문제 출처
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42586 (프로그래머스)
학습 키워드
스택(STACK) , 큐(QUEUE)
시도 방법
(1) 스택/큐 없이 LinkedList ,ArrayList 활용 (성공)
(2) 스택/큐를 활용 (성공)
내가 작성한 코드
스택/큐 없이 LinkedList , ArrayList 활용 (성공)
import java.util.List;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] progresses, int[] speeds) {
List<Integer> progressLinkedList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> speedLinkedList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i<progresses.length; i++) {
progressLinkedList.add(progresses[i]);
speedLinkedList.add(speeds[i]);
}
int count = 0 ;
while(progressLinkedList.size() != 0) {
//배포할 개수 확인
if(progressLinkedList.get(0) >= 100) {
progressLinkedList.remove(0);
speedLinkedList.remove(0);
count += 1 ;
} else {
if(count != 0) {
result.add(count);
count = 0 ;
}
//개발 진척 처리
for(int i = 0 ; i<progressLinkedList.size(); i++) {
progressLinkedList.set(i , progressLinkedList.get(i) + speedLinkedList.get(i) );
}
}
}
result.add(count); //마지막 배포
return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}코드 설명
progressLinkedList 는 진척상황이 들어있는 Integer형 리스트 자료형이다.
speedLinkedList 는 하루마다 진척상황을 각 작업에 대해 표현한 자료형이다.
기존 int[] progress , int[] speeds 을 LinkedList로 바꾼 이유는 ,
이 문제가 리스트 요소의 삭제를 요구하는 문제이기 때문이다.
그렇기에 기존 고정 크기 이면서 요소 삽/삭제에 비효율적인 int[] 보다는
ArrayList 등의 가변형 리스트를 선택했다.
그리고나서 progressLinkedList.size() 가 비어있지 않을때까지 계속 반복을 하면서 가장 앞의 요소 (get(0)) 가 100 이상이면 해당 작업과 진척상황을 제거 (remove(0)) 하고 배포할 작업 개수를 의미하는 count를 1증가시킨다.
만약 100이상이 아니면서 count가 0이 아니면 (배포할 작업이 있으면) 이를 result 에 추가하고 count를 0으로 초기화한다.
while이 끝나고 나서 count가 0이 아닌 경우는, 마지막으로 배포한 작업이 마지막 작업일때 count는 추가되지만 그 다음 while문을 타지 못하므로 이를 방지하고자 마지막 배포 처리를 한다.
처리 결과
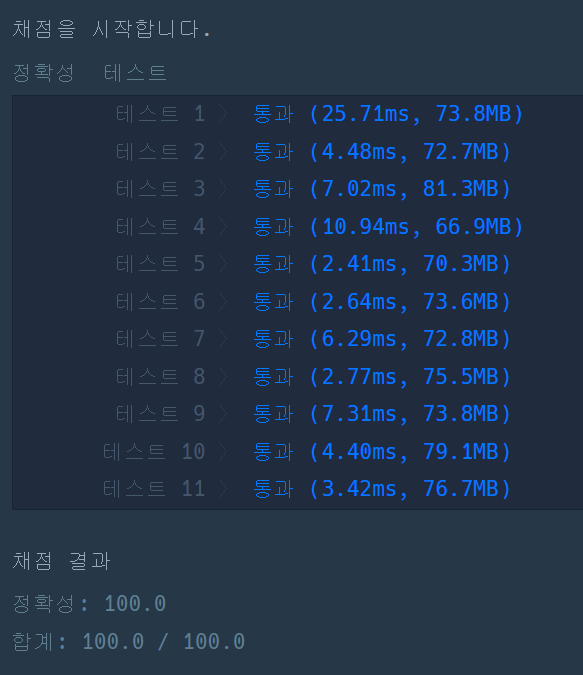
(2)스택/큐 기술 활용 (성공)
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
class Solution {
public static int[] solution(int[] progresses, int[] speeds) {
Queue<Integer> q_progresses = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> q_speeds = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
QueueMakerFromIntArray.make(progresses , q_progresses);
QueueMakerFromIntArray.make(speeds , q_speeds);
Deployment deployment = new Deployment(q_progresses , q_speeds);
Progress progress = new Progress(q_progresses , q_speeds);
while(!deployment.isEmpty()) {
int count = deployment.getDeployTaskCount();
if(count > 0) result.add(count);
progress.increaseProcess();
}
return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
class QueueMakerFromIntArray {
public static void make(int[] source , Queue<Integer> target) {
for(int arr : source) target.offer(arr);
}
}
class Deployment {
private Queue<Integer> q_progresses;
private Queue<Integer> q_speeds;
public Deployment(Queue<Integer> q_progresses , Queue<Integer> q_speeds) {
this.q_progresses = q_progresses;
this.q_speeds = q_speeds;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return q_progresses.isEmpty();
}
public int getDeployTaskCount() {
int count = 0 ;
while(!isEmpty()) {
if(q_progresses.peek() >= 100) {
q_progresses.poll();
q_speeds.poll();
count++;
} else {
break;
}
}
return count;
}
}
class Progress {
private Queue<Integer> q_progresses ;
private Queue<Integer> q_speeds ;
public Progress(Queue<Integer> q_progresses , Queue<Integer> q_speeds) {
this.q_progresses = q_progresses;
this.q_speeds = q_speeds;
}
//작업 진척 증가 (이부분은 큐가 오히려 불편할거 같은데..?)
