저번에는 X에 MySQL을 연동해보았는데,
이번 시간에는 만들어두었던 X에 MongoDB를 연동해보자.
➿.env
JWT_SECRET=abcdefg1234%^&*
JWT_EXPIRES_SEC=172800
BCRYPT_SALT_ROUNDS=10
HOST_PORT=9091
DB_HOST=mongodb+srv://username:userpassword@cluster0.nntqe0q.mongodb.net/?retryWrites=true&w=majority&appName=Cluster0.env의 DB_HOST에는 MongoDB URI를 올린다.
.env는 비밀이라서 gitignore에 올려놓고 깃허브에 올라가지 않도록 한다.
➿ db/database.mjs
import { config } from "../config.mjs";
import MongoDb from "mongodb";
let db;
export async function connectDB() {
return MongoDb.MongoClient.connect(config.db.host).then((client) => {
db = client.db();
// console.log(db);
});
}
export function getUsers() {
return db.collection("users");
}
export function getPosts() {
return db.collection("posts");
}커맨드 창에서 npm install mongodb 한다.
이후, 몽고디비와 연결을 확인했다.
➿ config.mjs
import dotenv from "dotenv";
dotenv.config();
function required(key, defaultValue = undefined) {
const value = process.env[key] || defaultValue;
if (value == null) {
throw new Error(`키 ${key}는 undefined!!`);
}
return value;
}
export const config = {
jwt: {
secretKey: required("JWT_SECRET"),
expiresInSec: parseInt(required("JWT_EXPIRES_SEC", 86400)),
},
bcrypt: {
saltRounds: parseInt(required("BCRYPT_SALT_ROUNDS", 10)),
},
host: {
port: parseInt(required("HOST_PORT", 9090)),
},
db: {
host: required("DB_HOST"),
},
};db 부분을 변경했다.
➿ data/auth.mjs
import MongoDb, { ObjectId } from "mongodb";
import { getUsers } from "../db/database.mjs";
const ObjectID = MongoDb.ObjectId;
export async function createUser(user) {
return getUsers()
.insertOne(user)
.then((result) => result.insertedId.toString());
}
// 로그인
export async function login(userid, password) {
const user = users.find(
(user) => user.userid === userid && user.password === password
);
return user;
}
export async function findByUserid(userid) {
return getUsers().find({ userid }).next().then(mapOptionalUser);
}
export async function findByid(id) {
return getUsers()
.find({ _id: new ObjectID(id) })
.next()
.then(mapOptionalUser);
}
function mapOptionalUser(user) {
return user ? { ...user, id: user._id.toString() } : user;
}💥MongoDB에서 user._id는 기본적으로 ObjectId 타입인데, 이걸 String으로 변환해서 id 필드를 새로 추가한 이유????????
✅ 1. 프론트엔드와의 호환성
ObjectId는 MongoDB 고유의 타입이기 때문에, 직접 JSON으로 내보낼 때 문제가 생기거나, 프론트엔드에서 다루기 불편할 수 있다.
대부분의 프론트엔드는 문자열만 기대하기 때문에, .toString() 해서 id로 명확하게 만들어주는 게 일반적이다.
예를 들면
{
"_id": { "$oid": "661f16a6b01c5e001e3e4a56" } // JSON 변환 시 ObjectId는 이렇게 표현됨
}→ 이런 건 프론트에서 쓰기 어려움
✅ 2. REST API 또는 JSON 응답에서 표준화
보통 API 응답에서는 _id 대신 id를 사용한다.
이건 프론트엔드 개발자에게 더 익숙하고 명확하기 때문이다.
// MongoDB 원본
{ _id: ObjectId("661f..."), name: "Alice" }
// 응답 변환 후
{ id: "661f...", name: "Alice" }✅ 3. 불변성을 유지하며 안전하게 가공
{ ...user, id: user._id.toString() }이 구조는 원래 객체(user)를 변경하지 않고,
새로운 객체를 만들면서 id 필드를 추가하는 불변성 패턴이다.
→ 안정적인 코드 작성을 위한 좋은 습관.
➿ controller/auth.mjs
// 회원가입을 진행하는 함수
export async function signup(req, res, next) {
const { userid, password, name, email, url } = req.body;
// 회원 중복 체크
const found = await authRepository.findByUserid(userid);
if (found) {
return res.status(409).json({ message: `${userid}이 이미 있습니다.` });
}
const hashed = bcrypt.hashSync(password, bcryptSaltRounds);
const users = await authRepository.createUser(userid, hashed, name, email);
const users = await authRepository.createUser({
userid,
password: hashed,
name,
email,
url,
});
const token = await createJwtToken(users.id);
console.log(token);
if (users) {
res.status(201).json({ token, userid });
}
}회원가입하는 이 부분만 변경이 되었다...
