참고
Tutorial: Accessing a relational database
pgx - PostgreSQL Driver and Toolkit
Connection 생성
기본 개념
Go는 표준화된 방법으로 DB를 사용할 수 있도록 database/sql이라는 표준 라이브러리를 제공한다.
이는 단순히 인터페이스이므로, 실제 구현체를 import해서 사용해야 한다.
공식문서를 살펴보면 다양한 PostgreSQL 드라이버가 있는 것 같은데, 그 중 jackc/pgx을 사용하기로 한다.
드라이버 특화 방식으로 연결하기
드라이버마다 조금씩 연결 방식이 다른데, jackc/pgx는 다음과 같다.
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/jackc/pgx/v4"
"log"
)
func main() {
connectionInfo := "postgres://USER_NAME:PASSWORD@RDBMS_URL:PORT_NUM/DATABASE_NAME"
connection, err := pgx.Connect(context.Background(), connectionInfo)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
defer closeDBConnection(connection, context.Background())
log.Println("success to establish DB Connection")
}
func closeDBConnection(connection *pgx.Conn, context context.Context) {
connection.Close(context)
}표준 방식으로 연결하기
당연히 database/sql을 사용해서 Connection을 만들 수 있다.
package main
import (
"database/sql"
_ "github.com/jackc/pgx/v4/stdlib" // 생략하면 안 됨
"log"
)
func main() {
connectionInfo := "postgres://USER_NAME:PASSWORD@RDBMS_URL:PORT_NUM/DATABASE_NAME"
connection, err := sql.Open("pgx", connectionInfo) // takes String
// sql.OpenDB(driver.Connector) // takes driver.Connector
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
defer connection.Close()
log.Print("success to establish connection")
}표준 인터페이스에 어떤 RDBMS를 사용할 것인가를 초기화 단계에 알려줘야 한다.
github.com/jackc/pgx의 경우 'postgress'가 아니고, 'pgx'이다.
github.com/lib/pg의 경우에는 'postgress;가 맞다.특별한 이유가 없으면 표준 인터페이스를 사용하는게 좋을 듯 하다.
참고
1. Connection 정보로 String이 아닌 객체를 넘겨줄 수도 있는데, 정확한 사용법은 RDBMS 드라이버마다 다르다.
2. `os.Getenv`를 사용하여 Credentials들을 은닉화 할 수 있다. (https://go.dev/doc/database/open-handle#:~:text=log.Fatal(err)%0A%7D-,Storing%20database%20credentials,-Avoid%20storing%20database)Connection Pool
앞서 살펴본 Connection은 사실 Connection Pool이다.
conn, err := sql.Open("pgx", connectionInfo)
stats := conn.Stats(); // sql.DBStats
// DBStats contains database statistics.
type DBStats struct {
MaxOpenConnections int // Maximum number of open connections to the database.
// Pool Status
OpenConnections int // The number of established connections both in use and idle.
InUse int // The number of connections currently in use.
Idle int // The number of idle connections.
// Counters
WaitCount int64 // The total number of connections waited for.
WaitDuration time.Duration // The total time blocked waiting for a new connection.
MaxIdleClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetMaxIdleConns.
MaxIdleTimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxIdleTime.
MaxLifetimeClosed int64 // The total number of connections closed due to SetConnMaxLifetime.
}sql.DB 구조체의 메서드를 통해 Conncection (Pool) 관련 설정을 할 수 있다. 참고
Query
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
반환값이 없는 작업을 수행할 때는 기본적으로 Exec을 사용한다.
func AddAlbum(alb Album) (int64, error) {
result, err := db.Exec("INSERT INTO album (title, artist) VALUES (?, ?)", alb.Title, alb.Artist)
if err != nil {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("AddAlbum: %v", err)
}
// Get the new album's generated ID for the client.
id, err := result.LastInsertId()
if err != nil {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("AddAlbum: %v", err)
}
// Return the new album's ID.
return id, nil
}RDBMS에 따라 Parameter Placeholde가 ?일 수도 $1일 수도 있다.
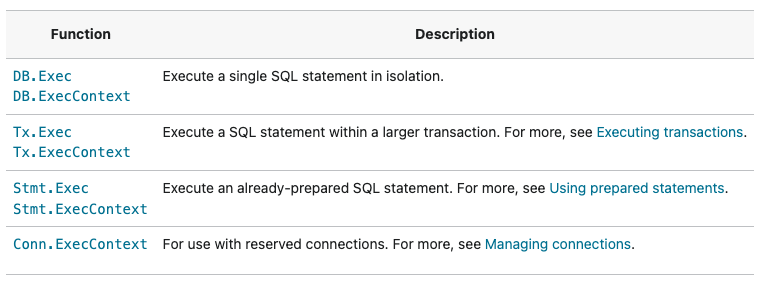
PostgreSQL은 $1 형식을 사용한다.용도에 따라 사용할 수 있는 다양한 Exec 메서드가 존재한다.
