옵셔널
Optional은 nil을 사용할 수 있는 타입과 없는 타입을 구분하기 위함이며, nil을 사용할 수 있는 Type을 Optional Type이라 부른다
옵셔널 타입은 기존 자료형을 Optional로 한번 감싼 Type
nil은 포인터가 아니라 특정 타입에 대한 값의 부재를 나타냄
0이나 공백이 아닌 값의 부재를 표현
- 옵셔널은 열거형
enum Optional<T> { // <T> 는 Array<T>같은 일반적인 타입
case None
case Some(T) //T의 의미는 옵셔널이 모든타입의 옵셔널이 될 수 있다는 뜻
}
let x: String ? = nill
// 는 아래와 동일
let x = Optional<String>.None
let x: String ? = "hello"
// 는 아래와 동일
let x = Optional<String>.Some("hello")
var y = x!
// 는 아래와 동일
switch x{
case Some(let value): y = value
case None: //예외 발생
}
let x: String? = ...
if let y = x{
// do something with y
}
// 는 아래와 동일
switch x {
case .Some(let y):
// do something with y
case .None:
break
}옵셔널 사용법
var display: UILabel?
if let label = display{
if let text = label.text{
let x = text.hashValue
...
}
}
// 아래와 동일
if let x = display?.text?.hashValue {...}
let s: String? = ...
if s != nill{
display.text = s
} else {
display.text = " "
}
// 아래와 동일
display.text = s ?? " "Optional Unwrapping
옵셔널 타입은 기존 자료형을 Optional로 한번 감싼 Type
옵셔널 타입에 저장된 값을 사용하기 위해서는 Optional을 벗겨줘야 하고 이 작업을 Optional Unwrapping 이라고 한다.
- Optional Unwrapping을 하기 위해선 절대 Unwrapping 하고자 하는 변수(상수)가 nil이면 안됨
let a: Int?
a = 4
print(\(a)) // Optional(4) 출력, Optional Unwrapping 가능
let b: Int? = nil
print(\(b)) // nil 출력, Optional을 벗길 수 없음강제 추출(Forced Unwrapping)
옵셔널 값이 nil이건 말건 옵셔널을 벗겨버리는 것
Optional로 선언된 변수(상수) 뒤에 !를 붙여줌
let a: Int?
a = 4
print(\(a!)) // 4 출력
let b: int? = nil
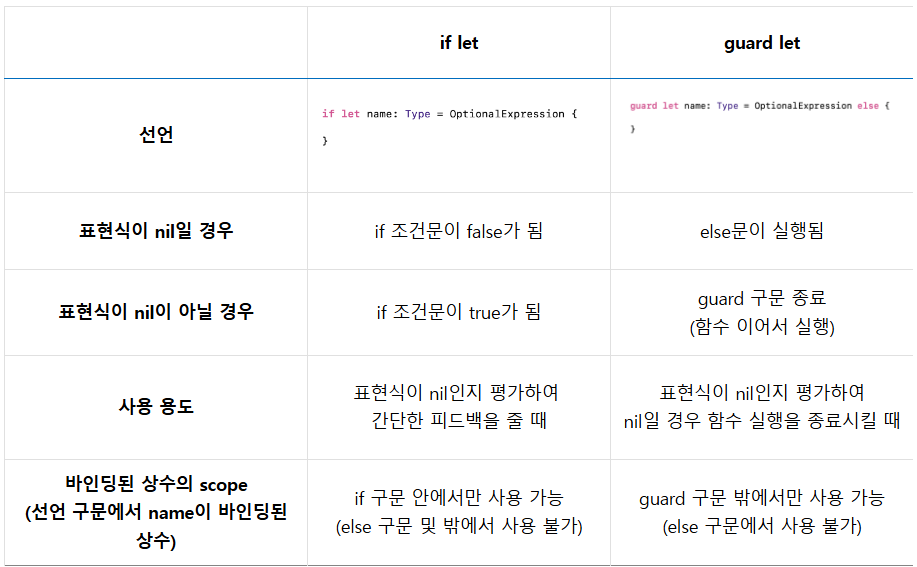
print(\(b!)) //에러Optional Binding
안전하게 Optional의 값을 Unwrapping 하는 방법
if let
let optionalNum: Int? = 4
if let nonOptionalNum = optionalNum {
//optionalNum이 nil이 아닐경우 Unwrapping하여 그 값을 nonOptionalNum에 대입
//nonOptionalNum은 해당 if문 안에서만 접근 가능
print(nonOptionalNum) // 4 출력
print(optionalNum) // Optional(4)출력
}else{
print(optionalNum)//optionalNum이 nil일경우
}- 바인딩 될 Non Optional Type 이름을 Optional Type 이름 그대로 사용 가능(실행 시점에서 가까운 곳에 선언된 변수를 사용)
let num: Int? = 4
if let num = num {
print(num)
}- 한번에 여러 개의 옵셔널 타입을 바인딩 할 경우 모두 nil이 아니여야 if 구문이 true
let name: String? = nil
let age: Int? = nil
if let name = name, let age = age{
// name != nil && age != nil 일 경우
}
if let name = name, let age = age, age > 5{
// name != nil && age != nil && age >5 일 경우
}guard let
guard문은 특성상 함수(메서드)에서만 쓰이며, guard 구문의 조건을 만족하지 못하면 else문으로 빠져서 함수의 실행을 종료 시킬 때 사용
guard let nonOptionalNum = optionalNum else{
// optionalNum이 nil일 경우
// nonOptionalNum 값 사용 불가
return
}
//optionalNum이 nil이 아닐경우
// nonOptionalNum값 사용가능- 함수(메서드)로 넘어온 파라미터 값을 바인딩할 경우 NonOptional Type이름을 Optional Type 이름 그대로 사용 가능
