priority scheduling 구현
Priority Scheduling
목표 및 고려사항
- PintOS는 FIFO 스케줄링을 사용한다. priority scheduling을 위해 FIFO 방식을 우선순위 방식으로 변경하기
- ready list를 스레드 우선순위로 정렬/삽입하기
- 준비 리스트(ready list)에 추가되는 스레드가 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 높은 우선순위를 가지면, 현재 스레드는 즉시 프로세서를 양보(yield)해야 한다.
- 스레드는 언제든지 자신의 우선순위를 높이거나 낮출 수 있다.
- 자신의 우선순위를 낮추어 더 이상 가장 높은 우선순위를 가지지 않게 되면 즉시 CPU를 양보해야 한다.
- 세마포어나 조건 변수와 같은 동기화 메커니즘을 사용하여 공유 자원에 대한 접근을 제어할 때, 이러한 잠금을 기다리는 스레드들 중에서 가장 높은 우선 순위를 가진 스레드를 선택해야한다.
수정 파일
- threads/thread.*
- threads/synch.*
1) ready_list를 스레드 우선순위로 정렬/삽입하기
thread_yield
void
thread_yield (void) {
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (curr != idle_thread)
//list_push_back (&ready_list, &curr->elem);
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &curr->elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
do_schedule (THREAD_READY);
intr_set_level (old_level);
}cmp_priority
bool cmp_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
struct thread *st_a = list_entry(a, struct thread, elem);
struct thread *st_b = list_entry(b, struct thread, elem);
return st_a->priority > st_b->priority;
}thread_unblock
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
//list_push_back (&ready_list, &t->elem);
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &t->elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}기존 cpu 양보는 fifo 방식으로 구현 되고있는데 준비 리스트에 삽입 할 때 우선순위가 높은 스레드가 내림차순으로 앞쪽으로 정렬 될 수있도록 list_insert_ordered를 활용한다.
정렬에 활용한 cmp_priority는 thread_wake_up 코드에서 깨울 때 ready_list에 정렬 삽입한 코드를 활용한다.
2) 준비 리스트(ready list)에 추가되는 스레드가 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 높은 우선순위를 가지면, 현재 스레드는 즉시 프로세서를 양보(yield)해야 한다.
thread_create
tid_t
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux) {
enum intr_level old_level;
...
thread_unblock (t);
old_level = intr_disable();
if (thread_get_priority() < priority)
thread_yield();
intr_set_level(old_level);
...
return tid;
}리스트를 관리할 때는 인터럽트틀 꺼쥬ㅗ여한다 깃 북 내용 적기
thread_wakeup
void thread_wake_up(int64_t os_ticks)
{
if (list_empty(&sleep_list))
return;
struct thread *t, *curr;
enum intr_level old_level;
old_level = intr_disable();
while (!list_empty(&sleep_list))
{
t = list_entry(list_front(&sleep_list), struct thread, elem);
if (t->wake_up_tick > os_ticks)
break;
list_pop_front(&sleep_list);
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &t->elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
}
curr = thread_current();
if (curr != idle_thread)
{
if (curr->priority < list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority)
{
thread_yield();
}
}
intr_set_level(old_level);
}thread_set_priority
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority) {
thread_current ()->priority = new_priority;
if(!list_empty(&ready_list))
{
struct thread *t = list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem);
if (new_priority < t->priority)
thread_yield();
}
}여기 까지 하면 준비리스트에 스레드 삽입 시 우선순위를 비교하여 선점하는 방식을 구현 완료했다.
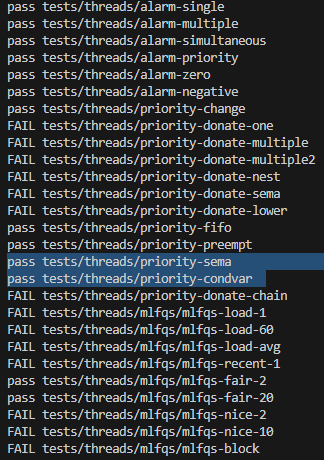
priority-change추가 통과!!
