Spring Framework
좋은 객체 지향 설계
객체 지향 프로그래밍
- 속성과 행위가 정의된
객체들의 모임을 파악 - 각각의 객체는 메시지를 주고 받고, 데이터를 처리(협력)
- 유연하고 변경에 용이
- 객체 지향 프로그램의 특징
- 캡슐화
- 상속성
- 추상화
다형성
역할과 구현을 분리
역할과 구현으로 구분하면 단순, 유연해짐- ex.연극에서 배역에 따라 배우가 달라질 수 있는 것
인터페이스- 역할
- 클라이언트는 역할(인터페이스)만 알고, 내부구조(구현체)에 의존적이지 않아야 함
구현체- 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스
다형성
- 클라이언트는 인터페이스에 의존하고, 실행 시점에서 유연하게 변경 가능해야 함
- 클라이언트를 변경하지 않고, 서버의 구현 기능을 유연하게 변경할 수 있어야함
SOLID 5가지 원칙
-
SRP(Single Responsibility Principle)
- 단일 책임 원칙
- 한 클래스는 하나의 책임을 가져야 함
변경에 대한 파급 효과가 적어야 함
-
OCP(Open/Closed Principle)- 개방 폐쇄 원칙
- 확장에는 열려 있고, 변경에는 닫혀 있어야 함
- 인터페이스(역할)를 구현한 기능을 구현체를 통하여 확장
- 클라이언트는 인터페이스를 의존하여 변경을 하지 않아야 함
-
LSP(Liskov Substitution Principle)
- 리스코프 치환 원칙
- 객체는 정확성을 깨뜨리지 않으면서 하위 객체로 바꿀 수 있어야 함
- 컴파일 영역의 문제가 아님
- ex. 자동차에서 엑셀은 앞으로 가는 기능 → 이 기능이 깨지면 안됨
-
ISP(Interface Segregation Principle)
- 인터페이스 분리 원칙
- 하나의 범용 인터페이스 X → 특정 클라이언트를 위한 인터페이스 여러개
- 인터페이스 분리 원칙
-
DIP(Dependency Inversion Principle)- 구체화에 의존 X → 추상화(인터페이스, 역할)에 의존 O
- 이 원칙을 따라야,
변경에 유연한 프로그래밍을 할 수 있음
다형성을 통한 주입
- MemberRepository 인터페이스를 구현한 두 클래스
interface MemberRepository {}
class MemoryMemberRepository implements MemberRepository {}
class JpaMemberRepository implements MemberRepository {}다형성을 이용, MemoryMembeRepository를 MemberRepository 타입에 초기화
class MemberSerivce() {
MemberReository memberRepository = new MemoryMemberRepository();
}- JpaMemberRepository로 대체
class MemberSerivce() {
MemberReository memberRepository = new JpaMemberRepository();
}- 클라이언트 코드가 역할(MemberRepository)와 구현(MemoryMemberRepository) 둘 다 의존함
- DIP, OCP를 지키지 못함
- 스프링의 DI 컨테이너를 통하여 의존관계 주입을 하여 해결
- 자바 기반의 웹 프레임워크
POJO (Plain Old Java Object)
무거운 객체를 만들어 코드의 가독성, 확장성, 유지보수가 떨어지는 단점을 보안하기 위해 등장한 개념- EJB (EnterpriseJavaBeans)
getter/setter로 구성된 순수한 형태의 기본 클래스
public class Score{
private int kor;
private int eng;
private int mat;
public int getKor() {return kor;}
public void setKor(int kor) {this.kor = kor;}
public int getEng() {return eng;}
public void setEng(int eng) {this.eng = eng;}
public int getMat() {return mat;}
public void setMat(int mat) {this.mat = mat;}
}- 조건
- 특정 규약(API)에 종속되지 않음
