<React.js, 스프링 부트, AWS로 배우는 웹 개발 101>(김다정 지음)을 따라 TO-DO 앱을 하나 만들 예정이다.
앞으로 쓸 대부분의 포스팅(이미지/글)은 위의 서적을 참고/출처로 작성되었음을 미리 밝힌다.
먼저 이 프로젝트에서 활용될 아키텍처 두 가지를 구분하자.
레이어트 아키텍처 패턴은 스프링 프로젝트 내부에서 어떻게 코드를 적절히 분리하고 관리할 것이냐에 대한 것이다. 코드의 분리 관리는 규모가 큰 코드를 다룰 수록 중요하다.
반면 REST 아키텍처 스타일은 클라이언트(브라우저)가 서비스를 이용하려면 어떤 형식으로 요청을 보내고 응답을 받는지에 대한 것이다. 클라이언트는 몇 개의 정해진 메서드로 이 서비스를 이용할 예정이다.
이렇게 REST 아키텍처 스타일을 따라 설계 및 구현된 서비스를 RESTful 서비스라고 한다.
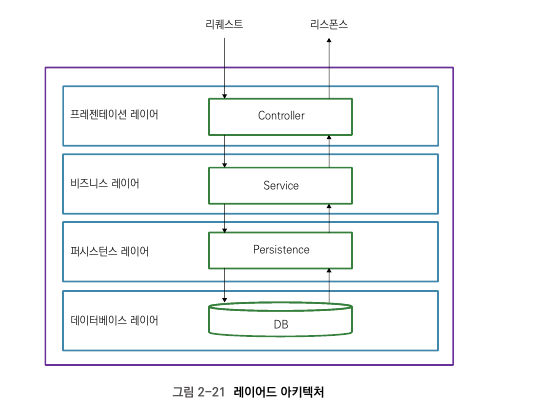
레이어드 아키텍처
레이어트 아키텍처 패턴은 애플리케이션 구성 요소를 수평으로 나눠 관리하는 것이다.
우선 수평으로 나누지 않고 한 메서드에 다 때려넣은 코드를 보자.
public String getTodo(Request request) {
// 요청 검사
if(request.userId == null) {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("error", "missing user id");
return json.toString();
}
List<Todo> todos = new ArrayList<>();
// 데이터베이스 콜
String sqlSelectAllPersons = "SELECT * FROM Todo where USER_ID = " + request.getUserID();
String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://mydb:3306/todo";
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl, "username", "password");
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sqlSelectAllPersons);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
long id = rs.getLong("ID");
String title = rs.getString("TITLE");
Boolean isDone = rs.getBoolean("IS_DONE");
todos.add(new Todo(id, title, isDone));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// handle the exception
}
// 응답 생성
JSONOBject json = new JSONObject();
JSONArray array = new JSONArray();
for(Todo todo : todos) {
JSONPObject todoJson = new JSONObject();
jsonObj.put("id", todo.getId());
jsonObj.put("title", todo.getTitle());
json.put("isdone", todo.isDone());
array.put(json);
}
json.put("data", array);
return json.toString();
}메서드를 분리한 웹 서비스
public String getTodo(Request request) {
// 요청 검사
if(request.userId == null) {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("error", "missing user id");
return json.toString();
}
List<Todo> todos = new ArrayList<>();
return this.getResponse(todos);
}
// 만약 다른 클래스에서 이 메소드(DB에서 Todo를 불러오는 작업을 하는)를 쓰게 된다면 그 클래서에 이 메소드를 똑같이 복붙해야 한다. 굉장히 비효율적. 차라리 class를 따로 빼서 쓰는 것이 나을 수도 있다. 이런 작업이 레이어로 나누는 것.
private List<Todo> getTodoFromPersistence(Request request) {
ArrayList<Todo> todos = new ArrayList<>();
// 데이터베이스 콜
String sqlSelectAllPersons = "SELECT * FROM Todo where USER_ID = " + request.getUserID();
String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://mydb:3306/todo";
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl, "username", "password");
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sqlSelectAllPersons);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
long id = rs.getLong("ID");
String title = rs.getString("TITLE");
Boolean isDone = rs.getBoolean("IS_DONE");
todos.add(new Todo(id, title, isDone));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// handle the exception
}
return todos;
}
private String get Response(List<Todo> todos) {
// 응답 생성
JSONOBject json = new JSONObject();
JSONArray array = new JSONArray();
for(Todo todo : todos) {
JSONPObject todoJson = new JSONObject();
jsonObj.put("id", todo.getId());
jsonObj.put("title", todo.getTitle());
json.put("isdone", todo.isDone());
array.put(json);
}
json.put("data", array);
return json.toString();
}
}레이어로 나눈다는 것은 메서드를 클래스 또는 인터페이스로 쪼개는 것이다.
이 범위는.. 클래스를 여러 레이어로 나누는 것부터, 아예 다른 애플리케이션으로 레이어를 분리하는 경우까지 법위가 다양하다.
레이어 사이에는 계층이 있다. 레이어는 자기보다 한 단계 하위의 레이어만 사용한다. 부장이 차장을 쪼고.. 차장이 과장을 쪼듯..
컨트롤러가 요청을 받는다.
컨트롤러는 서비스를 쫀다.
서비스는 퍼시스턴스를 쫀다.
퍼시스턴스는 요청한 데이터를 반환한다.
서비스는 데이터를 검토 및 가공한 후 컨트롤러에게 반환한다.
컨트롤러 또한 데이터를 검토 및 가공한 후 응답을 반환한다.
레이어를 적용한 예
public calss TodoService {
public List<Todo> getTodos(String userId) {
List<Todo> todos = new ArrayList<>();
// ... 비즈니스 로직
return todos;
}
}
public class WebController {
private TodoService todoService;
public String getTodo(Request request) {
// request validation
if(request.uerId == null) {
JSONObject json = new JSONObject();
json.put("error", "missing uer id");
return json.toString();
}
// 서비스 레이어
List<Todo> todos = service.getTodos(request.userId);
return this.getResponse(todos);
}
}