정리한 내용 중 잘못된 내용이 있을 수 있습니다. 잘못된 내용이 있다면 꼭 알려주세요.
1.자료구조 vs 객체
| 자료구조(Data Structure) | 객체(Object) |
|---|---|
| 데이터 그 자체 | 비지니스 로직과 관련 |
| 자료를 공개한다. | 자료를 숨기고, 추상화한다. 자료를 다루는 함수만 공개한다. |
| 변수 사이에 조회 함수와 설정 함수로 변수를 다룬다고 객체가 되지 않는다.(getter, setter) | 추상 인터페이스를 제공해 사용자가 구현을 모른 채 자료의 핵심을 조작할 수 있다. |
1-1.Vehicle 예제
//자료구조
public interface Vehicle {
double getFuelTankCapacityInGallons(); // 연료탱크 용량(갤런 단위)
double getGallonsOfGasoline(); // 가솔린(갤런 단위)
}
public class Car implements Vehicle {
double fuelTankCapacityInGallons;
double gallonsOfGasoline;
public double getFuelTankCapacityInGallons() {
return this.fuelTankCapacityInGallons;
}
public double getGallonsOfGasoline() {
return this.gallonsOfGasoline;
}
}//객체
public interface Vehicle {
double getPercentFuelRemain();
}
public class Car implements Vehicle {
double fuelTankCapacityInGallons;
double gallonsOfGasoline;
public Car(double fuelTankCapacityInGallons, double gallonsOfGasoline) {
if (fuelTankCapacityInGallons <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fuelTankCapacityInGallons must be greater than zero");
}
this.fuelTankCapacityInGallons = fuelTankCapacityInGallons;
this.gallonsOfGasoline = gallonsOfGasoline;
}
public double getPercentFuelRemain() {
return this.gallonsOfGasoline / this.fuelTankCapacityInGallons * 100;
}
}1-2.Shape 예제
public class Square {
public Point topLeft;
public double side;
}
public class Rectangle {
public Point topLeft;
public double height;
public double width;
}
public class Circle {
public Point point;
public double redius;
}
public class Geometry {
public final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
public double area(Object shape) throws NoSuchShapeException {
if (shape instanceof Square) {
Square s = (Square)shape;
return s.side * s.side;
} else if (shape instanceof Rectangle) {
Rectangle r = (Ractangle)shape;
return r.height * r.width;
} else if (shape instanceof Circle) {
Circle c = (Circle)shape;
return PI * c.redius * c.redius;
}
throw new NoSuchShapeException();
}
}절차적인 코드는 새로운 자료 구조를 추가하기 어렵다. 함수를 고쳐야 한다.
public class Square implements Shape {
private Point point;
private double side;
public double area() {
return side * side;
}
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
private Point topLeft;
private double height;
private double width;
public double area() {
return height * width;
}
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
private Point center;
private double redius;
public final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
public double area() {
return PI * c.redius * c.redius;
}
}자료구조와 객체는 상황에 맞게 선택하면 된다.
- 자료구조를 사용하는 절차적인 코드는 기본 자료 구조를 변경하지 않으면서 새 함수를 추가하기 쉽다.
- 절차적인 코드는 새로운 자료 구조를 추가하기 어렵다. 그러려면 모든 함수를 고쳐야 한다.
- 객체 지향 코드는 기존 함수를 변경하지 않으면서 새 클래스를 추가하기 쉽다.
- 객체 지향 코드는 새로운 함수를 추가하기 어렵다 그러려면 모든 클래스를 고쳐야 한다.
2.객체 - 디미터의 법칙
클래스 C의 메서드 f는 다음과 같은 객체의 메서드만 호출해야 한다
- 클래스 c
- 자신이 생성한 객체
- 자신의 인수로 넘어온 객체
- C 인스턴스 변수에 저장된 객체
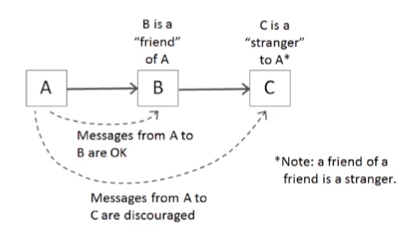
위 그림을 보면 A의 의존성을 가진 B가 있다.
