https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/description/
문제 설명
Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value target in an m x n integer matrix matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
Integers in each row are sorted in ascending from left to right.
Integers in each column are sorted in ascending from top to bottom.
예제
Example 1:
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
Output: false
제약사항
Constraints:
m == matrix.length
n == matrix[i].length
1 <= n, m <= 300
-109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
All the integers in each row are sorted in ascending order.
All the integers in each column are sorted in ascending order.
-109 <= target <= 109
처음에는 이분 탐색을 loop로 하면 간단하게 풀리겠다고 생각했다.
그리고 역시, 쉽게 풀렸다. 이분 탐색에 추가로 early return 만 만들어주었다. (첫 날, 스터디장님께 배운 구조👍)
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
def binary_search(arr, x):
l = 0
h = len(arr) - 1
mid = 0
while l <= h:
mid = (h + l) // 2
# x가 중간 값보다 작으면 오른쪽 부분을 무시합니다.
if arr[mid] < x:
l = mid + 1
# x가 중간 값보다 크면 왼쪽 부분을 무시합니다.
elif arr[mid] > x:
h = mid - 1
# x가 중간 값과 같으면 현재 (중간) 위치를 반환합니다.
else:
return True
# x가 리스트에 없으면 -1을 반환합니다.
return False
if (target < matrix[0][0] or target > matrix[-1][-1]) :
return False
for mat in (matrix) :
if (binary_search(mat, target)) :
return True
return False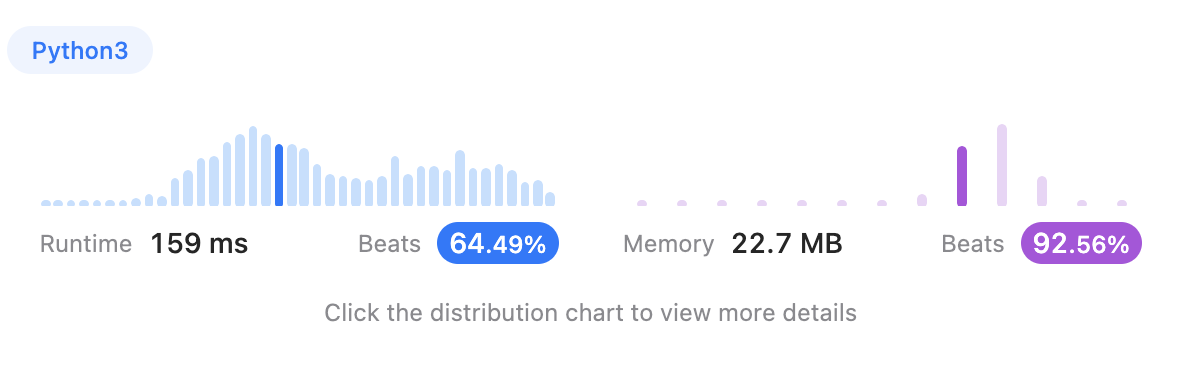
2 번째로, 분할 정복을 이용해서 matrix를 잘라주고 나머지 부분에만 이분 탐색을 해보자고 생각했다.
