List??
Project의 database가 있다고 하자. 그렇다면 하나의 database의 예시는 그 project의 속성들을 모두 list로 쭉 출력하는 것이다. 그런데 이 접근은 문제가 많다. 정보가 복잡해지면 말이다.
참고사항
column: 행 (세로줄) <- 예시에서는 속성들
row: 열 (가로줄) <- 예시에서는 개별 프로젝트들
문제1: Redundancy
아까의 예시에서 Project를 나열하다 보면, Project의 속성들 중 전화번호나 ID같은 부분들이 중복 될 수 있다. 어떤 사람이 일을 많이 한다면, 그 사람은 여러 프로젝트의 속성에 많이 입력될 수 있다.
문제2: Multiple themes
어떤 Project에는 manager 자체가 있을 수도, 없을 수도 있다. 그렇지만 List 는 모든 Project를 동일한 표에 다루므로 manager가 없다면 그 project의 manager column에는 빈칸을 둘 수 밖에 없다.
Modification Issues
그래서 문제1 과 문제2가 왜 문제인가?
데이터를 Modify할 때에 문제가 생긴다.
Deletion problem
한 Project가 사라졌다고 하자. 그렇다면, 그에 관련된 매니저의 data도 사라질 수 있다. 매니저의 이름을 보고 전화번호를 찾고 싶었지만, 그 매니저의 data가 통채로 사라졌기 때문에 어쩔 수가 없다.
Update Problem
만약 어떤 매니저가 바뀌었다고 하자. 그렇다면 그와 관련된 데이터인 전화번호, 이메일을 개별적으로 바꿔줘야 한다. 귀찮다.
Insertion Problem
Insert를 할 때에 column을 공란으로 비워둘 수 밖에 없는 문제가 생길 수 있다.
Relational Database
이를 해결하기 위한 Database의 유형. 특징들을 살펴보고 어떻게 List의 문제들을 해결하는지 보자.
특징들
A relational database stores information in tables. Each informational topic is stored in its own table
- In essence,a relational database will break-up a list into several parts. One part for each theme in the list
- A Project List would be divided into a CUSTOMER Table, a PROJECT Table, and a PROJECT_MANAGER Table
이렇게 나누었지만, 결국 하나의 Database이므로 서로를 연결해서 하나로 볼 방법이 필요하다. Realational Database에서는 Data의 Value로 서로를 연결한다.
이렇게 되면 Student data를 delete할 때에 Department data는 소실될 우려가 없다. Insertion, Modification 도 마찬가지.
SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) is an international standard for
creating, processing and querying databases and their tables
SQL select statement
List를 다시 만든다고 생각하면 편리하다.
Select Table.Column
From Table
Where <- Condition (can use 'and' operator)
SELECT CUSTOMER.CustomerLastName, CUSTOMER.CustomerFirstName, CUSTOMER.Phone,
COURSE.CourseDate, ENROLLMENT.AmountPaid, COURSE.Course, COURSE.Fee
FROM CUSTOMER, ENROLLMENT, COURSE
WHERE CUSTOMER.CustomerNumber
= ENROLLMENT.CustomerNumber
AND COURSE.CourseNumber
= ENROLLMENT.CourseNumber;
It returns a list by the condition queried.
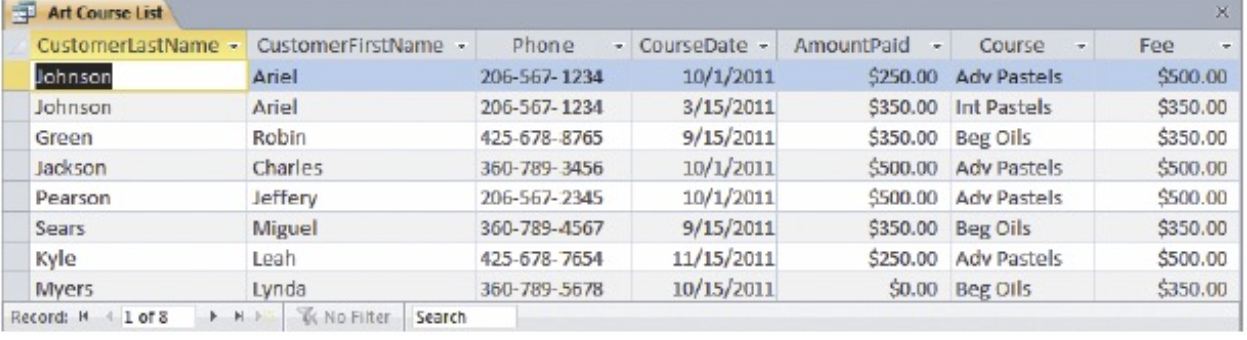
DB 정의
저번에 배웠던 정의를 SQL과 결부시켜 이해해 보자.
