buffer에 입력\q: 종료\! command: Linux 커맨드 실행- 등등 있음..
데이터 파일 입력
Fluffy Harold cat f 1993-02-04 \N
Claws Gwen cat m 1994-03-17 \N
Buffy Harold dog f 1989-05-13 \N
Fang Benny dog m 1990-08-27 \N
Bowser Diane dog m 1979-08-31 1995-07-29
Chirpy Gwen bird f 1998-09-11 \N
Whistler Gwen bird \N 1997-12-09 \N
Slim Benny snake m 1996-04-29 \N이 txt 파일을 입력하려면:
bard => COPY myTable FROM 'pet.txt' (FORMAT CSV, DELIMITER('\t'));SQL
DDL: Data Definition Language
- SQL의 DDL은 관계에 대한 명세를 쓸 수 있음
- 각 Relation의 스키마
- 각 attirube에 연결된 값의 도메인(정의역)
- 무결성 조건
- 인덱스 집합
- 각 Relation에 대한 보안과 인가 정보
- 물리적 저장소 구조
Domain types in SQL
char(n): n 고정 길이 문자열varchar(n): 최대 n 가변 길이 문자열int: 정수smallint: 작은 정수numeric(p,d): 고정소수점 실수real: 부동소수점 실수float(n): 최소 n개 숫자를 갖는 부동소수점 소수
Create Table
create table instructor (
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2));Integrity Constraints
not nullprimary key (A1, ..., An)foreign key (A1, ..., An) references r
예)
create table instructor (
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2),
primary key (ID),
foreign key (dept_name) references department)primary key는 자동으로 not null
Drop and Alter Table Constructs
drop table student: 테이블 스키마와 내용을 날려버림delete table student: 테이블 내용만 날림(DML)alter tablealter table r add A D- r 테이블에 D 도메인을 갖는 A attribute를 추가
alter table r drop A- attribute 제거는 많은 DB에서 지원하지 않음
DML (Data-Manipulation Language)
- select/insert/update/delete
- set operations
- ordering
- aggregate functions
- nested subqueries
- 일반적인 SQL 쿼리는 아래처럼 생김
select A1, A2, ... An
from r1, r2, ..., rm
where P- SQL 쿼리의 결과도 relation임.
select 문
- select 문은 attribute를 나열함
- projection operator 에 대응
- SQL은 case insensitive하므로 다음이 성립함
- 또 SQL은 중복을 허용하므로 중복을 제거하기 위해서는
distinct키워드를select다음에 써줘야함
select distinct dept_name
from instructor- asterisk는 모든 attribute를 의미함
select *
from instructor- 산술연산자
+,-,*,/를 혀용함
select ID, name, salary/12
from instructorwhere 문
- where은 결과가 반드시 만족해야하는 조건을 명시함
- boolean 연산자 (
and,or,not) - 비교 연산자 (
<,>,=, ...)
select name
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Comp. Sci.'
and salary > 80000from 문
- 카테시안 곱 ()에 대응됨
select *
from instructor, teachesJoin ()
select name, course_id
from instructor, teaches
where instructor.ID = teaches.IDselect section.course_id, semester, year, title
from section, course
where section.course_id = course.course_id
and dept_name = 'Comp. Sci.'
Natural Join
natural join은 공통되는 열을 딱 한 세트만 유지함
select *
from instructor
natural join teaches;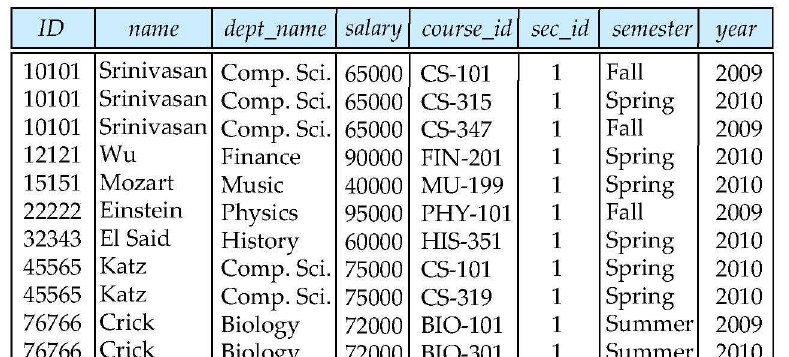
Danger in Natural Join