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
if (target < matrix[0][0] or target > matrix[-1][-1]):
return False
def binary_search(arr, target):
l = 0
h = len(arr) - 1
mid = 0
while l <= h:
mid = (h + l) // 2
if arr[mid] < target:
l = mid + 1
elif arr[mid] > target:
h = mid - 1
else:
return mid
return -1
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
if (target == matrix[-1][-1]):
return True
if (m == 1) :
if (binary_search(matrix[0], target) > -1) :
return True
return False
if (n == 1) :
if (binary_search([row[0] for row in matrix], target) > -1) :
return True
return False
# 행 개수가 더 작다면
if (m < n):
for i in range(m):
if (target >= matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i]):
if (max(binary_search(matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i: ], target), binary_search([row[n-2-i] for row in matrix[m-2-i:]], target)) > -1):
print(max(binary_search(matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i: ], target), binary_search([row[n-2-i] for row in matrix[m-2-i:]], target)) > -1)
return True
# 다 잘렸다면,
for i in range(m):
if (binary_search(matrix[i][:-m], target) > -1):
return True
return False
# 열 개수가 더 작다면
elif (n < m):
for i in range(n):
if (target >= matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i]):
if (max(binary_search(matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i: ], target), binary_search([row[n-2-i] for row in matrix[m-2-i:]], target)) > -1):
return True
# 다 잘렸다면,
for i in range(m - n):
if (binary_search(matrix[i], target) > -1):
return True
return False
# 정사각형 꼴이라면
else:
for i in range(m):
if (target >= matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i]):
if (max(binary_search(matrix[m-2-i][n-2-i: ], target), binary_search([row[n-2-i] for row in matrix[m-2-i:]], target)) > -1):
return True
return False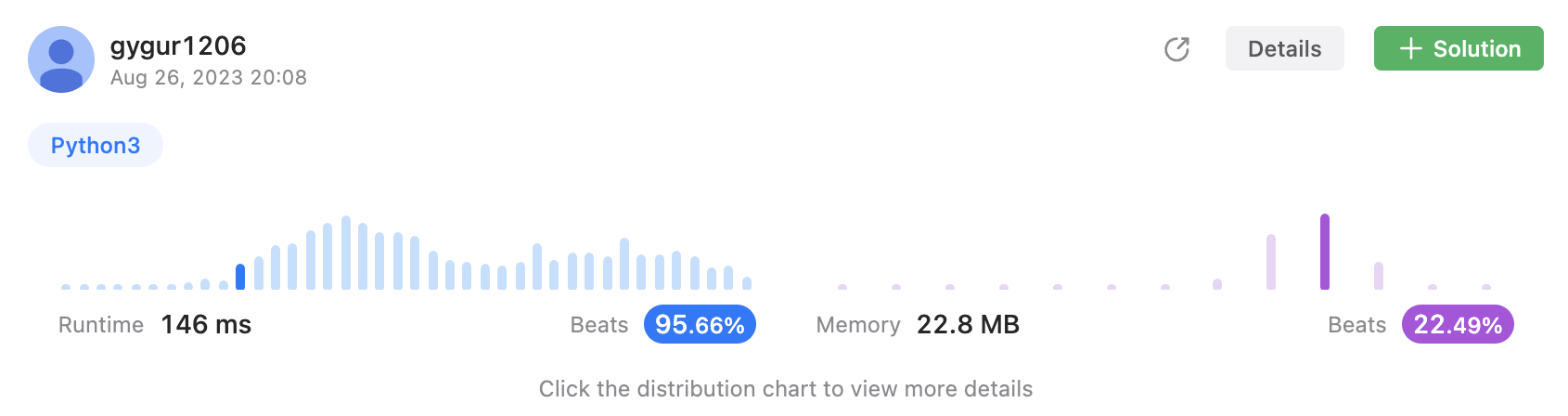

위와 같이 행을 m, 열을 n 이라고 두었을 때 사각형의 뒤의 인덱스부터 확인하면서 찾아야 할 범위를 줄여준다.
뒤부터 제거해주던 도중 값을 발견한다면 찾아서 return, 찾지 못한다면 줄여준 범위에만 이진 탐색을 사용해주었다.
그러면 이진 탐색을 사용했을 때 O(mlog(n)) 에서 O(m + 2log(n)) 로 시간 복잡도가 변해 크게 보았을 때는 O(max(n, m))의 시간 복잡도를 가지게 되므로 괜찮다고 생각했다.
회고
일단 결과는 괜찮게 나왔지만, 실행할 때마다 runtime이 크게 달라져서 실제로는 크게 체감이 되지 않는다. 그리고 코드도 굉장히 길게, 가독성이 좋지 않게 떨어졌다. 설명을 추가로 적어보면서, 최적화 할 수 있는 부분이 있을지 확인해보아야겠다.