해당 글은 Foundry Book의 코드를 정리하고 요약한 글입니다. 요약 글이기 때문에 빠진 부분이 있으며, 책을 먼저 읽고 오시면 이해가 더 잘 될거예요 :)
Foundry?
솔리디티로 컨트랙트 개발을 하다보면 여러 기능들이 필요하다. 자신이 작성한 함수가 정상적으로 돌아가는지, 컨트랙트가 소비하는 가스는 어느 정도인지 등 이러한 부분들을 채워주는 툴이 파운드리다. 파운드리는 패러다임에서 만들었으며, 옵티미즘과 메이커 다오같은 유명한 프로젝트들에서 사용할 정도로 매우 유용한 툴이다. 러스트로 만들어져서 테스트 속도가 매우 빠르고 기존에 솔리디티 개발자들이 만들었기 때문에 사용자 입장에서 직관적으로 사용할 수 있도록 만든 것이 특징이다.
설치
설치는 매우 간단하다. 맥을 기준으로 터미널에 아래 명령어를 입력하자.
curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
foundryup
프로젝트 관련 명령어
새 프로젝트 만들기
$ forge init hello_foundry
기존 프로젝트 가져오기
$ git clone https://github.com/abigger87/femplate
$ cd femplate
$ forge install
테스트 관련 명령어
기본적인 테스트 명령어
$ forge test특정 컨트랙트 테스트 명령어
$ forge test --match-contract <테스트_컨트랙트_이름> --match-test <테스트_이름>특정 경로에 있는 컨트랙트 테스트
$ forge test --match-path 경로/컨트랙트이름.t.sol실제 테스트 하기
한 가지 주의할 점은 테스트 할 함수는 항상 public 또는 external로 선언되어야 한다는 것. 그리고 테스트 파일을 만들기 전에 forge init <테스트 프로젝트 이름>으로 프로젝트를 만들고 나서 그 안에 테스트 파일을 작성해야 한다.
pragma solidity 0.8.17;
//Test 파일 임포트
import '../lib/forge-std/src/Test.sol';
//테스트 컨트랙트에 Test 상속
contract ContractBTest is Test {
uint256 testNumber;
function setUp() public {
testNumber = 42;
}
//테스트 할 함수 이름 앞에 test 작성
//pass가 되어야 성공
function testNumberIs42() public {
assertEq(testNumber, 42);
}
//fail 테스트 할 함수 이름 앞에 testFail 작성
//fail이 되어야 성공
function testFailSubtract43() public {
testNumber -= 43;
}
}
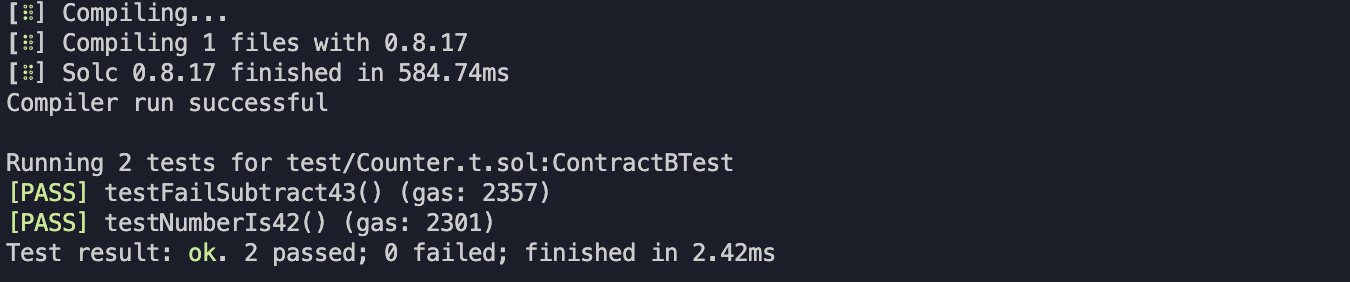
마지막 테스트 함수인 testFailSubtract43()는 아래와 같이 작성할 수 있다. 즉, testFail = testCannot + vm.expectRevert()
function testCannotSubtract43() public {
vm.expectRevert(stdError.arithmeticError);
testNumber -= 43;
}테스트 결과 성공!