- 특정 환경에 종속되지 않음
- 객체 지향적 원리에 충실
DI (DependencyInjection)
- 의존성 주입
- MVC 패턴과 같은 작업에서 많은 의존성 주입이 필요
강한 결합
- 객체를 다른
객체 안에서 생성하는 것은 강한 결합도(높은 의존성)를 가짐 - 하나의 객체의 변경 → 다른 객체의 변경
public class RecordViewImpl implements RecordView{
private RecordImpl record = new RecordImpl();
}약한 결합
외부에서객체를 생성하여 객체를 주입
생성자를 통한 주입
public class RecordViewImpl implements RecordView{
private RecordImpl record;
//[생성자 DI(의존성 주입) 방식
public RecordViewImpl(RecordImpl record){
super();
this.record= record;
}
}프로퍼티를 통한 주입
public class RecordViewImpl implements RecordView{
//프로퍼티 방식
public void setRecord(RecordImpl record){
this.record = record;
}
}IoC (Inversion Of Control)
- 제어 역전
- 스프링 프레임워크가
개발자의 코드를 호출
- 스프링 프레임워크가
Bean(빈) 객체
- 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체
- 이 빈들을 관리하는 컨테이너를
BeanFactory라고 함
- 이 빈들을 관리하는 컨테이너를
BeanFactory
- Bean 관리(생성, 조회, 반환)
ApplicationContext
- Bean 관리(생성, 조회, 반환)
- BeanFactory에서 부가기능을 추가
- 국제화가 지원하는 텍스트 메시지 관리
- 이미지 등 파일 자원을 로드할 수 있음
- 리스너로등록된 빈에게 이벤트 발생을 알림
1. XML파일로 빈 객체 생성 설정
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="record" class="di.RecordImpl"></bean>
<bean id="rvi" class="di.RecordViewImpl">
<constructor-arg ref="record"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>- class 속성으로 풀네임을 줘 빈 객체를 id속성의 명을 가진 빈 객체를 생성
<bean id="record" class="di.RecordImpl"></bean>- 생성자를 통한 주입
- 빈 객체 생성 후 constructor-arg 태그로 의존성 주입
- ref 속성
<bean id="rvi" class="di.RecordViewImpl">
<constructor-arg ref="record"></constructor-arg>
</bean> - ref 태그
<bean id="rvi" class="di.RecordViewImpl">
<constructor-arg>
<ref bean="record"/>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>- 프로퍼티를 통한 주입
- setter 메소드명의 'set'을 생략하고 첫 글자를 소문자로 바꿈
<bean id="rvi" class="di.RecordViewImpl">
<property name="record" ref="record"></property>
</bean>호출
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String resourceLocations = "applicationContext.xml";
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(resourceLocations);
RecordViewImpl rvi = (RecordViewImpl) ctx.getBean("rvi");
}
}- 위에서 만든
applicationContext.xmlxml 파일로GenericXmlApplicationContext객체 생성 하여 스프링 컨테이너 안에 Bean 객체 생성 - .getBean() : 생성된 빈 객체를 호출
