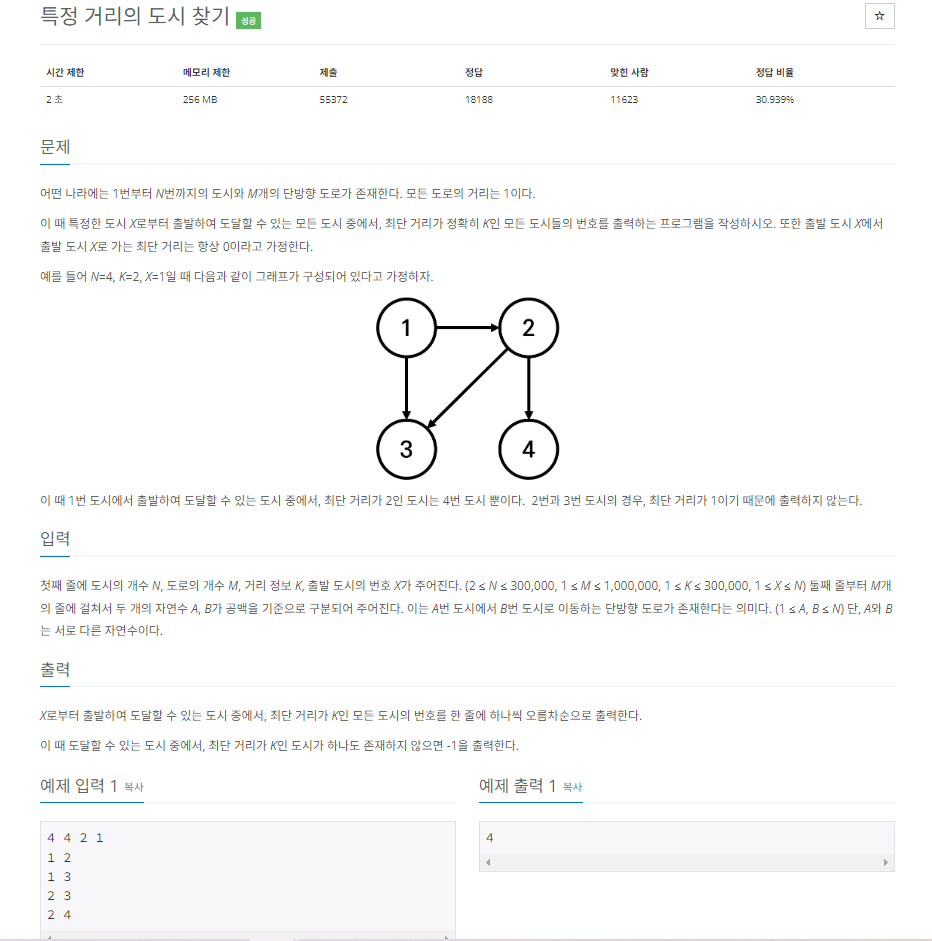
문제사항
실버 2단계 문제였다.
그래프 문제로, BFS 알고리즘을 사용하였다.
자료구조는 Queue/LinkedList를 사용하여 인접노드들을 탐색하며 X번호 도시부터 dist 배열 중 도시의 거리가 K가 될때 StringBuilder에 포함시키는 방식으로 풀었다.
실제로 너비 우선 탐색인 BFS는 여러 놈(?)을 한대씩 때리면서 가는 유형으로 Queue/LinkedList 사용하는 것이 보편적
알고리즘 분류
- 그래프
- 다익스트라
- BFS(너비 우선 탐색)
- 최단경로
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int N, M, K, X;
static int[] dist;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
X = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
dist = new int[N + 1];
//ArrayList Integer를 저장할 수 있는 ArrayList 객체를 저장하는 ArrayList
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
//정수를 저장할 수 있는 1번부터 n번까지 ArrayList 객체가 있어야 된다. (0번은 무의미함, 버리는 숫자)
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
dist[i] = -1; //각 도시의 거리는 초기값 -1
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph.get(a).add(b);
}
bfs(X);
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
if(dist[i] == K) sb.append(i + "\n");
}
if (sb.length() == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
static void bfs(int X) {
dist[X] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(X);
while (!q.isEmpty()) { //Queue가 비어있지 않다면 (반복문에서 Queue에서 숫자를 꺼내고 저장하고를 반복)
int now = q.poll(); //Queue에서 꺼내서 반환하며 삭제
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(now).size(); i++) {
int next = graph.get(now).get(i);
if (dist[next] == -1) {
dist[next] = dist[now] + 1;
q.offer(next); //Queue에 저장
}
}
}
}
}