Cheat Codes
foundry에서 유용하게 쓸 수 있는 함수들이다. vm 인스턴스를 사용해서 함수를 호출할 수 있다.
interface CheatCodes {
// This allows us to getRecordedLogs()
struct Log {
bytes32[] topics;
bytes data;
}
// Set block.timestamp
function warp(uint256) external;
// Set block.number
function roll(uint256) external;
// Set block.basefee
function fee(uint256) external;
// Set block.difficulty
function difficulty(uint256) external;
// Set block.chainid
function chainId(uint256) external;
// Loads a storage slot from an address
function load(address account, bytes32 slot) external returns (bytes32);
// Stores a value to an address' storage slot
function store(address account, bytes32 slot, bytes32 value) external;
// Signs data
function sign(uint256 privateKey, bytes32 digest)
external
returns (uint8 v, bytes32 r, bytes32 s);
// Computes address for a given private key
function addr(uint256 privateKey) external returns (address);
// Derive a private key from a provided mnemonic string,
// or mnemonic file path, at the derivation path m/44'/60'/0'/0/{index}.
function deriveKey(string calldata, uint32) external returns (uint256);
// Derive a private key from a provided mnemonic string, or mnemonic file path,
// at the derivation path {path}{index}
function deriveKey(string calldata, string calldata, uint32) external returns (uint256);
// Gets the nonce of an account
function getNonce(address account) external returns (uint64);
// Sets the nonce of an account
// The new nonce must be higher than the current nonce of the account
function setNonce(address account, uint64 nonce) external;
// Performs a foreign function call via terminal
function ffi(string[] calldata) external returns (bytes memory);
// Set environment variables, (name, value)
function setEnv(string calldata, string calldata) external;
// Read environment variables, (name) => (value)
function envBool(string calldata) external returns (bool);
function envUint(string calldata) external returns (uint256);
function envInt(string calldata) external returns (int256);
function envAddress(string calldata) external returns (address);
function envBytes32(string calldata) external returns (bytes32);
function envString(string calldata) external returns (string memory);
function envBytes(string calldata) external returns (bytes memory);
// Read environment variables as arrays, (name, delim) => (value[])
function envBool(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (bool[] memory);
function envUint(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (uint256[] memory);
function envInt(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (int256[] memory);
function envAddress(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (address[] memory);
function envBytes32(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (bytes32[] memory);
function envString(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (string[] memory);
function envBytes(string calldata, string calldata)
external
returns (bytes[] memory);
// Convert Solidity types to strings
function toString(address) external returns(string memory);
function toString(bytes calldata) external returns(string memory);
function toString(bytes32) external returns(string memory);
function toString(bool) external returns(string memory);
function toString(uint256) external returns(string memory);
function toString(int256) external returns(string memory);
// Sets the *next* call's msg.sender to be the input address
function prank(address) external;
// Sets all subsequent calls' msg.sender to be the input address
// until `stopPrank` is called
function startPrank(address) external;
// Sets the *next* call's msg.sender to be the input address,
// and the tx.origin to be the second input
function prank(address, address) external;
// Sets all subsequent calls' msg.sender to be the input address until
// `stopPrank` is called, and the tx.origin to be the second input
function startPrank(address, address) external;
// Resets subsequent calls' msg.sender to be `address(this)`
function stopPrank() external;
// Sets an address' balance
function deal(address who, uint256 newBalance) external;
// Sets an address' code
function etch(address who, bytes calldata code) external;
// Expects an error on next call
function expectRevert() external;
function expectRevert(bytes calldata) external;
function expectRevert(bytes4) external;
// Record all storage reads and writes
function record() external;
// Gets all accessed reads and write slot from a recording session,
// for a given address
function accesses(address)
external
returns (bytes32[] memory reads, bytes32[] memory writes);
// Record all the transaction logs
function recordLogs() external;
// Gets all the recorded logs
function getRecordedLogs() external returns (Log[] memory);
// Prepare an expected log with the signature:
// (bool checkTopic1, bool checkTopic2, bool checkTopic3, bool checkData).
//
// Call this function, then emit an event, then call a function.
// Internally after the call, we check if logs were emitted in the expected order
// with the expected topics and data (as specified by the booleans)
//
// The second form also checks supplied address against emitting contract.
function expectEmit(bool, bool, bool, bool) external;
function expectEmit(bool, bool, bool, bool, address) external;
// Mocks a call to an address, returning specified data.
//
// Calldata can either be strict or a partial match, e.g. if you only
// pass a Solidity selector to the expected calldata, then the entire Solidity
// function will be mocked.
function mockCall(address, bytes calldata, bytes calldata) external;
// Clears all mocked calls
function clearMockedCalls() external;
// Expect a call to an address with the specified calldata.
// Calldata can either be strict or a partial match
function expectCall(address, bytes calldata) external;
// Expect a call to an address with the specified
// calldata and message value.