func test(_ name: String?) {
guard let name = name else {
return
}
print(name)
}
func test() {
let num: Int? = 4
guard let num = num else{// 에러 사용불가
return
}
}- if let 처럼 한번에 여러개의 옵셔널 바인딩 가능
func test(_ name: String?, _ age: Int?) {
guard let name = name, let age = age, age < 5 else {
return
}
}정리
옵셔널 묵시적(암시적) 추출
Implicitly Unwrapped Optional(옵셔널 암시적 추출)은 Optional Type으로 선언하는 방법 중 하나로 Non-Optional Type으로 처리되어야 할 때 값을 자동으로 추출해 줌(특정 조전일 때만 추출)
//기존 Optional Type
var num: Int? = 4
var num2: Int = num //에러
//IUO(Implicitly Unwrapped Optional)
var num: Int! = 4
var num2: Int = num //가능- IUO를 쓴다고 원하는 떄에 다 자동으로 값이 Unwrapping 되는 것이 아니라 Optional Type을 Non-Optional Type에 대입할 때 별도의 추출 과정 없이 대입이 가능
- IUO도 강제 추출
var num: Int! = nil
var num2: Int = num // 에러- 프로퍼티 지연 초기화를 하기위해 사용(IBOultet, API에서 IUO를 return한 경우)
??연산자(Nil-Coalescing Operation)
??연산자를 통하여 옵셔널 바인딩을 간단히 할 수 있다.
Optional Type에 값이 있을 경우 해당 값을 아닐경우 ??연산자 뒤의 값을 return
- Nil-Coalescing에 사용되는 Optional Type과 Non-Optional Type은 Optional을 제외하면 동일한 Type이어야 함
Optional Expression ?? Non-Optional Expression기존)
if let name = name {
print("hello, \(name)")
} else {
print("hello, what's your name?")
}??연산자 사용)
print("hello, "+(name ?? "what's your name?"))옵셔널 체이닝(Optional Chaining)
옵셔널을 연쇄적으로 사용하는 것
.(dot)을 통해 내부 프로퍼티나 메서드에 연속적으로 접근할 때 옵셔널 값이 하나라도 껴 있을 경우 옵셔널 체이닝이라고 함
person.contacts?.address // 하나라도 nil일 경우 nil 반환
person?.contacts?.address // 하나라도 nil일 경우 nil 반환- 옵셔널 체이닝의 결과값의 타입은 마지막 표현식의 옵셔널 타입이다
- 옵셔널 체이닝의 마지막 표현식은 옵셔널이더라도 ?를 생략한다
- 옵셔널 체이닝의 표현식 중 하나라도 nil이라면, 이어지는 표현식은 평가하지 않고 nil을 리턴
함수가 껴있는 옵셔널 체이닝
sturct Person {
var name: String
var contacts: Contacts
init(name: String, email: String, address: String){
self.name = name
contacts = Contacts(email: email, address: ["home" : address])
}
func getContacts() -> Contacts?{
return contacts
}
func getContacts2() -> Contacts2{
return contacts
}
}
person?.getContacts()?.email // 함수의 리턴값의 속성에 접근할 때
let function = person?.getContacts2 // function은 Optional Type
function?().email // 함수 자체가 옵셔널일 경우
let function2 = person?.getContacts // funtion은 Optional Type
function?()?.email // 함수 자체도 옵셔널, 리턴 값도 옵셔널 일 경우딕셔너리가 껴있는 옵셔널 체이닝
- 딕셔너리에서 key를 통해 value를 얻을 땐 해당 key가 없을 수도 있기 때문에 무조건 Optional Type이 리턴
- 딕셔너리의 key 값으로 얻은 value 값의 속성에 접근 할 때에는 []? 사용
let dic: [String : String] = ["name" : "abc"]
dic["name"]?.count- 딕셔너리 타입이 Optional일 경우에는 ?[]? 사용
let dic: [String : String]? = ["name" : "abc"]
dic?["name"]?.count참조
개발자 소들이