➿ middleware/auth.mjs
req.userid = user.userid; //이거를
req.id = user.id; // 이거로 변경했당➿ data/post.mjs
import { getPosts } from "../db/database.mjs";
import MongoDb, { ReturnDocument } from "mongodb";
import * as UserRepository from "./auth.mjs";
const ObjectID = MongoDb.ObjectId;
// 모든 포스트를 리턴
export async function getAll() {
return getPosts().find().sort({ createAt: -1 }).toArray();
}
// 사용자 아이디(userid)에 대한 포스트를 리턴
// 조건을 만족하는 모든 요소를 배열로 리턴
export async function getAllByUserid(userid) {
return getPosts().find({ userid }).sort({ createAt: -1 }).toArray();
}
// 글 번호(id)에 대한 포스트를 리턴
// 조건을 만족하는 첫 번째 요소 하나를 리턴
export async function getById(id) {
return getPosts()
.find({ _id: new ObjectID(id) })
.next()
.then(mapOptionalPost);
}
// 포스트 작성
export async function create(text, id) {
console.log("id: ", id);
return UserRepository.findByid(id).then((user) =>
getPosts()
.insertOne({
text,
createAt: new Date(),
useridx: user.id,
name: user.name,
userid: user.userid,
url: user.url,
})
.then((result) => {
return getPosts().findOne({ _id: result.insertedId });
