예외
프로그램이 실행되는 동안 발생할 수 있는 비정상적인 상태
- 자바의 예외처리
- Exception 클래스 정의
- 기본적인 예외는 자바에 미리 정의된 예외를 통해 처리가능
- 사용자가 필요한 예외를 직접 정의 가능
- 예상되는 예외는 미리 처리해주면 프로그램의 종료를 피할 수 있음
- 예외처리는 프로그램의 신뢰도 향상
Exception Handling
- try ~ catch ~ finally

try블록에서 예외가 발생 했을 경우 : 0 ➡ 1 ➡ 2 ➡ 3 ➡ 4
try블록에서 예외가 발생하지 않았을 경우 : 0 ➡ 1 ➡ 3 ➡ 4
예외 처리의 순서
- 구체적 예외 ➡ 일반적 예외
try { ... }
catch (구체적 예외 1) { ...Exception Handling 1... }
catch (구체적 예외 2) { ...Exception Handling 2... }
catch (일반적 예외) { ...Exception Handling... }
finally {
// 예외 유무와 관계없이 가장 마지막에 발생
// 자원 정리 작업에 많이 활용
}Exception Class
- 주요 예외 클래스
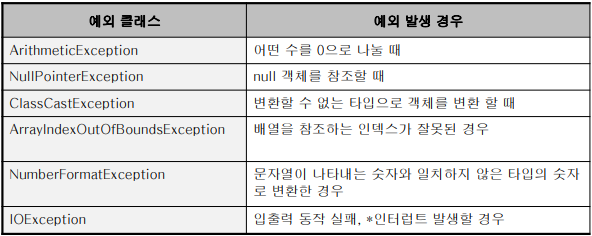
- 예외(Exception)의 구분
- Checked Exception : 컴파일할 때 확인되는 예외 -> 반드시 예외 처리가 필요함
- Unchecked Exception : 실행 시점에서 확인되는 예외 -> 예외 처리 없어도 컴파일 됨
- 예외 처리가 필요한 시점
파일을 다루는 경우
파일이 없거나 다른 프로세스에 의해 사용중인 경우입출력을 다루는 경우
이미 닫힌 입출력 스트림에 대해 작업하려 할 경우네트워크를 이용한 데이터 통신
서버나 클라이언트 한 쪽에서 응답이 없는 경우
네트워크 상태가 좋지 않아 정해진 시간 동안 데이터를 받지 못하는 경우
throws&throw
throws: 해당 메소드가 특정 예외가 발생 할 수도 있다고 알려주는 구문
➡ 이 메소드를 사용하는 곳으로 예외 처리 책임을 전가throw: 예외를 발생 시키는 구문throw new Exception();
강제 예외 발생
throw new SomeException(arg);
public class ThrowsExcept {
// Checked Exception
public void executeExcept() throws IOException {
System.out.println("강제 예외 발생");
throw new IOException("강제 예외"); // 강제 예외 발생
}
// Unchecked Exception
public void executeRuntimeExcept() {
System.out.println("런타임 오류");
throw new RuntimeException("런타임 예외");
}
}private static void throwExceptEx() {
ThrowsExcept except = new ThrowsExcept();
try {
except.executeRuntimeExcept();
except.executeExcept();
} catch (RuntimeException e) { // except.excuteRuntimeExcept()의 throw 구문으로 인해 RuntimeException e 발생
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) { // except.excuteExcept()의 throw 구문으로 인해 IOException e 발생
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}사용자 예외 처리
- 사용자 예외 class 생성
class CustomArithException extends ArithmeticException {
// 예외 상황 필드
private int num1, num2;
public CustomArithException(String message, int num1, int num2) {
super(message);
// 예외 상황 정보 저장
this.num1 = num1;
this.num2 = num2;
}
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public int getNum2() {
return num2;
}
public class ThrowsExcept {
public double divide(int num1, int num2) {
if (num2 == 0) {
// ArithmeticException
// 구체적 예외로 전환하여 throw 하는 것이
// 1. 코드 가독성을 높이고
// 2. 예외 상화 정보를 담을 수 있다.
throw new CustomArithException("사용자 정의 예외", num1, num2);
}
return num1 / num2;
}
}private static void throwExceptEx() {
// 사용자 정의 예외 사용
try {
System.out.println(except.divide(100, 0));
} catch (CustomArithException e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
// 예외 상황 확인
System.err.println("나누어지는 수:" + e.getNum1());
System.err.println("나누는 수:" + e.getNum2());
}
}