A is a B
class A extends B
상속되지 않는 것.
아래 3가지 빼고는 모두 상속됨 (초기화 블록은 다루지 않음)
1. 생성자(Constructor)
- 자식 클래스는 부모 클래스의 생성자를 상속받지 않음
- 생각해보면 당연한 것; 자식 클래스는 자신의 생성자를 명시적으로 정의해야 함
- 부모 클래스의 생성자를 호출하려면 super() 키워드를 사용
2. private 멤버 변수 및 메서드
- 자식 클래스는 부모 클래스의 private 멤버 변수와 메서드를 직접 상속받지 않음
- 그러나 메서드를 이용한 접근은 가능 : 부모 클래스의 public 또는 protected 메서드를 통해 접근할 수 있다.
3. static 메서드
- static 메서드는 클래스 자체에 속하므로 상속의 개념이 아님
- 따라서 자식 클래스는 부모 클래스의 static 메서드를 상속받지 않지만, 부모 클래스의 static 메서드를 사용할 수 있긴 하다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
child.accessMethods();
Parent.staticMethod(); // 가능: static 메서드는 클래스 이름으로 접근
Child.staticMethod(); // 가능: 부모 클래스의 static 메서드를 자식 클래스 이름으로도 접근 가능
}
}상속시 주의사항
1. constructor 상속
- base class의 constructor는 상속이 안됨
- derived class에서 사용하려면,
super를 이용- 자식클래스의 first statement에서 사용해야 함
- 자식의 필드를 super의 인자로 전달할 수 없다.(왜냐하면, 부모의 생성자 호출 시점에 필드는 초기화 되지 않기에)
- 별다른 super를 호출하지 않는다면 부모의 no-argument constructor가 호출된다
- 따라서 부모 클래스에 매개변수가 있는 생성자만 정의된 경우(기본 생성자를 따로 정의하지 않으면 java에서 만들지 않음),
super를 쓰지 않으면 컴파일 에러가 발생한다.
2.this constructor for constructor chaining
- 다른 생성자를 활용해 정의하는 것
- 반드시 생성자의 첫 번째 문장이어야 함