우리는 User로서
- track things
- Use forms to enter, read, delete and query data
- Produce reports
이런 것들을 할 수 있다.
Metadata
저번에 중요하게 다뤘던 개념.
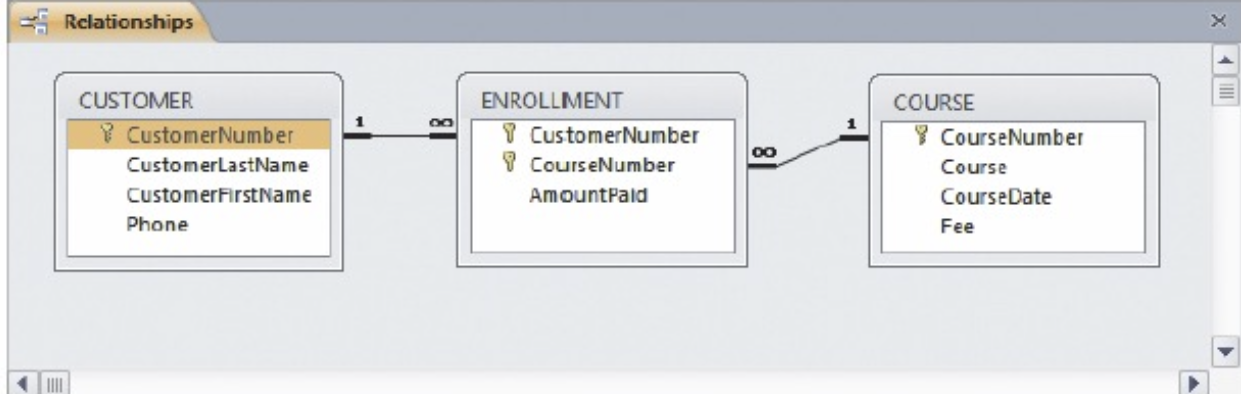
Relationship에 대한 data가 abstracted된 형태로 적혀있다.
그런데 1과 무한대는 무슨 뜻인가?
Customer한명당 Enrollment를 많이 할 수 있다. 반면 Enrollment하나에 Customer 여러명이 있을 수는 없다. 이를 나타내는 diagram이다.
DBMS
Functions of DBMS
• Create databases
• Create tables
• Create supporting structures
• Read database data
• Modify database data (insert, update, delete)
• Maintain database structures
• Enforce rules
• Control concurrency
• Provide security
• Perform backup and recovery
Referential Integrity Constraints
Referential integrity constraints ensure that the values of a column in one table are valid based on the values in another table
만약 한 Table에 CustomerID column에 5가 있다면, Customer table에도 CustomerID를 5로 가진 Customer가 있어야 한다.
DBMS는 이를 철저하게 Check해 준다.(Enforce rules)
Database Application
A database application is a set of one or more computer programs that
serves as an intermediary between the user and the DBMS
Functions of Database Applications
• Create and process forms
• Process user queries
• Create and process reports
• Execute application logic
• Control database applications
별로 수업에서 비중있게 안다룸.
Personal Database systems
• Personal database systems typically:
– Have one application
– Have only a few tables
– Are simple in design
– Involve only one computer
– Support one user at a time
이것도 DB임. 저번과 헷갈리지 말자.
Enterprise-Class Database Systems
• Enterprise-Class database systems typically:
– Support several users simultaneously
– Include more than one application
– Involve multiple computers
– Are complex in design
– Have many tables
– Have many databases
Commercial DBMS products
• Example Desktop DBMS Products
– Microsoft Access
• Example Organizational DBMS Products
– Microsoft’s SQL Server
– Oracle’s Oracle
– Sun Microsystem’s MySQL
– IBM’s DB2