// Calldata can either be strict or a partial match
function expectCall(address, uint256, bytes calldata) external;
// Gets the _creation_ bytecode from an artifact file. Takes in the relative path to the json file
function getCode(string calldata) external returns (bytes memory);
// Gets the _deployed_ bytecode from an artifact file. Takes in the relative path to the json file
function getDeployedCode(string calldata) external returns (bytes memory);
// Label an address in test traces
function label(address addr, string calldata label) external;
// When fuzzing, generate new inputs if conditional not met
function assume(bool) external;
// Set block.coinbase (who)
function coinbase(address) external;
// Using the address that calls the test contract or the address provided
// as the sender, has the next call (at this call depth only) create a
// transaction that can later be signed and sent onchain
function broadcast() external;
function broadcast(address) external;
// Using the address that calls the test contract or the address provided
// as the sender, has all subsequent calls (at this call depth only) create
// transactions that can later be signed and sent onchain
function startBroadcast() external;
function startBroadcast(address) external;
// Stops collecting onchain transactions
function stopBroadcast() external;
// Reads the entire content of file to string, (path) => (data)
function readFile(string calldata) external returns (string memory);
// Get the path of the current project root
function projectRoot() external returns (string memory);
// Reads next line of file to string, (path) => (line)
function readLine(string calldata) external returns (string memory);
// Writes data to file, creating a file if it does not exist, and entirely replacing its contents if it does.
// (path, data) => ()
function writeFile(string calldata, string calldata) external;
// Writes line to file, creating a file if it does not exist.
// (path, data) => ()
function writeLine(string calldata, string calldata) external;
// Closes file for reading, resetting the offset and allowing to read it from beginning with readLine.
// (path) => ()
function closeFile(string calldata) external;
// Removes file. This cheatcode will revert in the following situations, but is not limited to just these cases:
// - Path points to a directory.
// - The file doesn't exist.
// - The user lacks permissions to remove the file.
// (path) => ()
function removeFile(string calldata) external;
// Return the value(s) that correspond to 'key'
function parseJson(string memory json, string memory key) external returns (bytes memory);
// Return the entire json file
function parseJson(string memory json) external returns (bytes memory);
// Snapshot the current state of the evm.
// Returns the id of the snapshot that was created.
// To revert a snapshot use `revertTo`
function snapshot() external returns (uint256);
// Revert the state of the evm to a previous snapshot
// Takes the snapshot id to revert to.
// This deletes the snapshot and all snapshots taken after the given snapshot id.
function revertTo(uint256) external returns (bool);
// Creates a new fork with the given endpoint and block,
// and returns the identifier of the fork
function createFork(string calldata, uint256) external returns (uint256);
// Creates a new fork with the given endpoint and the _latest_ block,
// and returns the identifier of the fork
function createFork(string calldata) external returns (uint256);
// Creates _and_ also selects a new fork with the given endpoint and block,
// and returns the identifier of the fork
function createSelectFork(string calldata, uint256)
external
returns (uint256);
// Creates _and_ also selects a new fork with the given endpoint and the
// latest block and returns the identifier of the fork
function createSelectFork(string calldata) external returns (uint256);
// Takes a fork identifier created by `createFork` and
// sets the corresponding forked state as active.
function selectFork(uint256) external;
// Returns the currently active fork
// Reverts if no fork is currently active
function activeFork() external returns (uint256);
// Updates the currently active fork to given block number
// This is similar to `roll` but for the currently active fork
function rollFork(uint256) external;
// Updates the given fork to given block number
function rollFork(uint256 forkId, uint256 blockNumber) external;
// Fetches the given transaction from the active fork and executes it on the current state
function transact(bytes32) external;
// Fetches the given transaction from the given fork and executes it on the current state
function transact(uint256, bytes32) external;
// Marks that the account(s) should use persistent storage across
// fork swaps in a multifork setup, meaning, changes made to the state
// of this account will be kept when switching forks
function makePersistent(address) external;
function makePersistent(address, address) external;
function makePersistent(address, address, address) external;
function makePersistent(address[] calldata) external;
// Revokes persistent status from the address, previously added via `makePersistent`
function revokePersistent(address) external;
function revokePersistent(address[] calldata) external;
// Returns true if the account is marked as persistent
function isPersistent(address) external returns (bool);
/// Returns the RPC url for the given alias
function rpcUrl(string calldata) external returns (string memory);
/// Returns all rpc urls and their aliases `[alias, url][]`
function rpcUrls() external returns (string[2][] memory);
}
이후에도 내용이 많지만 필요할 때마다 책에서 검색해서 찾는 것이 훨씬 나을 것 같다.