item8. finalize와 cleaner 사용을 피하라
객체 소멸자인 finalize와 cleaner는 느리고 수행 시기를 예측할 수 없다.
finalize(): JVM에 의하여 garbage collection이 수행될 때, 호출되는 함수 [depreciated]- 주로 해당 인스턴스와 연관된 자원들에 대한 Releasing을 위하여 설계됨
finalize()내부에 Strong Reference를 갖도록 코딩되어 있을 경우, 제거된 객체가 부활할 수 있음- 동작 중 발생된 예외에 대해, 예외 처리 로직 설계가 불가능하다 (예외 발생시, 그 즉시 종료됨)
- 자바 8까지 사용됨
Cleaner클래스:finalize()의 역할을 물려받음 (기능의 대체는 절대 아님, 문제점이 여전히 존재)- 자신이 수행할 쓰레드를 제어할 수 있다는 면에서
finalize()보다는 낫다. - cleaning action 도중 발생하는 예외는 모두 무시됨
- The thread runs until all registered cleaning actions have completed and the cleaner itself is reclaimed by the garbage collector.
- 자신이 수행할 쓰레드를 제어할 수 있다는 면에서
Cleanup functions, like finalizers, are run when an object is found to be unreachable from any class or thread. Unlike a finalizer, a cleanup function holds the state needed for cleanup separately from the object because we want the object to be reclaimed as soon as it is unreachable. The cleanup function must be able to work independently from the object. If there are any references to the object from the cleanup function it would still be reachable and could not be reclaimed. Any state needed for the cleanup must be encapsulated in the cleanup function.
- C++의 소멸자(destructor)와는 다른 개념이다.
- C++의 소멸자는 객체가 소멸될 때, 자원을 Releasing 하기 위해 사용됨
- 프로그래머가 의도적으로 비메모리 자원을 회수한다.
- 반대로 자바는 garbage collector가 이러한 기능을 수행하며, 수행 시기는 예측할 수 없다.
문제1. finalize()가 호출되는 시기를 예측할 수 없다.
- 그렇다면, garbage Collection을 강제화 하는 방법으로 문제점을 해결할 수 있지 않을까?
System.gc(): 가비지 컬렉션을 보장하진 않음
Runs the garbage collector. Calling the
gcmethod suggests that the Java Virtual Machine expend effort toward recycling unused objects in order to make the memory they currently occupy available for quick reuse. When control returns from the method call, the Java Virtual Machine has made a best effort to reclaim space from all discarded objects.
System.runFinalization(): finalize가 수행되는 것을 보장하진 않음
Runs the finalization methods of any objects pending finalization. Calling this method suggests that the Java Virtual Machine expend effort toward running the
finalizemethods of objects that have been found to be discarded but whosefinalizemethods have not yet been run. When control returns from the method call, the Java Virtual Machine has made a best effort to complete all outstanding finalizations.
그렇기 때문에, finalize(), Cleaner 를 쓴다는 것은 단순하게 안전망을 설치해주기 위한 목적에 불구하다.
(만약 자원 회수가 이루어지지 않았다고 해도, 언젠가는 해주는 것이 아예 안해주는 것 보단 낫기 때문)
파생되는 문제점
- 공유 자원에 대해서
finalize()로 자원을 Release한다면 Deadlock 발생 가능 FileDescriptor로 파일을 참조한 후,finalize()로 Release할 경우 수행 시기의 불확실성으로 인하여 외부에서 해당FileDescriptor값으로 외부에서 해당 파일에 접근할 수 있다. (file descriptor leak)
문제2. finalize() 와 Cleaner 는 심각한 성능 문제를 야기한다
실제, AutoClosable 을 구현한 클래스를 통해 가비지 컬렉터가 수거하는 시간 보다 대략 50배 정도 느리다.
(finalize()가 가비지 컬렉션의 효율을 떨어뜨린다)
Why do finalize() have a severe performance penalty?
문제3. finalize()를 사용한 클래스는 finalizer 공격에 취약하다
finalize()메소드 내부에서도 자바 코드 작성 가능- 해당 클래스를 상속 받은 서브 클래스에서
finalize()를 상속받아 슈퍼 클래스의 멤버에 접근 가능 - 주로, garbage collection이 자주 발생하는
생성자 및 직렬화로직이 타겟이 된다.