- 같은 이름을 가진 관련없는 attribute를 조심해야 함
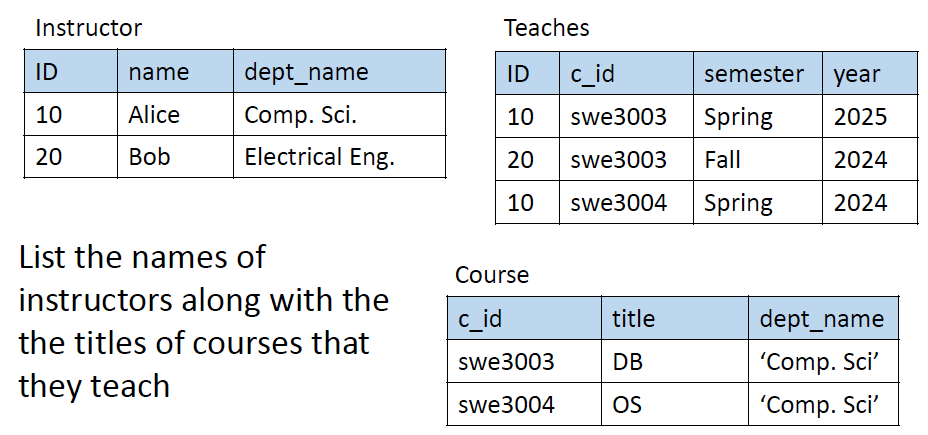
- 이 문제에서 아래와 같이 쿼리를 짜면 instructor.dept_name이 course.dept_name과 같아야하는 조건이 추가로 생김
select name, title
from instructor
natural join teaches
natural join course;- 그래서 이렇게 바꿔야 함
select name, title
from instructor
natural join teaches, course
where teaches.course_id = course.course_id;Rename () Operation
- as 문을 통해 이름을 바꿀 수 있음
select ID, name, salary/12 as monthly_salary
from instructor- as는 생략 가능 (Oracle DBMS에서는 반드시 생략)
select ID, name, salary/12 monthly_salary
from instructorString Operations
- 문자열 매칭 연산자
=,like- percent
%- 어떤 부분문자열이든 가능 - underscore
_- 문자 한개
- percent
- 이름에
dar이 들어가는 instructor들의 이름을 출력
select name
from instructor
where name like '%dar%'- 100%라는 문자열을 찾으려면
where percentage like '100\%' escape '\'- 패턴은 case sensitive함
- 여러 문자열 연산이 가능
- concatenation (using
||) UPPER(),LOWER()LENGTH(),SUBSTRING(str, position, length)
- concatenation (using
Sorting: order by 문
- 모든 instructor를 이름의 알파벳 순서로 출력
select name
from instructor
order by nameRange query and tuple comparison
between
select name
from instructor
where salary between 90000 and 100000- 순서쌍 비교
select name, course_id
from instructor, teaches
where (instructor.ID, dept_name) = (teaches.ID, ’Biology’);집합 연산
union,intersect,except- 위 연산들은 자동으로 중복을 제거함
- multiset 연산을 사용하면 중복을 유지함
union all,intersect all,except all
(select c_id
from course
where semester = 'Fall' and year = 2024)
union
(select c_id
from course
where semester = 'Spring' and year = 2025)Null
- null은 알수 없는 값이나 존재하지 않는 값을 의미
is null로 null check
select name
from instructor
where salary is nullThree Valued Logic
null과의 비교연산은 항상unknown을 반환함5 < null,null <> null,null = null
- Three valued logic은 진리값
unknown을 추가함(unknown or true) = true(unknown or false) = unknown(unknown or unknown) = unknown(unknown and true) = unknown(unknown and false) = false(unknown and unknown) = unknown(not unknown) = unknown
P is unknown은P가unknown일때만true- where문에서
unknown의 결과는false로 처리
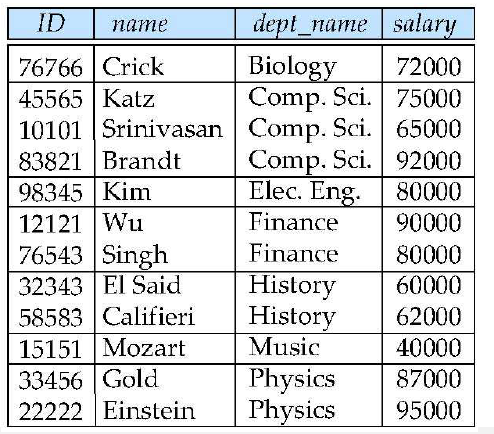
Aggregate Functions
- avg, min, max, sum, count
- 멀티셋의 column에 대해서 연산을 수행함
select avg(salary)
from instructor
where dept_name= 'Comp. Sci.';select count(distinct ID)
from teaches
where semester = 'Spring'
and year = 2014select count(*)
from course;Aggregate functins - group by
select dept_name, avg(salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name;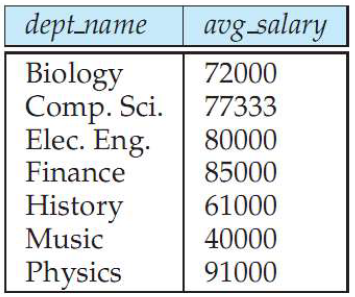
- instructor가 없는 department는 나오지 않음
- select 문에서 aggregate함수 없이 사용하는 attribute는 반드시
group by뒤에도 있어야 함.