})
);
}
// 포스트 변경
export async function update(id, text) {
return getPosts()
.findOneAndUpdate(
{ _id: new ObjectID(id) },
{ $set: { text } },
{ returnDocument: "after" }
)
.then((result) => result);
}
// 포스트 삭제
export async function remove(id) {
return getPosts().deleteOne({ _id: new ObjectID(id) });
}
function mapOptionalPost(post) {
return post ? { ...post, id: post._id.toString() } : post;
}import MongoDb, { ReturnDocument } from "mongodb"에서 ReturnDocument는 MongoDB Node.js 드라이버에서 제공하는 enum(열거형)이다.
주로 findOneAndUpdate() 같은 메서드에서 "업데이트 결과로 어떤 문서를 반환할지"를 지정할 때 사용된다.
➿ controller/post.mjs
export async function createPost(req, res, next) {
const { text } = req.body;
const posts = await postRepository.create(text, req.id);
res.status(201).json(posts);
}
// 포스트를 변경하는 함수
export async function updatePost(req, res, next) {
const id = req.params.id;
const text = req.body.text;
const post = await postRepository.getById(id);
if (!post) {
return res.status(404).json({ message: `${id}의 포스트가 없습니다` });
}
if (post.useridx != req.id) {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
const updated = await postRepository.update(id, text);
res.status(200).json(updated);
}
// 포스트를 삭제하는 함수
export async function deletePost(req, res, next) {
const id = req.params.id;
const post = await postRepository.getById(id);
if (!post) {
return res.status(404).json({ message: `${id}의 포스트가 없습니다` });
}
if (post.useridx != req.id) {
return res.sendStatus(403);
}
await postRepository.remove(id);
res.sendStatus(204);
}변경된 부분들!
➿ app.mjs
import express from "express";
