Lecture 1.2
Dept. of Information Systems Hanyang University
Slide Reference: fundamentals of database systems, pearson
Outline
-
Introduction
-
An Example
-
Characteristics of the Database Approach
-
Actors on the Scene
여기 밑에는 ppt에 없음.
-
Workers behind the Scene
-
Advantages of Using the DBMS Approach
-
A Brief History of Database Applications
Overview
-
Traditional database applications
- Store textual or numeric information
-
Multimedia databases
- Store images, audio clips, and video streams digitally
Uses of Databases
-
Data warehouses and online analytical processing (OLAP) systems
-
Extract and analyze useful business information from very large databases
-
Support decision making
-
-
Real-time and active database technology
- Control industrial and manufacturing processes
Introduction
Basic Chacteristics and Components of DB
Database
Collection of related data
-
Known facts that can be recorded and that have implicit meaning
-
Miniworld or universe of discourse (UoD)
- ??
-
Represents some aspect of the real world
-
Logically coherent collection of data with inherent meaning
-
Built for a specific purpose
Example of a large commercial database
- Amazon.com
Database management system (DBMS)
-
Collection of programs
-
Enables users to create and maintain a database
Defining a database
-
Specify the data types, structures, and constraints of the data to be stored
-
https://www.oracle.com/database/what-is- database.html
Meta-data
-
Database definition or descriptive information
-
Stored by the DBMS in the form of a database catalog or dictionary
Manipulating a database
-
Query and update the database miniworld
-
Generate reports
Sharing a database
- Allow multiple users and programs to access the database simultaneously
Application program
- Accesses database by sending queries to DBMS
Query
- Causes some data to be retrieved
Transaction
- May cause some data to be read and some data to be written into the database
Protection includes:
- System protection
- Security protection
Maintain the database system
- Allow the system to evolve as requirements change over time
Figure 1.1
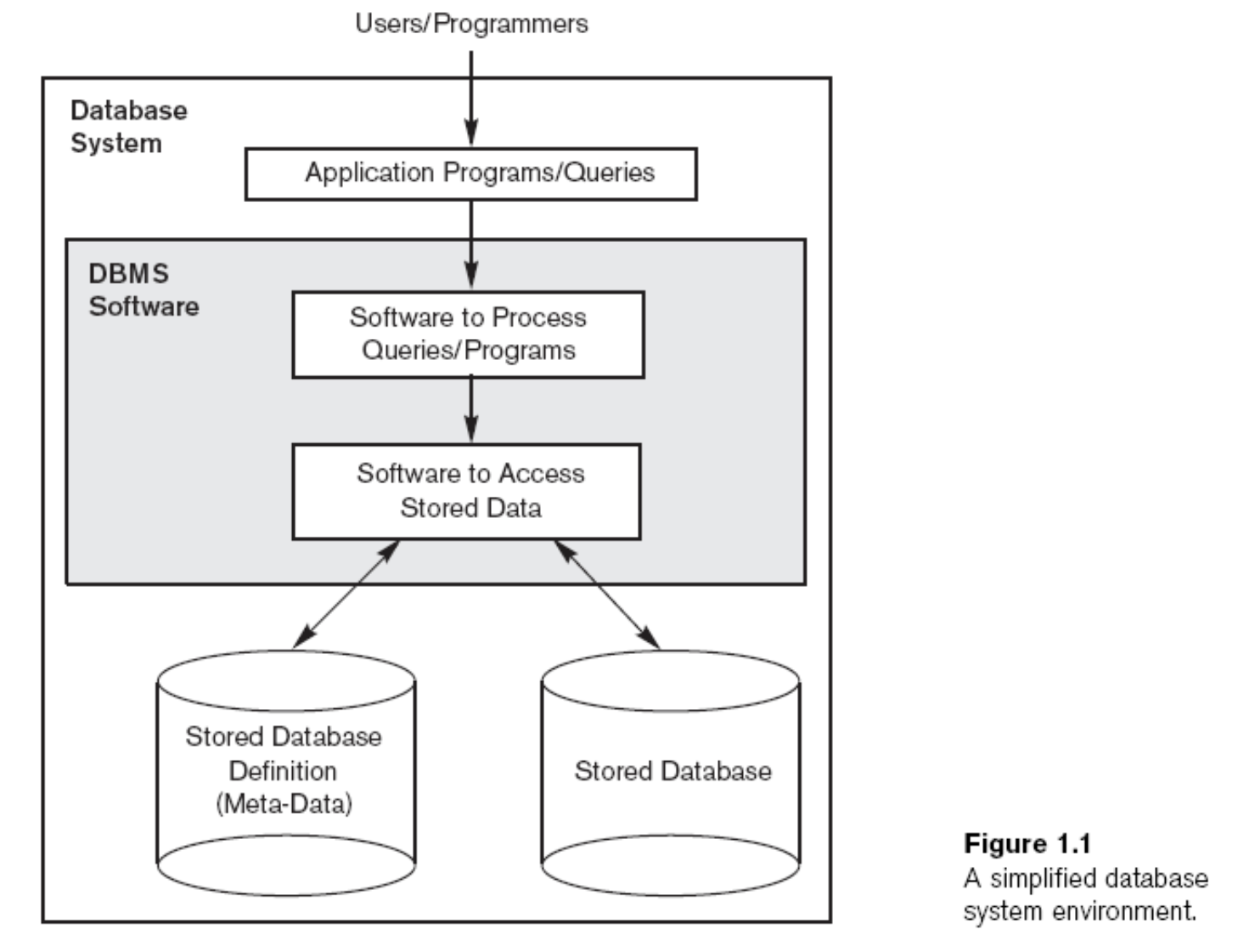
위의 내용들을 총정리한 그림
An Example
UNIVERSITY database
Information concerning students, courses, and grades in a university environment
-
Data records
-
STUDENT
-
COURSE
-
SECTION
-
GRADE_REPORT
-
PREREQUISITE
-
Specify structure of records of each file by specifying data type for each data element
- String of alphabetic characters
- Integer
Construct UNIVERSITY database
Store data to represent each student, course, section, grade report, and prerequisite as a record in appropriate file
-
Relationships among the records
-
Manipulation involves querying and updating
Examples of queries:
-
Retrieve the transcript
-
List the names of students who took the section of the `Database¨ course offered in fall 2020 and their grades in that section
- sql로 이 명령문을 바꾸기 혹은 sql을 읽고 의미가 뭔지 해석하는 문항 나올 수 있다.
-
List the prerequisites of the `Database¨ course
Examples of updates:
-
Change the class of `Smith¨ to sophomore
-
Create a new section for the `Database¨ course for this semester
-