A에서 B를 호출하는 건 괜찮다.
하지만 A에서 C를 호출하는건 안된다고 하는 것이 디미터의 법칙이다.
예를들면 계층형 아키텍처에서 controller에서 service를 호출하는건 괜찮지만,
controller에서 repository를 호출하는건 안된다.
내 친구까지만 호출하고, 내 친구의 친구는 호출하지 말자.
책에서 휴리스틱이라는 개념이 나온다.
휴리스틱: 경험에 기반하여 문제를 해결하기 위해 발견한 방법
의사결정을 단순화하기 위한 법칙들 -> 경험적으로 만들어낸 법칙
우리가 배우는 클린코드도 휴리스틱이다.
기차 충돌
디미터의 법칙을 알아보고자 할때 기차 충돌에 관한 개념이 등장한다.
디미터의 법칙에 어긋나는 상황인 기차 충돌의 코드를 보자.
// 객체 - 기차 충돌, 디미터의 법칙 위배
final String outputDir = ctxt.getOptions().getScratchDir().getAbsolutePath();
// 자료구조 - OK
final String outputDir = ctxt.options.scratchDir.absolutePath;
// 객체에 대한 해결책이 아니다. getter를 통했을 뿐, 값을 가져오는 것은 자료구조이다.
ctxt.getAbsolutePathOfScratchDirectoryOption();
ctxt.getScratchDirectoryOption().getAbsolutePath();
// 왜 절대 경로로 가져올까.. 근본 원인을 생각해보자!
// 객체는 자료를 숨기고 자료를 다루는 함수만 공개한다.
BufferedOutputStream bos = ctxt.createScratchFileStream(classFileName);3.DTO
DTO(Data Transfer Object) = 자료구조
다른 계층 간 데이터를 교환할 때 사용
- 로직없이 필드만 갖는다.
- 일반적으로 클래스명이 Dto(or DTO)로 끝난다
- getter/setter를 갖기도 한다.
*beans
Java Beans: 데이터 표현이 목적인 자바 객체
- 멤버 변수는 private 속성이다.
- getter와 setter를 가진다.
public class AddressDto {
private String street;
private String zip;
public AddressDto(String street, Strin zip) {
this.street = street;
this.zip = zip;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getZip() {
return zip;
}
public void setZip(String zip) {
this.zip = zip;
}
}4.Active Record
public class Employee extends ActiveRecord {
private String name;
private String address;
...
}
// ----
Employee bob = Employee.findByName("Bob Martin");
bob.setName("Robert C. Martin");
bob.save();Active Record는 Database row를 객체에 맵핑하는 패턴
- 비지니스 로직 메서드를 추가해 객체로 취급하는건 바람직하지 않다.
- 비지니스 로직을 담으면서 내부 자료를 숨기는 개체는 따로 생성한다.
- 하지만.. 객체가 많아지면 복잡하고, 가까운 곳에 관련 로직이 있는 것이 좋으므로 현업에서는 Entity에 간단한 메서드를 추가해 사용한다.
Active Record Vs Data Mapper
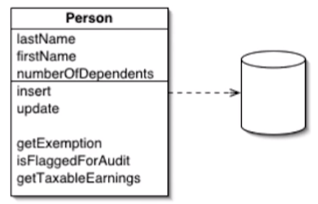
Acrive Record
- 객체가 row를 담을 뿐 아니라 Database에 대한 접근을 포함한다.
- Person의 속성을 담을 뿐 아니라, 생성 수정도 객체 안에서 수행할 수 있다.
- 사례 - Ruby on rails
Data Mapper
- row를 담는 객체와 database에 접근할 수 있는 객체가 분리되어 있다.
- Person은 값만 담고 있고, 생성 수정 등 액션은 Person Mapper에서 담당한다.
- 사례 - Hibernate