2. 자바코딩과 어노테이션을 이용한 객체 주입 설정
설정
Config.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Config {
RecordImpl record = new RecordImpl();
@Bean
public RecordImpl record() {
return new RecordImpl();
}
@Bean(name = "rvi")
public RecordViewImpl getRecordViewImpl() {
RecordViewImpl rvi = new RecordViewImpl();
rvi.setRecord(record()); // setter 프로퍼티를 통해서 DI
return rvi;
}
}- @Configuration 어노테이션으로 빈 객체 생성 클래스로 설정
- @Bean 어노테이션으로 빈 객체 생성 설정
- @Bean(name="빈객체명")
호출
main 메소드
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
RecordViewImpl rvi = ctx.getBean("rvi", RecordViewImpl.class);- 위에서 만든
Config.java에서 어노테이션 설정AnnotationConfigApplicationContext객체 생성 시 해당 .class파일 설정 하여 IoC컨테이너 생성 → 빈 객체 생성 주입하는 코딩
3. 빈 객체 자동 생성 및 연결
설정
applicationContext.xml
<context:component-scan base-package="스캔할 패키지명"></context:component-scan>- 컨테이너 설정 파일인인 .xml에
context:component-scan태그로 스캔할 패키지명 설정context:annotation-config태그는 자동 연결하는 태그이나 위 태그 하나로 처리 가능
RecordImpl.java
@Component
public class RecordImpl implements Record{
//
}RecordViewImpl.java
@Component
public class RecordViewImpl implements RecordView{
@Autowired
private RecordImpl record = null;
public RecordViewImpl(RecordImpl record){this.record= record;}
public void setRecord(RecordImpl record){this.record = record;}
}- @Component 어노테이션으로 빈 객체 자동 생성 대상으로 지정
- ("이름")으로 이름 지정
- @Autowired를 의존성 주입되는 부분에 설정하여 자동 주입 대상으로 지정
호출
String resourceLocations = "applicationContext.xml";
GenericXmlApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext(resourceLocations);
RecordViewImpl record = (RecordViewImpl)ctx.getBean("recordViewImpl");AOP (Apect Oriented Programming)
- 관점 지향 프로그래밍
- 모듈에서 사용하는 공통적인 기능을 분리
- 스프링 프레임워크 : DI, AOP
- 스프링 시큐리티 : 세션 (인증 권한)
- 스프링 배치 : 페이지 모듈화
- 스프링 인터그레이션 : 시스템간 연동을 위한 메시징 프레임워크
- 스프링 소셜 : 소셜 네트워크 연동
- ...
- 모듈은 상속/구현 관계 없이, 기능을 분리하여 관리하기 위함
| Aspect | 핵심기능을 제외하고 공통의 기능 |
| Advice | Aspect이 실행되는 위치를 구현한 것 |
| Jointpoint | Advice가 Target에 적용되는 시점 |
| Point cut | Joint point의 상세 |
| Target | Aspect가 적용되는 대상 |
프록시 패턴
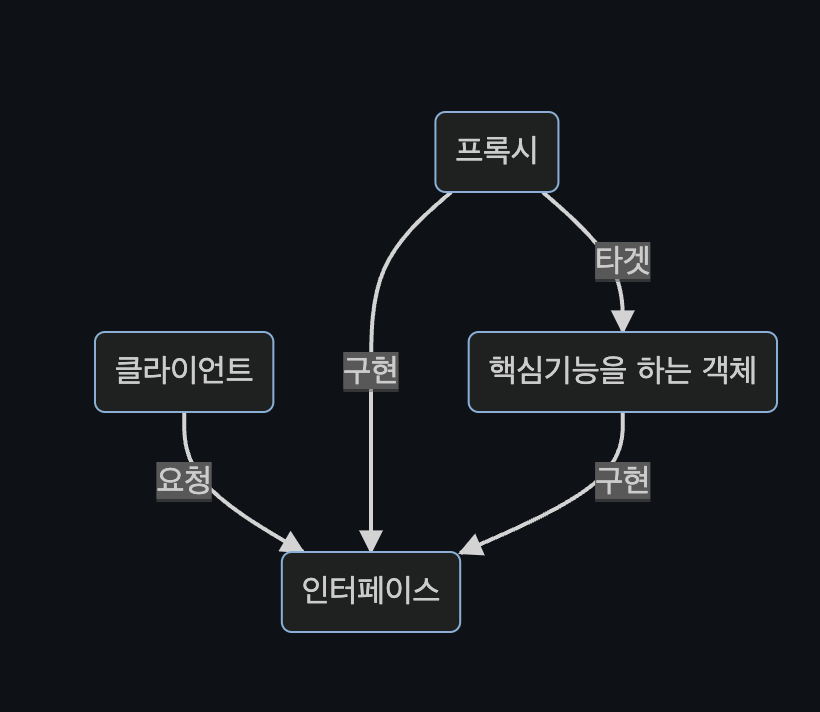
- CGlib proxy
- 특정 메소드만 프록시화