- Lock: semaphore, condition variable
- When selecting a thread from set of threads waiting for a lock(or condition variable), select the one with highest priority
-> 세마포어나 조건 변수와 같은 동기화 메커니즘을 사용하여 공유 자원에 대한 접근을 제어할 때, 이러한 잠금을 기다리는 스레드들 중에서 가장 높은 우선 순위를 가진 스레드를 선택하여 깨워야한다. - lock의 대기자 목록인 waiters도 priority 기준으로 내림차순 정렬로 변경한다.
- When selecting a thread from set of threads waiting for a lock(or condition variable), select the one with highest priority
sema_down,cond_wait
- waiters에 스레드를 삽입할 때 priority가 높은 스레드가 앞부분에 위치하도록 정렬한다.
- list_insert_ordered를 활용한다.
- sema→waiters를 정렬할 때 사용하는 cmp_thread_priority 함수는 ready_list를 정렬할 때 사용한 함수를 그대로 사용한다.
- cond→waiters를 정렬할 때 사용하는 cmp_sema_priority 함수는 아래에서 새로 선언한다.
sema_down
void sema_down (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
while (sema->value == 0) { //세마포어 값이 0인 경우, 세마포어 값이 양수가 될 때까지 대기
//list_push_back (&sema->waiters, &thread_current ()->elem);
list_insert_ordered(&sema->waiters, &thread_current()->elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
thread_block (); //스레드는 대기 상태에 들어감
}
sema->value--; // 세마포어 값이 양수가 되면, 세마포어 값을 1 감소
intr_set_level (old_level);
}cond_wait
void cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) {
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
//list_push_back (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem);
list_insert_ordered(&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem, cmp_sema_priority, NULL);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}cmp_sema_priority
- cond→waiters를 정렬할 때 사용할 함수를 새로 선언한다.
- 인자로 전달되는 elem으로 바로 스레드에 접근할 수 없기 때문에, 이전의 cmp_thread_priority를 쓸 수 없어서 새로 선언해야 한다!
- 두 semahore 안의 'waiters 중 제일 높은 priority'를 비교해서 높으면 true를 반환하는 함수
bool cmp_sema_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
struct semaphore_elem *sema_a = list_entry(a, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *sema_b = list_entry(b, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct list *waiters_a = &(sema_a->semaphore.waiters);
struct list *waiters_b = &(sema_b->semaphore.waiters);
struct thread *root_a = list_entry(list_begin(waiters_a), struct thread, elem);
struct thread *root_b = list_entry(list_begin(waiters_b), struct thread, elem);
return root_a->priority > root_b->priority;
}sema_up , cond_signal
sema_up
void sema_up(struct semaphore *sema)
{
struct thread *t;
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT(sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable();
if (!list_empty(&sema->waiters)) {
// 깨우기전 waiters에 들어있는 스레드가 donate를 받아 우선순위가 달라졌을 수 있기 때문에 재정렬
list_sort(&sema->waiters, cmp_priority, NULL);
t = list_entry(list_pop_front(&sema->waiters), struct thread, elem);
thread_unblock(t);
}
sema->value++;
intr_set_level(old_level);
thread_yield();
// 현재스레드를 우선순위 순서로 list에 삽입하고 스케줄링하여 우선순위가 높은 스레드가 실행되도록 함
}cond_signal
sema우선순위 순서대로 정렬 후 맨 앞에 있는 우선 순위 높은 semaphore를 up한다 모니터, 세마 도식화
void cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED) {
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters)) {
list_sort(&cond->waiters, cmp_sema_priority, NULL);
sema_up (&list_entry (list_pop_front (&cond->waiters), struct semaphore_elem, elem)->semaphore);
}
}이렇게 하면 sema, condvar test 통과
Donation
struct thread 구조체 필드변경
struct list donations; // 해당 스레드에게 기부를 해준 스레드
struct list_elem d_elem; // donations 리스트를 위한 list_elem
struct lock *wait_on_lock; // 기다리고 있는 잠금
int original_priority; // 기부를 받기 전의 기존 우선순위
init_thread donations 초기화
t->original_priority = priority;
t->wait_on_lock = NULL;
list_init(&(t->donations));lock 요청 시 donation
lock_acquire
- lock을 요청했을 때, 이미 holder(lock을 점유하고 있는 스레드)가 있다면 holder 보다 우선순위가 큰 경우 holder에게 priority를 기부한다.
