
Desc
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a digit between 0 and 9 (inclusive).
The triangular sum of nums is the value of the only element present in nums after the following process terminates:
- Let
numscomprise ofnelements. Ifn == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer arraynewNumsof lengthn - 1. - For each index
i, where0 <= i < n - 1, assign the value ofnewNums[i]as(nums[i] + nums[i+1]) % 10, where%denotes modulo operator. - Replace the array
numswithnewNums. - Repeat the entire process starting from step 1.
Return the triangular sum of nums.
Example 1:
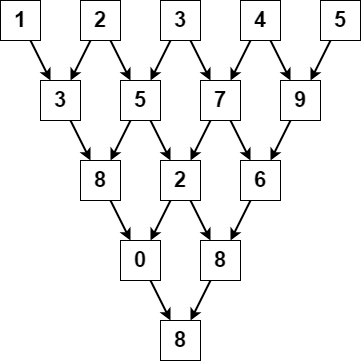
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 8 Explanation: The above diagram depicts the process from which we obtain the triangular sum of the array.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5] Output: 5 Explanation: Since there is only one element in nums, the triangular sum is the value of that element itself.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 9
Code
class Solution:
def triangularSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums)
while n > 1:
for i in range(n - 1):
nums[i] = (nums[i] + nums[i + 1]) % 10
n -= 1
return nums[0]Code Desc
✅ 새로운 임시 배열을 생성하면, 공간 복잡도가 크게 늘어난다.
문제의 예시 그림을 살펴보면, 각 단계에서 왼쪽부터 오른쪽으로 원소의 값을 순회함을 알 수 있다. 그리고 각 단계마다 리스트의 길이는 1씩 줄어든다.
리스트의 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 순회하므로 원소 2개를 더한 값을 nums[i]에 넣으면 된다.
즉, nums[i] = (nums[i] + nums[i + 1]) % 10 임을 유추해 볼 수 있다.
문제의 조건에서 리스트안에 원소가 1개라면, 더 이상 갱신을 하지 않고 종료한다.
따라서, 리스트의 길이가 1보다 클 때, 리스트를 순회하면서, nums[i]의 값을 갱신한다.
모든 값을 갱신했다면, 리스트의 길이를 1만큼 줄인다.
위의 과정을 리스트의 길이가 1보다 같거나 작아지지 않을 때 까지 반복한다.