import postsRouter from "./router/posts.mjs";
import authRouter from "./router/auth.mjs";
import { config } from "./config.mjs";
import { connectDB } from "./db/database.mjs";
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use("/posts", postsRouter);
app.use("/auth", authRouter);
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.sendStatus(404);
});
connectDB()
.then(() => {
app.listen(config.host.port);
})
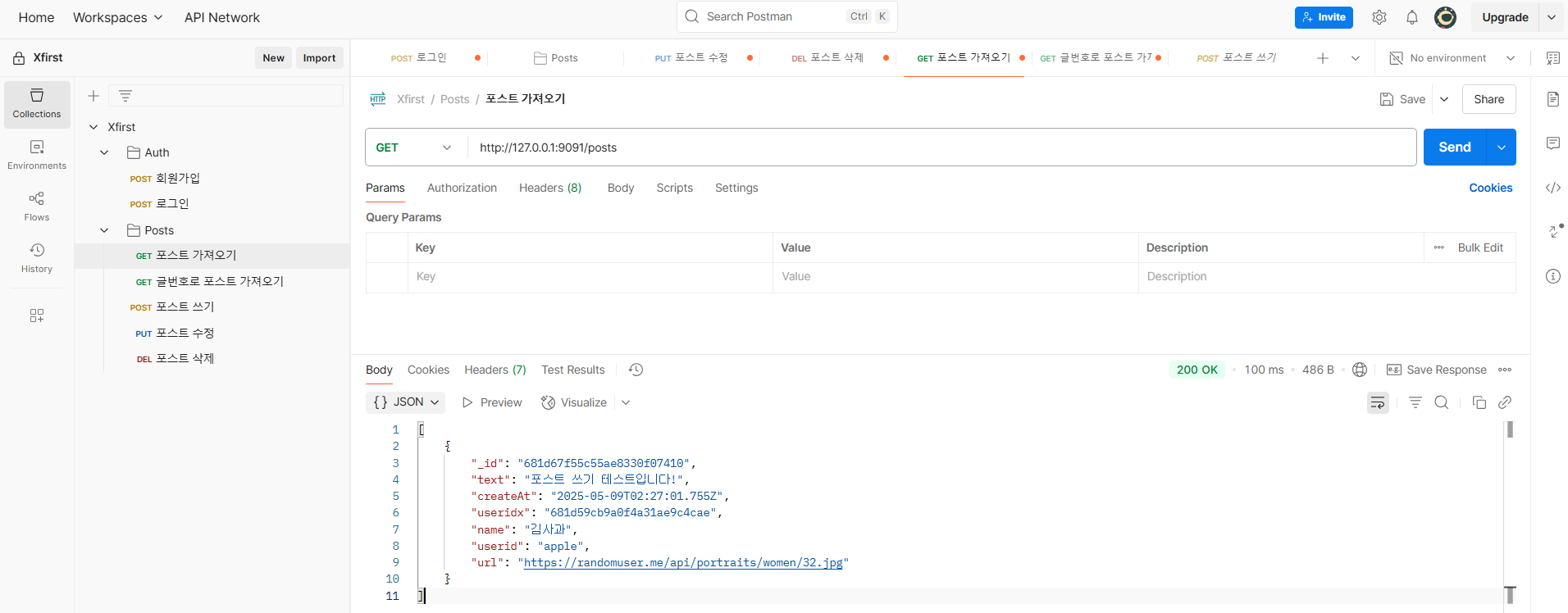
.catch(console.error);❇️ Postman에서 결과 확인
