한 일
- ServletContext
- 쿠키 (Cookie)
- DB연결 (MySQL)
- 커넥션 풀 (ConnectionPool DBCP)
- 데이터 소스 (DataSource)
ServletContext
-
ServletContext클래스는 톰캣 컨테이너 실행 시 각 컨텍스트(웹 애플리케이션)마다 한 개의 ServletContext객체를 생성함.
-
톰캣 컨테이너가 종료되면 ServletContext객체도 소멸됨.
-
사용: getServletContext() 으로 리턴
-
세션, 리퀘스트와 차이점
세션은 브라우저별로 따로 관리되지만 컨텍스트는 하나밖에 없으므로 브라우저가 달라도 공유됨.
리퀘스트는 그 요청을 가지고있는 페이지에서만 사용/저장됨.(리퀘스트를 다른페이지에서 사용하려면 forward과정 필요)
Controller.java서블릿
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// getContextPath: Context의 주소를 표시함
ServletContext context = getServletContext(); // 현재 이 어플리케이션의 context객체 리턴
// context에 저장한 hits를 가져옴
Integer hits = (Integer)context.getAttribute("hits");
// (Integer): getAttribute는 object를 리턴하기때문에 int형으로 변환해줌
// 가져온 hits에 값이 없을 경우(=최초호출시 값이 없음)
if(hits == null) hits = 0; // hits를 0으로 초기화
else hits++; // hits에 저장된 값이 있을 경우 +1 해줌
context.setAttribute("hits", hits); // hits라는 속성값을 context에 저장
// context에 저장된 hits를 출력
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("Hits: "+ hits);
// ServletContext: 톰캣 컨테이너 실행 시 각 웹 어플리케이션(컨텍스트)마다 하나의 객체를 생성함. 톰캣컨테이너가 종료되면 같이 소멸됨.
// 세션은 브라우저별로 따로 관리되지만 컨텍스트는 브라우저가 달라도 공유됨. 리퀘스트는 그 요청에서만 사용됨
}~ 참고 ~
- 세션, 리퀘스트, 컨텍스트의 속성값을 가져올땐 getAtrribute를 사용.
=>getAtrribute로 속성값을 불러올땐 object를 리턴하므로 처음 저장했던 형태로 변환이 필요.(String, integer등) - 주소창의 데이터를 가져올땐 getParameter를 사용.
쿠키 (Cookie)
- 쿠키는 브라우저에 저장됨 (사용자가 직접조회가능 => 보안에 약함)
- 서버와 브라우저 사이의 text 데이터를 교환함
- 사이트별로 20개까지 저장가능
- Name과 value가 쌍으로 묶여있음 (이름과 값이 모두 문자열임)
- 생성자: Cookie(String name, String value)
- 사용:
먼저 생성자로 생성 + 객체에 이름과 값 저장 -> 객체명.setMaxAge(초)로 쿠키의 저장시간설정 -> response.addCookie(객체명)으로 객체의 정보를 쿠키에 저장
Cookies.java서블릿
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter(); // 프린터객체생성
out.println("<html>");
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies(); // 쿠기배열 생성
if (cookies == null) {
// 쿠키배열에 값이 null값일 경우
out.println("쿠키없음<br/>"); // 쿠키없음 출력
} else {
// 쿠키배열에 값이 있을 경우
//=> 반복문을 이용해 배열이 끝날때까지 각 이름과 값을 name과 value에 저장해 같이 출력
for (Cookie retrievedCookie : cookies) {
String name = retrievedCookie.getName();
String value = retrievedCookie.getValue();
out.println(name+" = "+value+"<br/>");
}
}
// user, Son의 이름과 값을 가진 c1쿠키를 생성
Cookie c1 = new Cookie("user", "Son");
Cookie c2 = new Cookie("user2", "Kim");
c1.setMaxAge(300); // 쿠키의 유효시간: 300초
c2.setMaxAge(300);
response.addCookie(c1); // c1을 쿠키에 저장
response.addCookie(c2);
out.println("Cookie save.<br/>");
out.println("<html>");
}=> 실행해보면 최초실행땐 Cookie배열에 아무것도 없으므로 '쿠키없음'이 출력되지만 새로고침을 해주면 생성한 c1, c2의 이름과 값이 출력된다
세션과 쿠키 (session cookie)
- 세션: 서버에 저장됨
세션id는 서버측에서 자동생성됨. 사용자가 변경불가.