- wait_on_lock(내가 기다리고 있는 lock)으로 설정한다.
- holder도 lock을 요청해둔 상태라면, holder가 요청한 lock의 holder에게도 priority 기부가 이어져야 한다.
void lock_acquire (struct lock *lock) {
struct thread *t = thread_current();
struct thread *holder;
ASSERT(lock != NULL);
ASSERT(!intr_context());
ASSERT(!lock_held_by_current_thread(lock));
if (lock->holder != NULL) {
t->wait_on_lock = lock;
if (!thread_mlfqs) {
if (thread_get_priority() > lock->holder->priority) {
list_insert_ordered(&lock->holder->donations, &t->d_elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
while (t->wait_on_lock != NULL) {
holder = t->wait_on_lock->holder;
if (t->priority > holder->priority) {
holder->priority = t->priority;
t = holder;
}
else break;
}
}
}
}
sema_down(&lock->semaphore);
thread_current()->wait_on_lock = NULL;
lock->holder = thread_current();
}lock 반환시 donation 이전 priority로 복귀
- 현재 스레드가 lock을 반환할 때, 이 lock을 요청한 스레드가 있어서 donation을 받았다면, 해당 스레드에게 받은 donation은 반납해야 한다.
- 기부를 해준 스레드 목록인 donations 목록에서 현재 반환될 lock을 요청했던 스레드를 찾아서 제거한다.
- 제거하고 나서 남은 donations 목록 중에서 가장 높은 priority를 가진 스레드의 priority로 현재 스레드의 priority를 재지정해준다.
void lock_release (struct lock *lock) {
ASSERT(lock != NULL);
ASSERT(lock_held_by_current_thread(lock));
struct thread *cur = lock->holder;
struct thread *start = list_entry(list_begin(&cur->donations), struct thread, d_elem);
struct thread *end = list_entry(list_end(&cur->donations), struct thread, d_elem);
for (struct thread *idx = start; idx != end; idx = list_entry(list_next(&idx->d_elem), struct thread, d_elem)) {
if (idx->wait_on_lock == lock) {
list_remove(&idx->d_elem);
idx->wait_on_lock = NULL;
}
}
if (!thread_mlfqs) {
if (!list_empty(&cur->donations)) {
cur->priority = list_entry(list_front(&cur->donations), struct thread, d_elem)->priority;
}
else
cur->priority = cur->original_priority;
}
lock->holder = NULL;
sema_up (&lock->semaphore);
}
thread_set_priority
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority) {
thread_current()->original_priority = new_priority;
if (list_empty(&thread_current()->donations))
{
thread_current()->priority = new_priority;
}
if (!list_empty(&ready_list) && list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority > new_priority)
thread_yield();
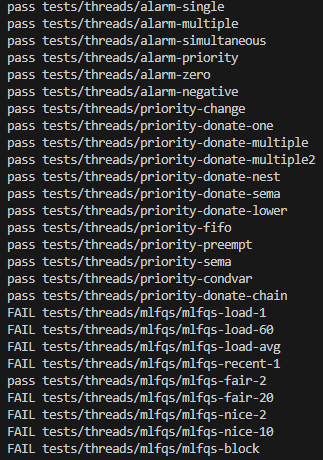
}이렇게 하면 mlfqs를 제외한 모든 테스트 케이스가 통과하게 된다.