ex) 객체 생성 후 -> 기본 값 -> 생성자 (단순 초기화)
// 수정 될 수 없는 코드 (외부 API라고 가정)
public class Bank {
public boolean isAuthenticated() {
return false;
}
public Bank() {
if (!isAuthenticated()) {
throw new SecurityException("당신은 접근할 수 없습니다");
}
}
// target method
public void transferMoney(int money) {
System.out.println(money + "원이 이체되었습니다");
}
}// 공격자의 코드
public class Attacker extends Bank {
@Override
protected void finalize() {
System.out.println("공격 성공");
this.transferMoney(10000);
}
}
// Driver Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank toAttack = null;
try {
toAttack = new Attacker();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
// garbage Collector가 [new Attack()]를 수거할 때,
// 오버라이드 된 finalize()가 실행됨
System.gc();
}
}결과
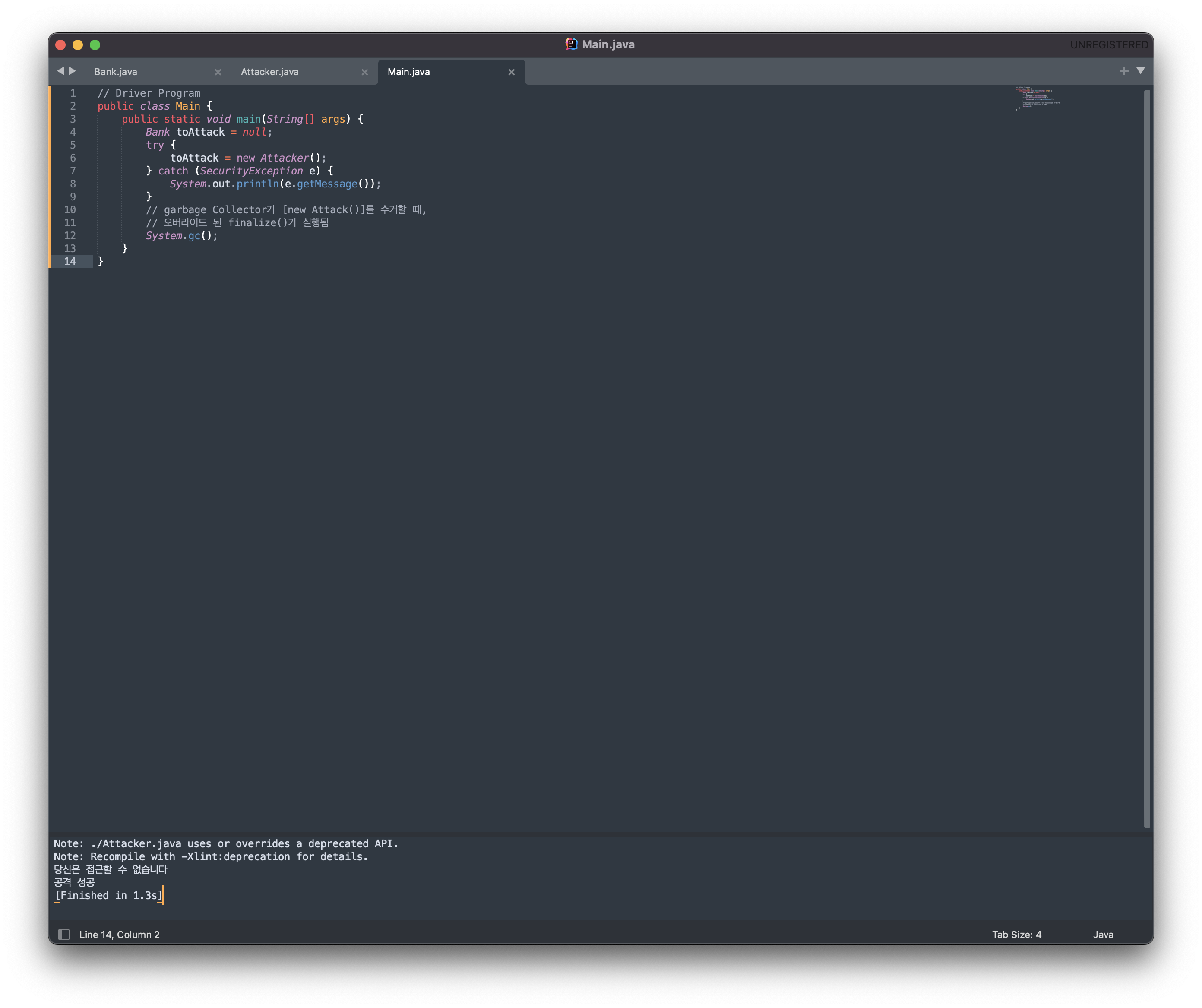
오버라이드된 finalize() 내부에서 공격자의 코드가 실행될 수 있으므로, 객체 생성 및 여러가지 악의적인 공격이 가능해진다.
Countermeasure
finalclass : 클래스의 상속을 막는다finalfinalize() : 메소드의 오버라이드를 막는다- Cleaner 사용
finalizer() 나 Cleaner 를 대체할 수 있는 방법
인스턴스를 사용하고 난 후, 더 이상 해당 인스턴스를 사용하지 않을 때 연결된 자원들을 모두 Releasing 하고 싶은 경우
- 각 인스턴스는 자신이 닫혔는지(=유효한지) 추적하는 방식으로 자원에 대한 접근을 제어한다.
-
AutoCloseable를 구현한 클래스를 설계한다. -
이 때 오버라이드하는
close()메소드는 필드에 값을 써서자신이 닫혔는지(=유효한지) 기록하는 용도로 쓰인다 -
그 외의 메소드는 필드의 값을 참조하여 유효하지 않다면 Exception을 던지는 방식으로 구현한다.
// Cleaner + AutoClosable
// Cleaner 로직이 실행되는 비율이 적을수록 성능 증가, AutoClosable.close()가 많아야한다.
public class Room implements AutoClosable {
private static final Cleaner cleaner = Cleaner.create();
// Cleaning Action 정의 (Runnable)
private static class State implements Runnable {
int numJunkPiles;
State(int numJunkPiles){this.numJunkPiles = numJunkPiles;}
// Cleaner에 의해 정확히 1번만 호출된다.
@Override public void run() {
numJunkPiles = 0;
}
}
private final State state;
private final Cleaner.Cleanable cleanable;
public Room(int numJunkPiles) {
state = new State(numJunkPiles);
cleanable = cleaner.register(this, state); // cleaner를 조립 (대상 인스턴스, 행위)
}
// AutoClosable.close() 오버라이드
// close가 수행될 때, Cleaning action
@Override public void close() {
cleanable.clean();
}
}