public void increaseProcess() {
for(int i = 0 ; i< q_progresses.size(); i++) {
int tmp1 = q_progresses.poll();
int tmp2 = q_speeds.poll();
q_progresses.offer(tmp1+tmp2);
q_speeds.offer(tmp2) ;
}
}
}
코드 설명
흐름 자체는 (1)의 방법과 동일하다.
다만 Queue 개념을 사용했다는 점과 기능을 클래스화에서 "배포" 기능과 "진척" 기능의 책임을 구분함으로써 좀 더 객체지향에 맞게 구현을 한 것이다.
처리 결과
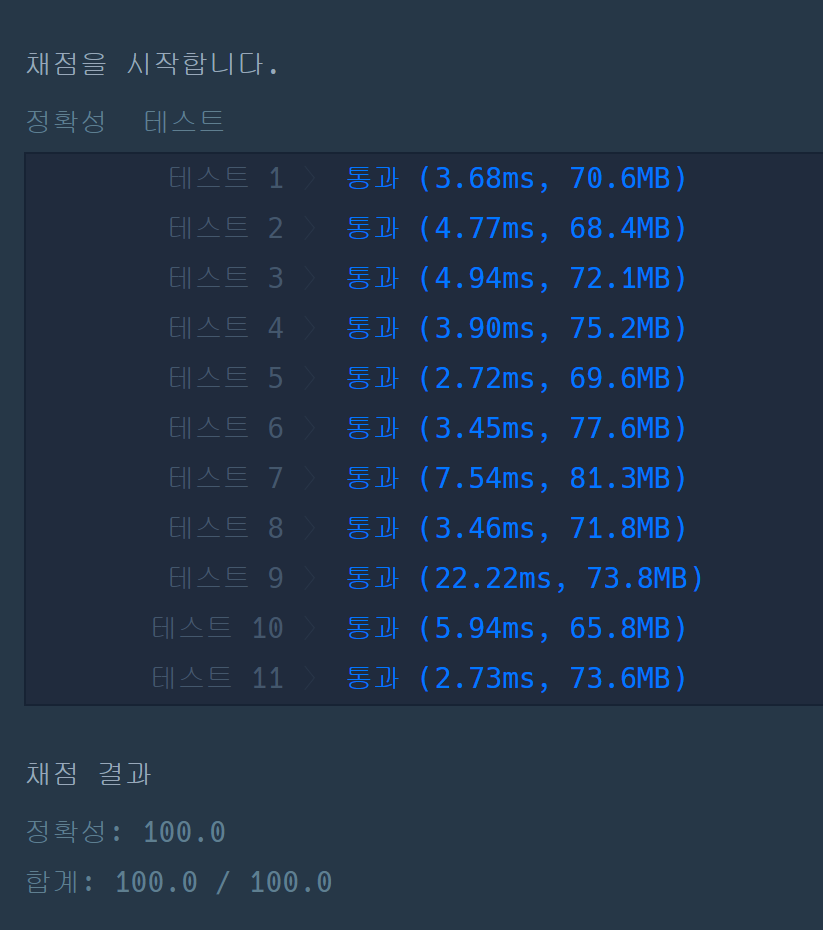
새롭게 알게된 점
-
ArrayList 와 LinkedList를 언제 어떤 것을 사용하면 좋을지 알 수 있었다.
ArrayList는 조회성능이 좋으나 삽삭 성능이 좋지 않음
LinkedList는 삽삭 성능은 좋으나 조회 성능이 안좋음 -
Queue 를 구현하려면 LinkedList 구현체를 사용해야 함을 알았다.
다음에 풀어볼 문제 - 올바른괄호
#99클럽 #코딩테스트 준비 #개발자 취업 #항해99 #TIL