/* erroneous query */
select dept_name, ID, avg(salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name;- 은 Group할 attribute들
- 는 aggregate function
- 는 attribute
Aggregate functions - having
select dept_name, avg(salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name
having avg(salary) > 42000;Null and Aggregation
select sum(salary), avg(salary)
from instructor- 여기에서 salary가 null인 튜플은 무시됨
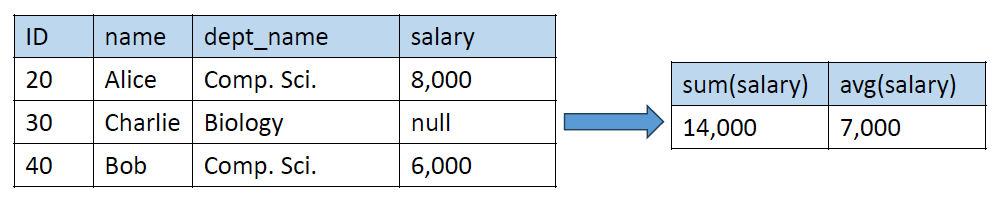
- 모두 null이면 null이 됨
count(*)를 제외한 operation들은 null이 있는 tuple을 무시함
Nested Subquery
-
set membership test(in, not in)
-
set comparison (some, all)
-
set cardinality
-
Find IDs of students who take DB class
select student_id
from Take
where course_id IN
(select course_id
from Course
where title = 'DB')- Find names of students who do not take DB class
select student_name
from Student
where student_id NOT IN
(select student_id
from Take
where course_id IN
(select course_id
from Course
where title = 'DB'))- Find the total number of (distinct) students take course taught by the instructor with ID 10101
select count(distinct ID)
from takes
where c_id IN
(select course_id
from teaches
where teaches.ID = 10101);Set Comparison - some
- Biology department에서 적어도 한명보다 salary가 높은 instructor들의 이름을 찾으시오
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T, instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary
and S.dept_name = 'Biology';이건 some 문을 이용해서 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있음
select name
from instructor
where salary > some
(select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Biology');Definition
all
select name
from instructor
where salary > all
(select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Biology');Definition
빈 Relation 테스트: exist
- exist는 subquery가 nonempty라면 true를 반환함
Correlation Variables
- correlated subquery는 subquery가 바깥 쿼리의 값에 의존하는 경우임.
- 적어도 한개 이상의 수업을 들은 학생의 이름들을 출력하시오
select distinct name
from Student s
where exists
(select 1
from Take t
where t.ID = s.ID);- Biology department에서 모든 수업을 들은 모든 학생을 출력
select distinct S.ID, S.name
from student as S
where not exists
((select course_id
from course
where dept_name = 'Biology')
except
(select T.course_id
from takes as T
where S.ID = T.ID));중복 tuple의 존재 검사
- unique: 서브쿼리의 결과에서 중복이 없을때만 true
select T.course_id
from course as T
where unique
(select R.course_id
from section as R
where T.course_id = R.course_id
and R.year = 2009);From 문에서의 subquery
select dept_name, avg_salary
from (select dept_name,
avg(salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
group by dept_name)
where avg_salary > 42000;with문
- with은 임시적인 view를 정의할 수 있음.
with max_budget(value) as
(select max(budget)
from department)
select budget
from department, max_budget
where department.budget = max_budget.value;with을 이용한 복잡한 쿼리
with dept_total(dept_name, value) as
(select dept_name, sum(salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name),
dept_total_avg(value) as
(select avg(value)
from dept_total)
select dept_name
from dept_total, dept_total_avg
where dept_total.value >= dept_total_avg.value;Scalar Subquery
- 한개 값만 기대하는 subquery
select dept_name,
(select count(*)
from instructor
where department.dept_name = instructor.dept_name) as num_instructors
from department;- 한개 이상의 tuple이 반환되면 에러
delete from
- 모든 instructor 삭제
delete from instructordelete from instructor
where dept_name = 'Finance';- Watson building에 위치한 department와 연관된 instructor 삭제
delete from instructor
where dept_name in
(select dept_name
from department
where building = 'Watson');- 평균 급여보다 급여가 적은 instructor들 삭제
delete from instructor
where salary <
(select avg(salary)
from instructor);위 케이스에서 tuple을 삭제할때마다 평균 salary가 변화하게됨.
SQL은 이를 해결하기 위해
- 우선 avg salary를 사용해서 삭제할 모든 tuple을 검색하고
- 그 이후에 위에서 찾은 tuple을 제거함
insert into
insert into course
values ('CS-437', 'Database Systems', 'Comp. Sci.', 4);이는 아래와 동치
insert into course (course_id, title, dept_name, credits)
values ('CS-437', 'Database Systems', 'Comp. Sci.', 4);- 모든 instructor를 student relation에 추가
insert into student
select ID, name, dept_name, 0
from instructorupdate set
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.03
where salary > 100000;
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.05
where salary <= 100000;- 만약 이 두 순서를 바꾼다면? 문제가 발생한다.
- 이때는 case문을 사용 가능
update instructor
set salary = case
when salary <= 100000 then salary * 1.05
else salary * 1.03
endScalar subquery를 이용한 update
update student S
set tot_cred =
(select sum(credits)
from takes
natural join course
where S.ID = takes.ID
and takes.grade <> 'F'
and takes.grade is not null);- 만약 들은 과목이 없다면 tot_creds를 null로 설정할 것임.
update student S
set tot_cred =
(select case
when sum(credits) is not null then sum(credits)
else 0
end
from takes
natural join course
where S.ID = takes.ID
and takes.grade <> 'F'
and takes.grade is not null);