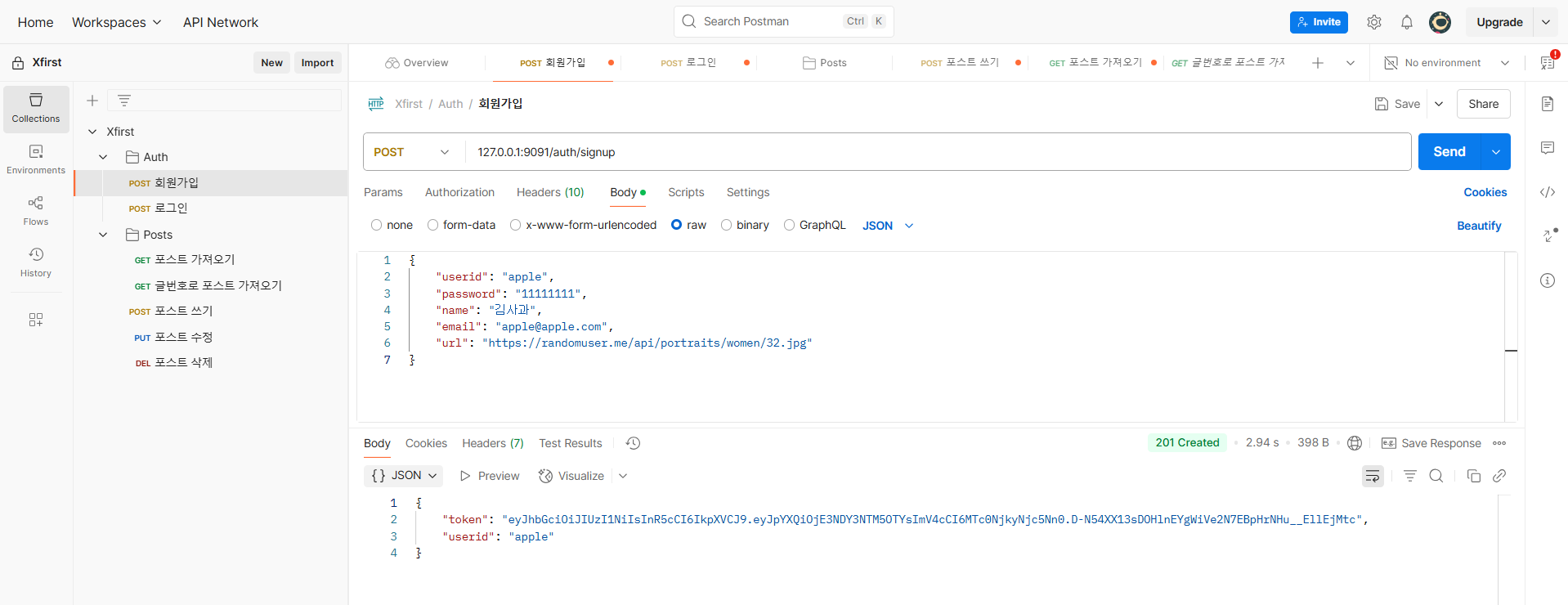
회원가입
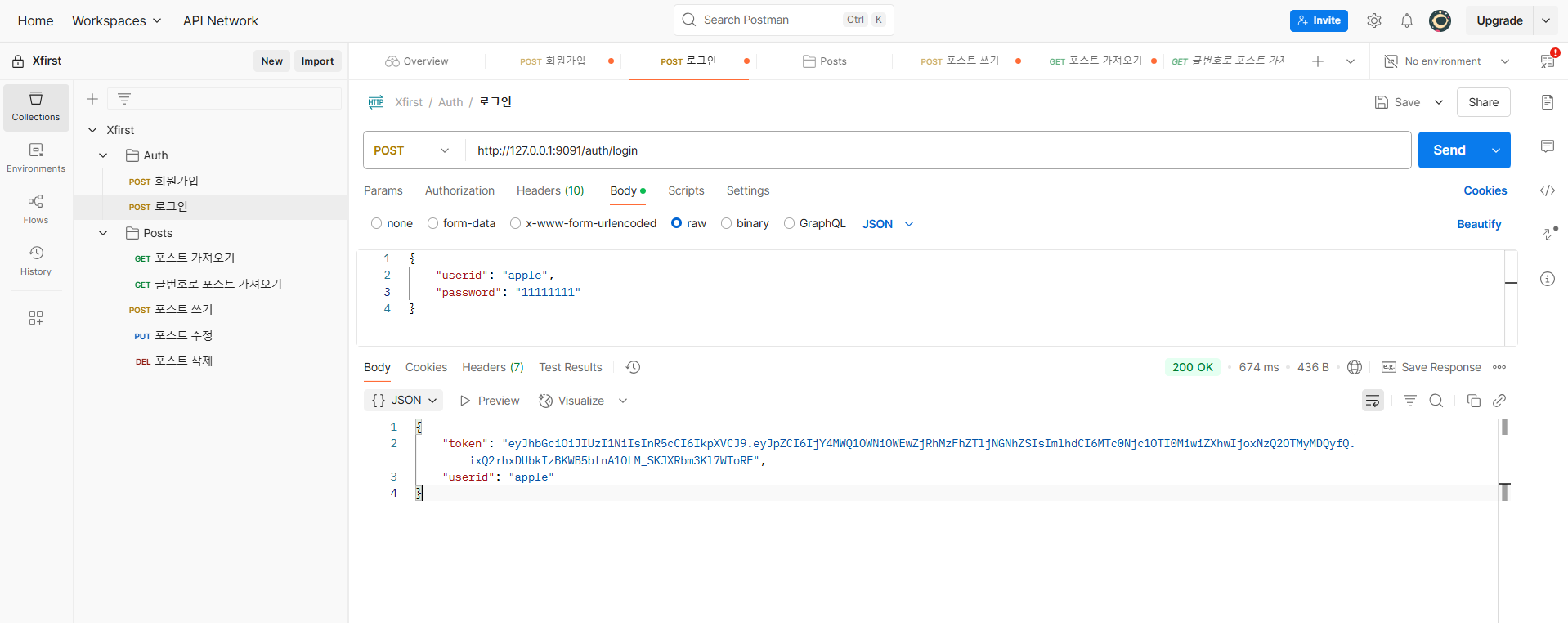
로그인
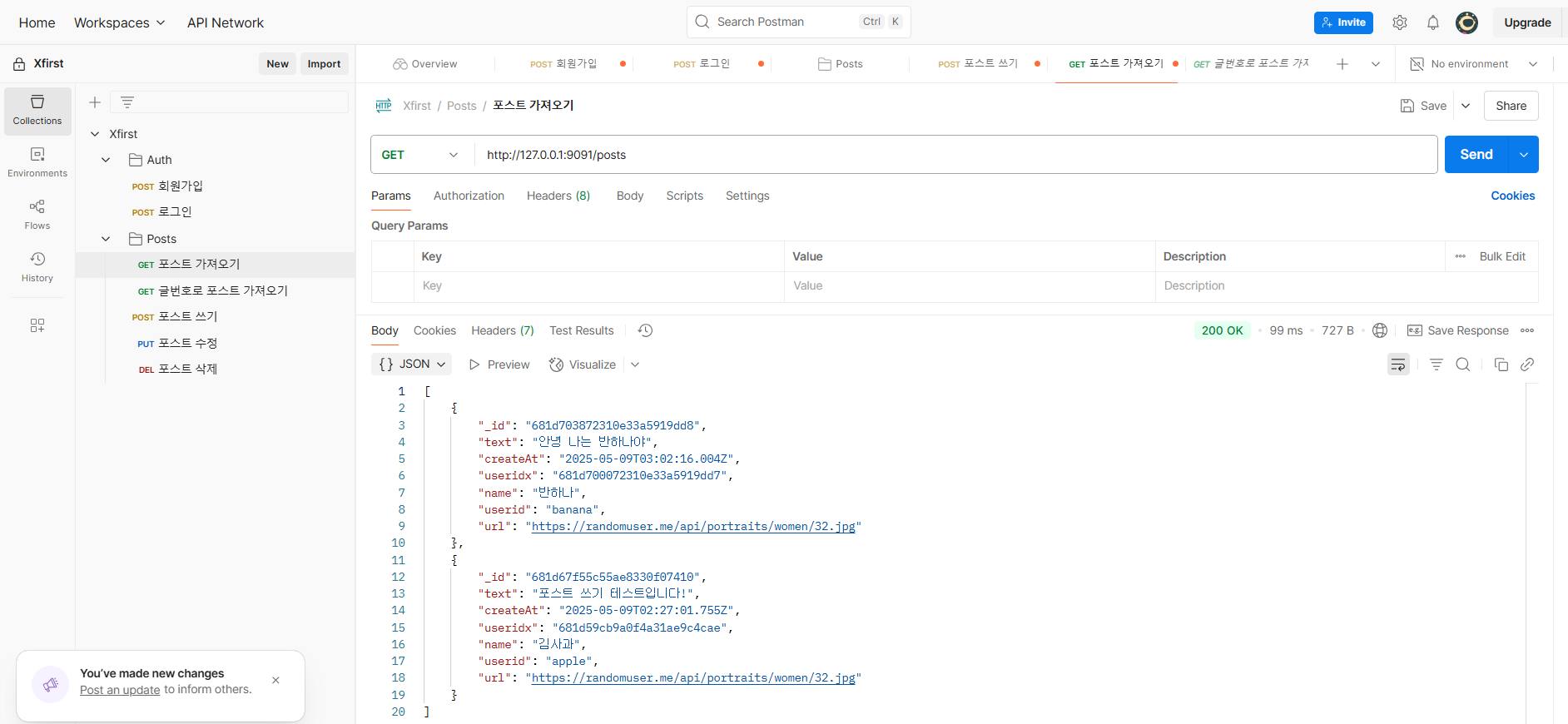
포스트 가져오기
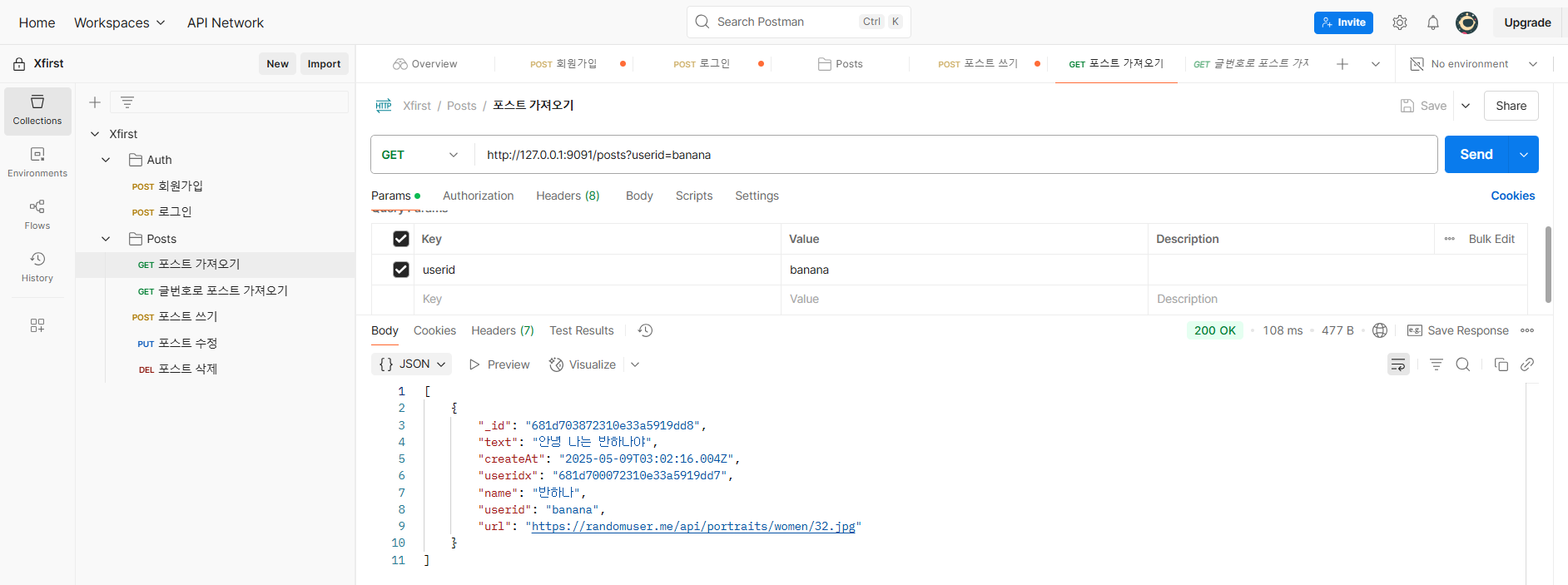
글번호로 포스트 가져오기
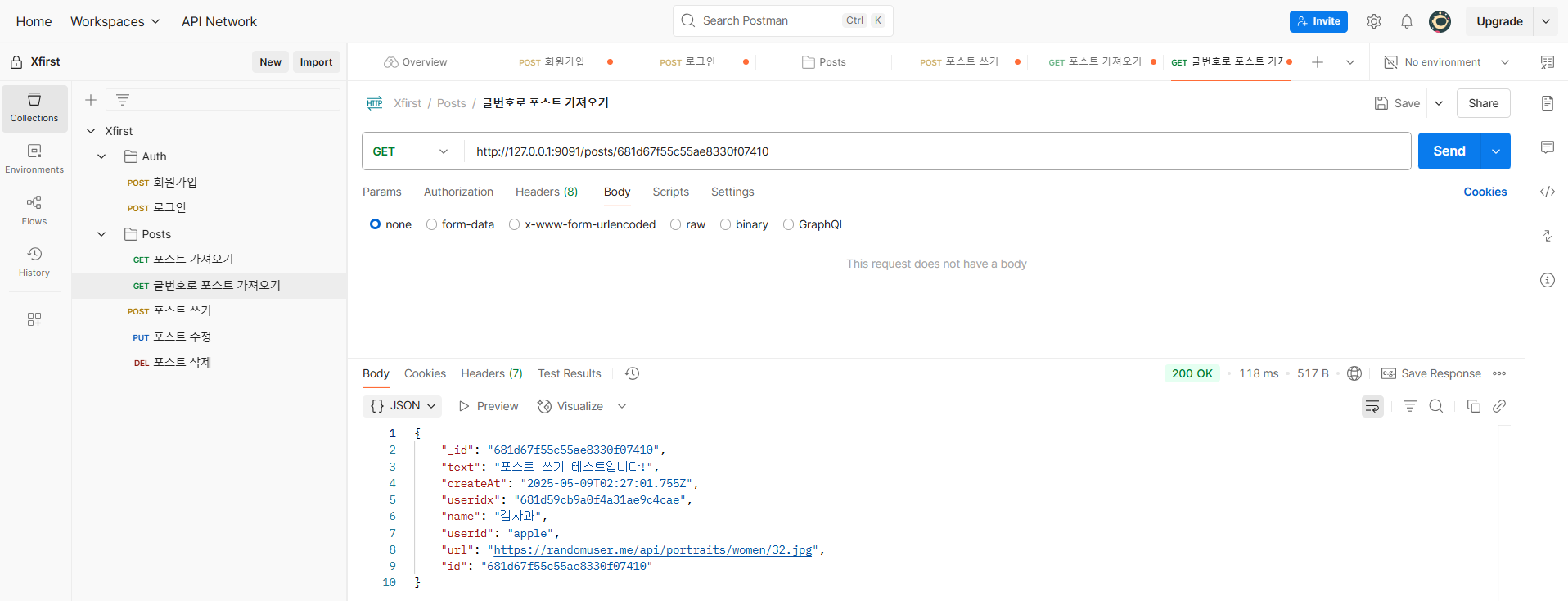
포스트 수정
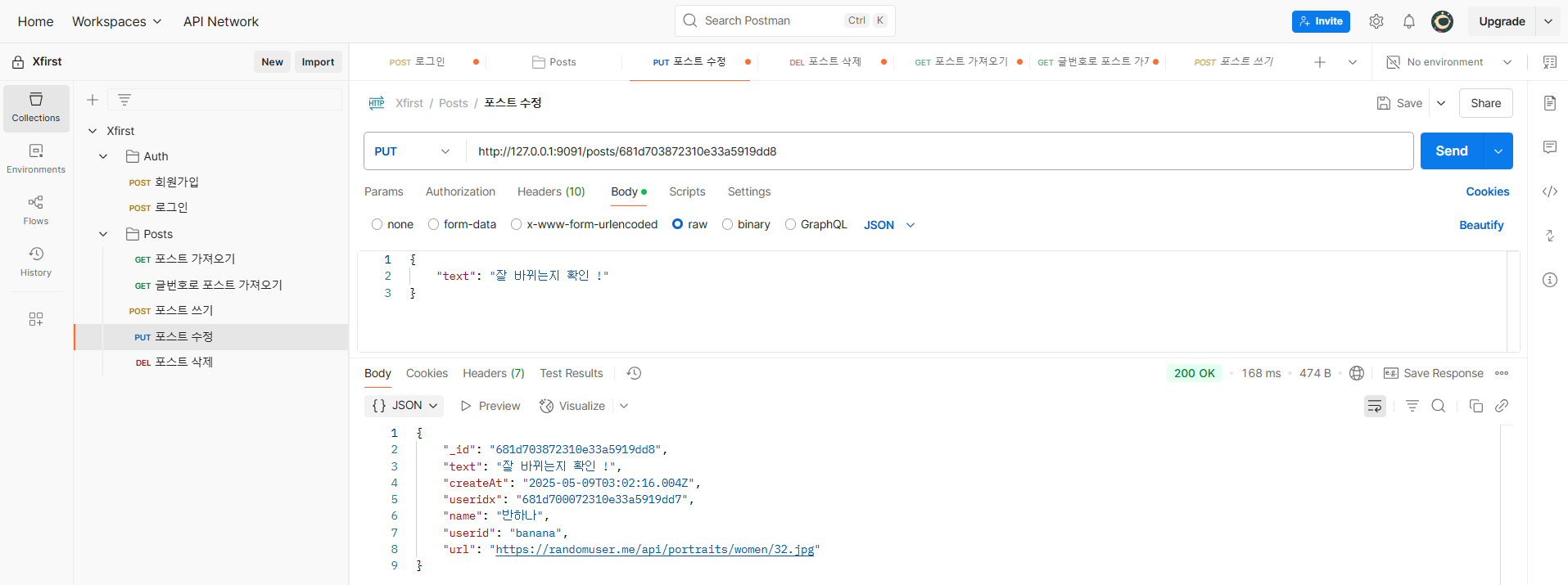
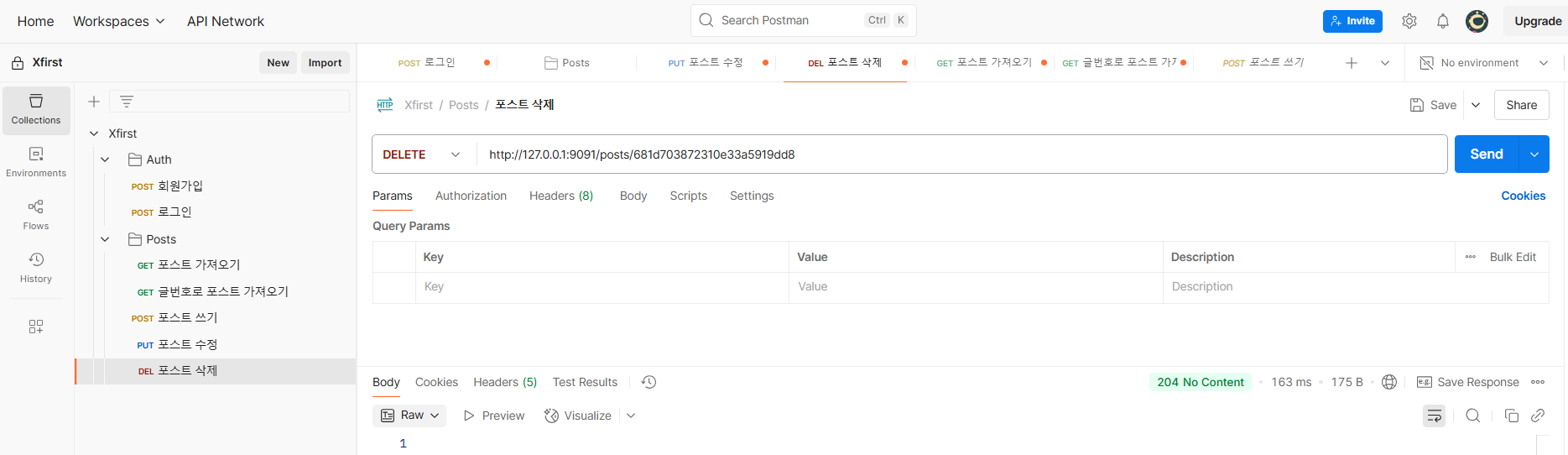
포스트 삭제
MongoDB Atlas에서 저장된 데이터들을 확인
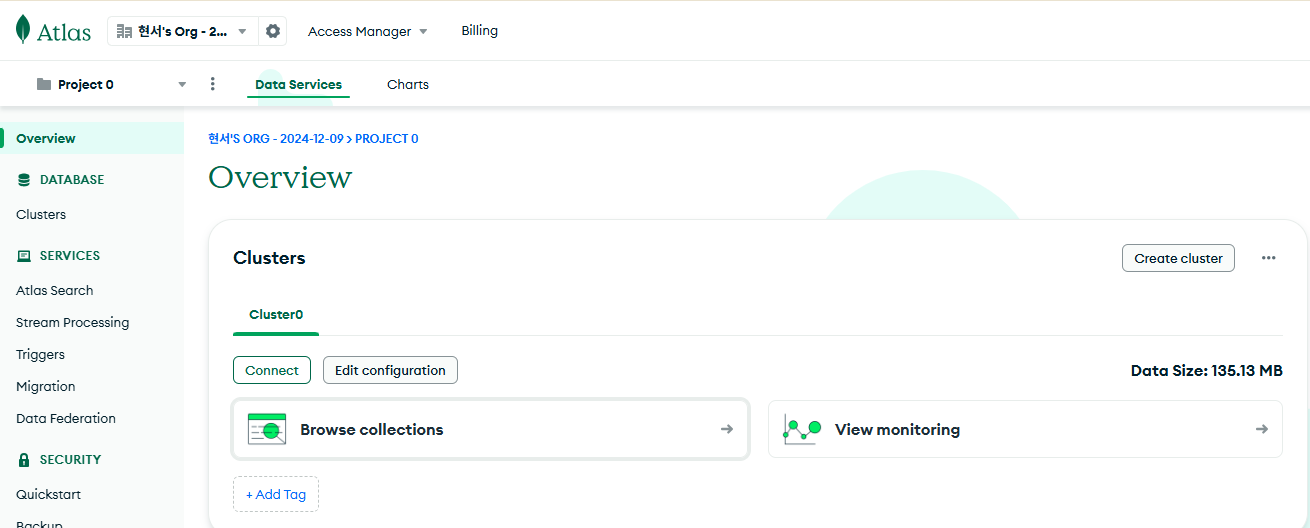
여기서 Browse collections를 클릭!
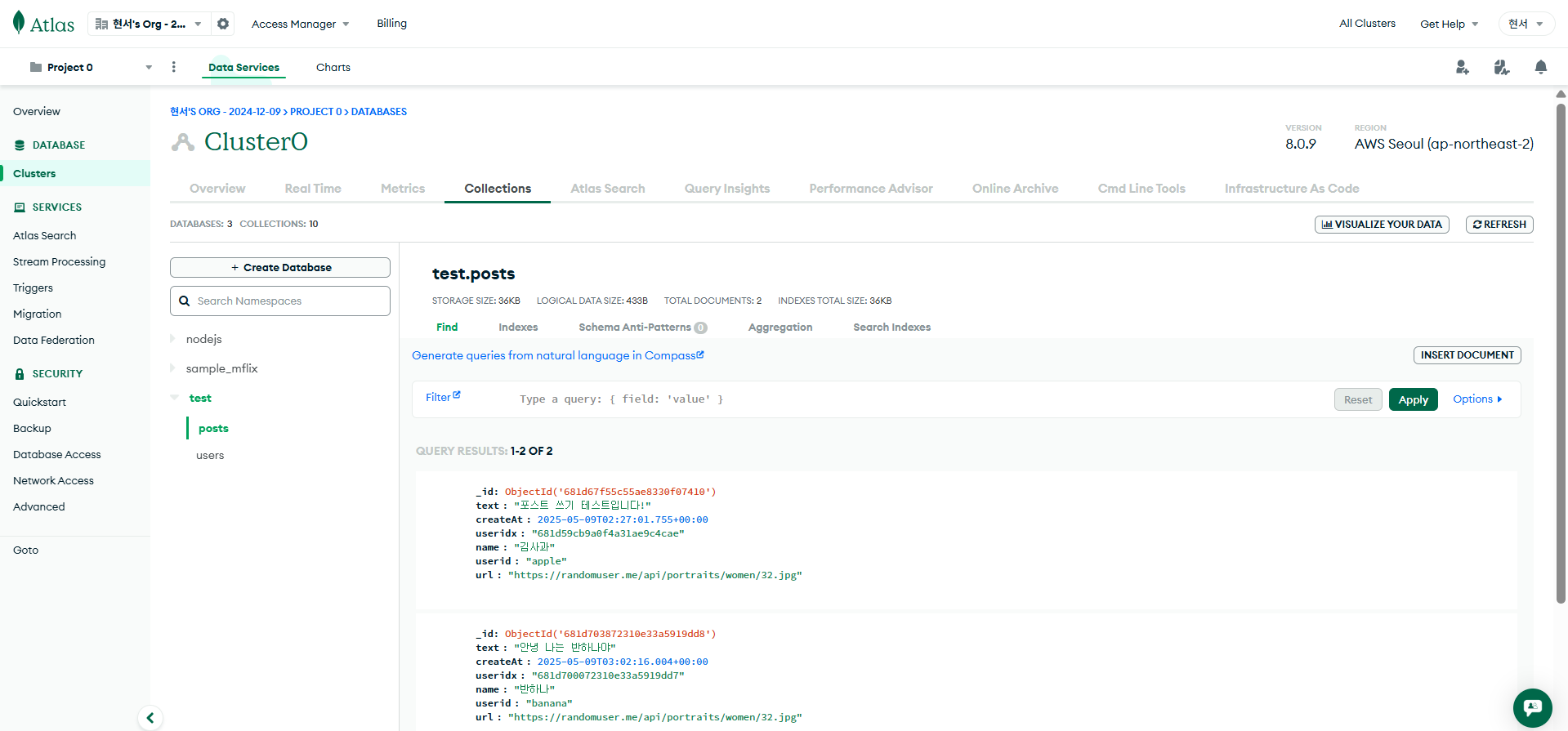
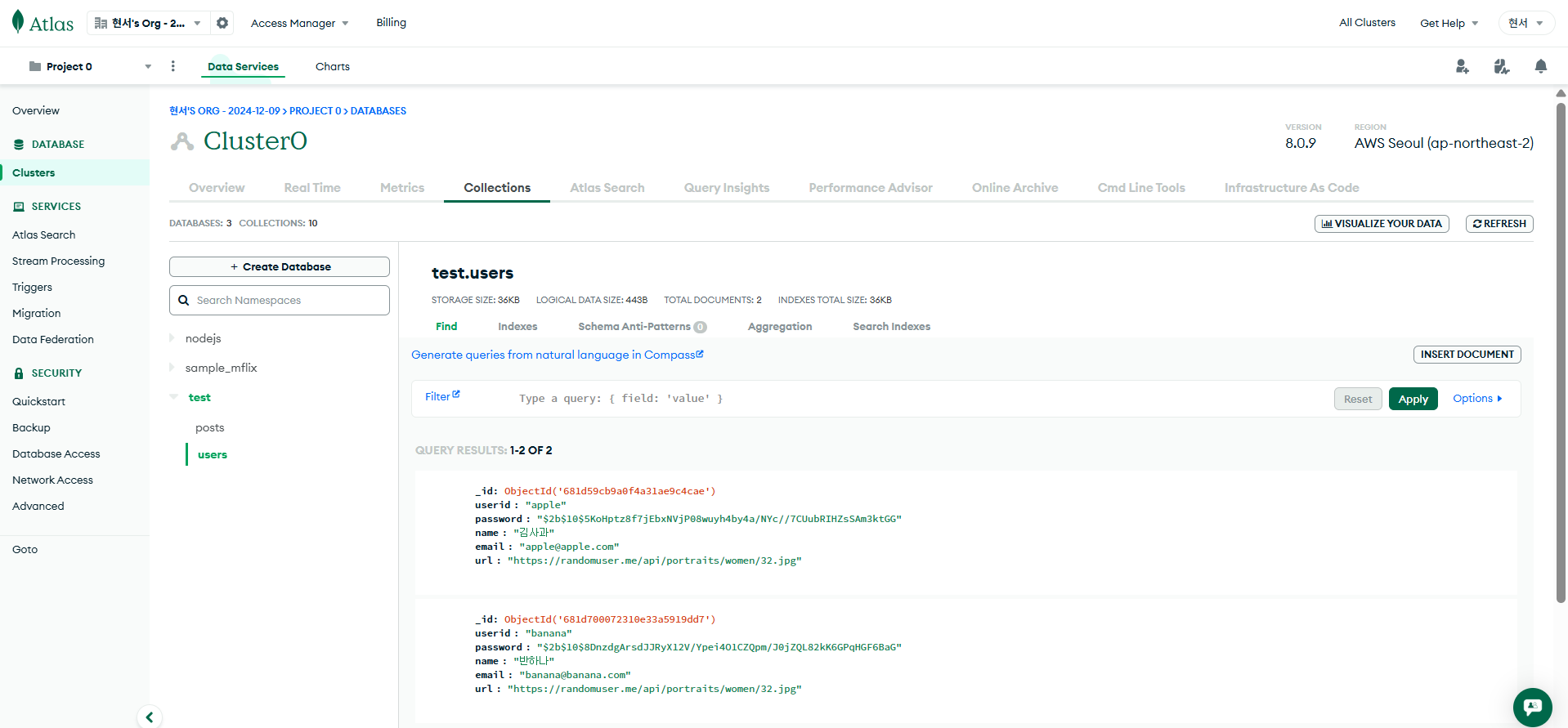
데이터 잘 들어갔는지 확인 완료