SELECT
Single Row
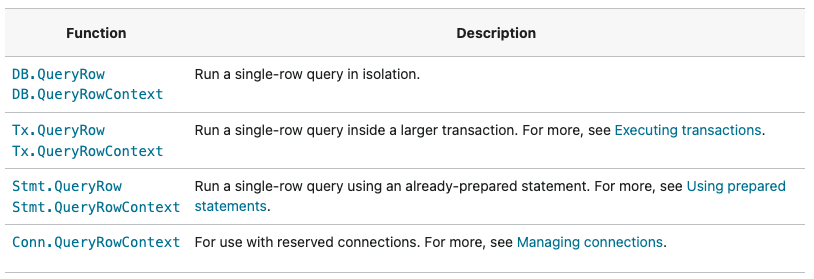
PK로 조회같이 결과 값이 단 건이 경우에는 QueryRow를 사용한다.
func canPurchase(id int, quantity int) (bool, error) {
var enough bool // 쿼리 결과값을 받을 변수를 선언
// 쿼리 수행
// sql.Row Type
row := db.QueryRow("SELECT (quantity >= ?) from album where id = ?", quantity, id)
// 결과값을 parsing해서 변수에 할당, 파라미터로 Ref를 전달해야 함
err := row.Scan(&enough)
if err != Nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("canPurchase %d: unknown album", id)
}
return enough, nil
}QueryRow로 실행시킨 쿼리의 결과값이 여러 건인 경우, Scan을 수행하면 맨 처음 찾은 값만 반환한다.
Multi Row
func albumsByArtist(artist string) ([]Album, error) {
// sql.Rows Type
rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM album WHERE artist = ?", artist)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer rows.Close()
// An album slice to hold data from returned rows.
var albums []Album
// Loop through rows, using Scan to assign column data to struct fields.
for rows.Next() {
var alb Album
if err := rows.Scan(&alb.ID, &alb.Title, &alb.Artist,
&alb.Price, &alb.Quantity); err != nil {
return albums, err
}
albums = append(albums, album)
}
if err = rows.Err(); err != nil {
return albums, err
}
return albums, nil
}Single Row랑 크게 다른게 없다.
다만 rows.Close를 호출해서 자원을 반납함을 확인할 수 있는데,
기본적으로 sql.Rows는 rows.Next를 통해 모든 loop을 돌면 묵시적으로 자원을 반납하는데,
에러가 발생하는 경우를 고려해서 defer를 통해 명시적으로 반환하는 것을 권장한다.
Null
특정 컬럼이 Null인 경우를 고려할 수 있다.
var s sql.NullString // NullBool, NullFloat64, NullInt32, NullInt64, NullString, NullTime
err := db.QueryRow("SELECT name FROM customer WHERE id = ?", id).Scan(&s)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
name := "Valued Customer" // 마치 기본값 처럼 사용할 수 있다.
// Valid(not null)이면
if s.Valid {
// 조회된 값을 사용
name = s.String
}Scan
위에서 살펴본 것처럼, Scan을 사용하면 RDBMS의 데이터 타입을 Golang의 비슷한 데이터타입으로 Convert 해준다.
구체적으로 어떤 값으로 변환되는지, 어떻게 변환하는지는 RDBMS 드라이버에 따라 다르다. (다음을 참고)
Transaction
앞서 다룬 예제에서는 따로 트랜잭션을 설정하지 않았기 때문에, RDBMS의 기본 설정에 따라 Rollback, Commit 될 것이다.
Commit, Rollback
Isolation Level
Trial and Error
PostgreSQL의 array 다루기
PostgreSQL은 array 타입을 지원하는데, Golang에서 이를 다룰 때 단순히 Array(또는 Slice)를 사용하면 된다.
CREATE TABLE Person (
...
hobbies varchar[64] notnull, // {"soccer", "bascketball"} 형식으로 저장한다.
...
)var hobbies []string
row := conn.QueryRow("SELECT hobbies from Person",...)
err := row.Scan(&hobbies) // 알아서 PostgreSQL Array를 Golang Slice로 변환한다.