서버측에 저장되므로 보안에 유리
JSP세션은 하나의 사용자의 브라우저당 하나가 만들어짐. 같은pc라도 브라우저가 다르면 다른 세션으로 저장됨 - 쿠키: 클라이언트의 브라우저에 저장됨
개인로컬에 저장되어 사용자가 직접 조회가능 => 해킹등의 보안에 약함
세션에 대해서는 3일차 참고
DB연결 (MySQL)
- 드라이버는 DB별로 다르지만(oracle, MySQL 등) 구현에 사용하는 JDBC인터페이스는 공통임
- 드라이버 넣기
1) 프로젝트에 : 각 프로젝트의 webcontent/WEB-INF/lib에 넣어줌
2) 톰캣프로그램에 : C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 9.0\lib 에 넣어줌
=> 자주쓸거면 톰캣에 넣는게 편함. 프로젝트 하나하나에 넣어줄필요없음.
로딩코드: Class.forName("JDBC드라이버이름")
커넥션 풀 (ConnectionPool DBCP)
-
개념: (DB와 연결이 하나만 되어있다면 순차적으로 처리하지만)
연결이 여러개일 경우 클라이언트의 요청이 오면 커넥션을 빌려주고 처리가 끝나면 커넥션을 반납받아 pool에 저장하는 방식을 말한다. -
사용목적: 자바에서 직접 DB에 연결해 사용하면 매번 사용자의 요청에 따라 매번 드라이버를 로드, 커넥션객체를 생성, 연결, 종료해야하기때문에 커넥션풀을 사용해 간단히 사용할 수 있게함
-
connection pool 설정 : WebContent/META-INF/context.xml 에 작성함
Context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context>
<Resource name="jdbc/webshop" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxActive="20" maxIdle="5" maxWait="10000"
username="사용자명" password="패스워드" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/사용할DB이름?useSSL=false"/>
</Context>=> username에는 DB를 사용할 사용자의 이름을, password는 그 사용자의 비밀번호를 입력한다.(DB에 미리 설정해둔 대로)
url에는 사용할 DB의 주소를 입력하는데, DB이름 뒤의 ?useSSL=false는 SSL설정을 사용하지 않겠다는 의미이다.
Connect.java(servlet) doGet메서드
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8"); // 한글설정(서블릿으로 한글출력하려면 필요)
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Connection conn = null; // 톰캣에 커넥터를 추가해줬으므로 Connection을 사용할수있음
try {
// 0. 드라이버 로딩 (생략가능. JDK6버전 이하는 반드시 필요)
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 1. DB연결
conn = DriverManager.getConnection( // DB주소(SSL속성은 번거로우니 꺼줌), 유저id, 비밀번호
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/webshop?useSSL=false", "root", "1234");
} catch (SQLException e) {
// DB를 찾지 못했을때 발생하는 예외
out.println("DB에 연결 실패...");
return;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// 드라이버를 못찾을때 발생하는 예외
out.println("드라이버 클래스를 찾을 수 없습니다.");
return;
}
// 실패없이 여기까지 내려오면 성공
out.println("DB연결 테스트 완료!");
try {
conn.close(); // conn종료
} catch (SQLException e) {
out.println("DB연결 종료과정에서 에러발생...");
}데이터 소스 (DataSource)
- ConnectionPool을 관리하는 목적으로 사용되는 객체.
데이터 소스 인터페이스를 통해 커넥션 객체를 빌려오고 반납하는 작업을 구현함.
여기서 Resource의 주소는 Context.xml의 resource url과 동일해야 한다.
DatasourceDemo.java(servlet)
// context.xml의 <Resource>와 연결해줌
@Resource(name="jdbc/webshop")
private DataSource ds; // 데이터소스 ds로 DB연결
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8"); // 한글설정(서블릿으로 한글출력하려면 필요)
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Connection conn = null; // 톰캣에 커넥터를 추가해줬으므로 Connection을 사용할수있음
try {
conn = ds.getConnection(); // DB연결
} catch (SQLException e) {
out.println("DB에 연결 실패...");
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
out.println("DB연결 테스트 완료!");
try {
conn.close(); // 실제로는 conn을 닫는것 대신에 connection을 connection pool로 보냄(요청이 올때까지 대기중인 커넥션풀로 보낸다는뜻)
} catch (SQLException e) {
out.println("DB연결 종료과정에서 에러발생...");
}
}ConnectionPool과 DataSource를 이용해 DB연결하기 예제
위의 커넥션 풀에서 작성한 connection.xml과 Connect서블릿, 데이터 소스에서 작성한 DatasourceDemo서블릿.
이 3개의 페이지를 작성했다면 예제를 실행해본다.
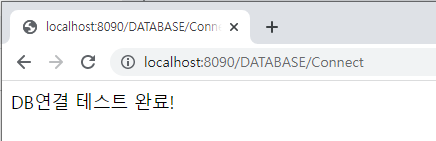
=> DB와 연결이 되었다면 이런 화면이 나온다.