Enter a grade of `A¨ for `Smith¨ in the `Database¨ section of last semester
Phases for designing a database:
-
Requirements specification and analysis
-
Conceptual design
-
Logical design
-
Physical design
Characteristics of the Database Approach
-
Traditional file processing
- Each user defines and implements the files needed for a specific software application
-
Database approach
- Single repository maintains data that is defined once and then accessed by various users
-
Main characteristics of database approach
-
Self-describing nature of a database system
-
Insulation between programs and data, and data abstraction
-
Support of multiple views of the data
-
Sharing of data and multiuser transaction processing
-
Self-Describing Nature of a Database System
- Database system contains complete definition of structure and constraints
Meta-data
Describes structure of the database
-
Database catalog used by:
-
DBMS software
-
Database users who need information about database structure
-
Insulation Between Programs and Data
-
Program-data independence
- Structure of data files is stored in DBMS catalog separately from access programs
-
Program-operation independence
-
Operations specified in two parts:
-
Interface includes operation name and data types of its arguments
-
Implementation can be changed without affecting the interface
-
-
Data Abstraction
Allows program-data independence and program-operation independence
-
Conceptual representation of data
- Does not include details of how data is stored or how operations are implemented
-
Data model
- Type of data abstraction used to provide conceptual representation
여기 밑에서부터는 별로 비중있게 수업 x
Support of Multiple Views of the Data
View
Subset of the database, Contains virtual data derived from the database files but is not explicitly stored
Multiuser DBMS
Users have a variety of distinct applications
- Must provide facilities for defining multiple views
Sharing of Data and Multiuser Transaction Processing
- Allow multiple users to access the database at the same time
Concurrency control software
-
Ensure that several users trying to update the same data do so in a controlled manner
- Result of the updates is correct
-
Online transaction processing (OLTP) application
Transaction
-
Central to many database applications
-
Executing program or process that includes one or more database
Isolation property
Each transaction appears to execute in isolation from other transactions
Atomicity property
Either all the database operations in a transaction are executed or none are
Actors on the Scene
Database administrators (DBA) are responsible for:
-
Authorizing access to the database
-
Coordinating and monitoring its use
-
Acquiring software and hardware resources
Database designers are responsible for:
-
Identifying the data to be stored
-
Choosing appropriate structures to represent and store this data
End users
- People whose jobs require access to the database
Types
-
Casual end users
-
Naive or parametric end users
-
Sophisticated end users
-
Standalone users
System analysts
-
Determine requirements of end users
-
Application programmers
-
Implement these specifications as programs