*this와 super를 동시에 쓸 수 없음
주의 : this로 호출된 다른 constructor에서 super를 호출하는 것은 가능
3. private 멤버는 다른 클래스에서 사용될 수 없다.
proxy access 는 가능
// 부모 클래스
class SuperClass {
// 슈퍼클래스의 private 메서드
private void privateMethod() {
System.out.println("Private method in SuperClass");
}
// 슈퍼클래스의 public 메서드
public void publicMethod() {
System.out.println("Public method in SuperClass calling the private method");
privateMethod(); // private 메서드를 호출
}
}
// 자식 클래스
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
// 자식 클래스에서 슈퍼클래스의 public 메서드를 통해 간접적으로 private 메서드를 호출
public void accessSuperPrivateMethod() {
System.out.println("SubClass calling SuperClass's publicMethod");
publicMethod(); // 슈퍼클래스의 public 메서드를 호출, 이 메서드는 내부적으로 private 메서드를 호출
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubClass subClass = new SubClass();
subClass.accessSuperPrivateMethod(); // SubClass를 통해 슈퍼클래스의 private 메서드에 간접적으로 접근
}
}4. package access
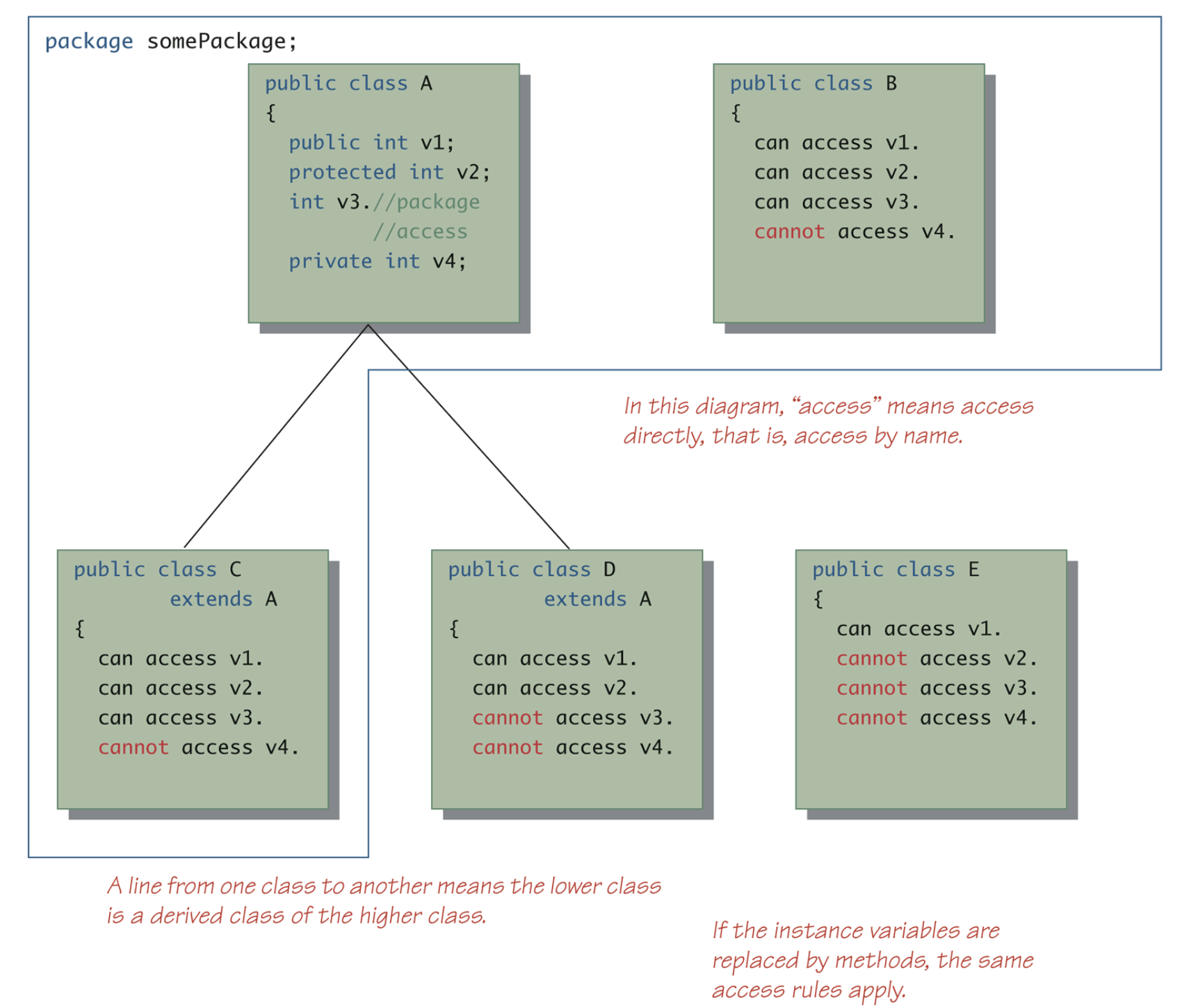
- protected 멤버에 대해, 다른 패키지에 정의된 자식 클래스는 접근이 가능하다.
- public만 package에 자유롭다; protected, default, private은 안된다.
* 같은 package의 클래스들은 같은 namespace에 들어가 다른 package내 같은 이름과 구분해 준다.
