오늘은 original repository를 fork 한 후 original repository의 최신 commit을 유지하며 repo를 관리하는 방법에 대해 정리해보겠습니다.
보통 fork를 통해 클론이 완료되면, 당신의 저장소에는 "origin"이라는 이름의 원격(remote)이 생기게 됩니다. 이 원격은 GitHub에서 당신이 fork한 저장소를 가리킵니다. origin이라는 이름 때문에 헷갈리지 마세요. 이것은 당신이 포크한 원본 저장소를 가리키는 것이 아닙니다. 원본 저장소를 추적하는 데 도움이 되도록 우리는 "upstream"이라는 이름의 또 다른 원격을 추가할 것입니다.
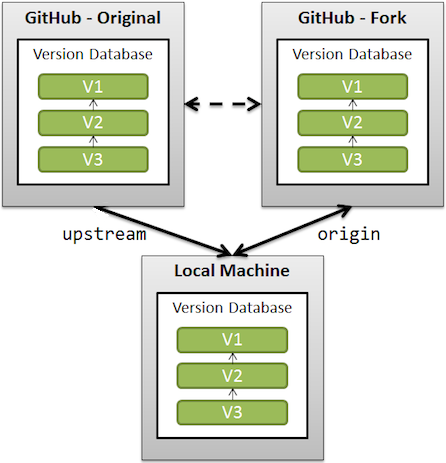
origin: is your fork: your own repo on GitHub, clone of the original repo of GitHubupstream: generally refers to the original repo that you have forked
(see also "Definition of “downstream” and “upstream”" for more on upstream term)
github official 문서에도 아래와 같이 정리되어있습니다.
When a repo is cloned, it has a default remote called origin that points to your fork on GitHub, not the original repo it was forked from.
To keep track of the original repo, you need to add another remote named upstream
이제 아래와 같이 upstream remote를 연결하여 merge 혹은 rebase 해줍니다.
$ cd PROJECT_NAME
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/ORIGINAL_OWNER/ORIGINAL_REPOSITORY.git
# This will set your upstream to the repository you forked from. Then do this:
$ git fetch upstream
# This will fetch all the branches including master from the original repository.
# then: (like "git pull" which is fetch + merge)
$ git merge upstream/master master
# or, better, replay your local work on top of the fetched branch
# like a "git pull --rebase"
$ git rebase upstream/masterReference
- https://docs.github.com/ko/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/working-with-forks/fork-a-repo
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3903817/pull-new-updates-from-original-github-repository-into-forked-github-repository
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9257533/what-is-the-difference-between-origin-and-upstream-on-github/9257901#9257901