5.final : 상속 방지 // override 금지
- final class : 상속 방지
- final method : override 금지
- final field : constant처리
6. Access 허용 변화 : 허용치를 높인다; 제한은 불가
활용
[활용 예시 - StringTokenizer를 상속받아 기능 강화]
원래 StringTokenizer는 한 번에 한 번씩 문자열의 토큰을 생성하는 기능을 제공하지만, 기본적으로 두 번째 순회 또는 반복을 지원하지 않는다
하지만 상속으로 기능을 강화할 수 있다
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class CustomStringTokenizer {
private String originalString;
private StringTokenizer tokenizer;
private String delim;
private boolean returnDelims;
// Constructor for default delimiters
public CustomStringTokenizer(String str) {
this.originalString = str;
this.delim = " \t\n\r\f"; // default delimiters
this.returnDelims = false;
this.tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(str);
}
// Constructor with custom delimiters
public CustomStringTokenizer(String str, String delim) {
this.originalString = str;
this.delim = delim;
this.returnDelims = false;
this.tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(str, delim);
}
// Constructor with custom delimiters and returnDelims flag
public CustomStringTokenizer(String str, String delim, boolean returnDelims) {
this.originalString = str;
this.delim = delim;
this.returnDelims = returnDelims;
this.tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(str, delim, returnDelims);
}
// Reset method: reinitialize the tokenizer
public void reset() {
this.tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(this.originalString, this.delim, this.returnDelims);
}
// Delegate methods to the tokenizer
public boolean hasMoreTokens() {
return tokenizer.hasMoreTokens();
}
public String nextToken() {
return tokenizer.nextToken();
}
// Main method for demonstration
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomStringTokenizer tokenizer = new CustomStringTokenizer("Hello World");
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(tokenizer.nextToken());
}
// Reset the tokenizer
tokenizer.reset();
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(tokenizer.nextToken());
}
}
}
Object class
java.lang에 포함 -> 자동으로 import- 모든 클래스의 조상
equals,toStringmethod는 모든 클래스가 상속 받음
equals 정의법
-
null 검사 + 같은 타입인지 검사
-
Object o에서o는 반드시 타입 캐스팅되어야 한다. 그 후에 필드 동일성을 검사한다.
public boolean equals(Object otherObject) {
if(otherObject == null) {
return false;
} else if (getClass( ) != otherObject.getClass( )) {
return false;
} else {
Employee otherEmployee = (Employee)otherObject; r
eturn (name.equals(otherEmployee.name) &&
hireDate.equals(otherEmployee.hireDate));
}
}getClass() VS instanceof operator
모두 타입 체크 용
getClass()는 final 메서드다 => override불가능
obj instanceof ClassA
- true : classA 거나 그 자식 클래스 타입
- false : 그 외
- 차이를 예시로 이해하자
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Parent();
Child child = new Child();
Parent parentChild = new Child();
System.out.println(parent instanceof Parent); // true
System.out.println(child instanceof Child); // true
System.out.println(child instanceof Parent); // true
System.out.println(parentChild instanceof Parent); // true
System.out.println(parentChild instanceof Child); // true
}
}
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Parent();
Child child = new Child();
Parent parentChild = new Child();
System.out.println(parent.getClass() == Parent.class); // true
System.out.println(child.getClass() == Child.class); // true
System.out.println(parentChild.getClass() == Parent.class); // false
System.out.println(parentChild.getClass() == Child.class); // true
}
}
getClass() 메서드는 다형성(polymorphism)에서 부모 클래스 타입의 변수로 참조된 자식 클래스 객체의 정확한 타입을 알 수 있게 해준다.
class Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Some generic animal sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bark");
}
public void fetch() {
System.out.println("Dog is fetching");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow");
}
public void scratch() {
System.out.println("Cat is scratching");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal myAnimal1 = new Dog();
Animal myAnimal2 = new Cat();
// 다형성을 이용하여 상위 클래스 타입 변수로 메서드 호출
myAnimal1.makeSound(); // 출력: Bark
myAnimal2.makeSound(); // 출력: Meow
// instanceOf를 사용하여 실제 객체 타입에 따라 다른 동작 수행
if (myAnimal1 instanceof Dog) {
Dog myDog = (Dog) myAnimal1;
myDog.fetch(); // 출력: Dog is fetching
}
if (myAnimal2 instanceof Cat) {
Cat myCat = (Cat) myAnimal2;
myCat.scratch(); // 출력: Cat is scratching
}
}
}