the purpose of design pattern
- to reuse solution already solved
- facilitate communication
- for making more flexible and reusable design
the definition of design pattern(example: iterator patterns)
A solution to a problem in a context
- context: recurring situation in which pattern applies
- ex: collection of objects
- problem: constraint to acheive the goal, or goal itself
- ex: not exposing implementation of collection but need to step through object
- solution: what do you after about problem
- Structure of component and relationship
- run-time mechanism
- ex: encapsulate iterator to separate class - make iterator to interface
- give resposibility to collection to make new concrete class that implementation iterator interface
collection: like array, list, set, queue, map…. can contain many element in itself
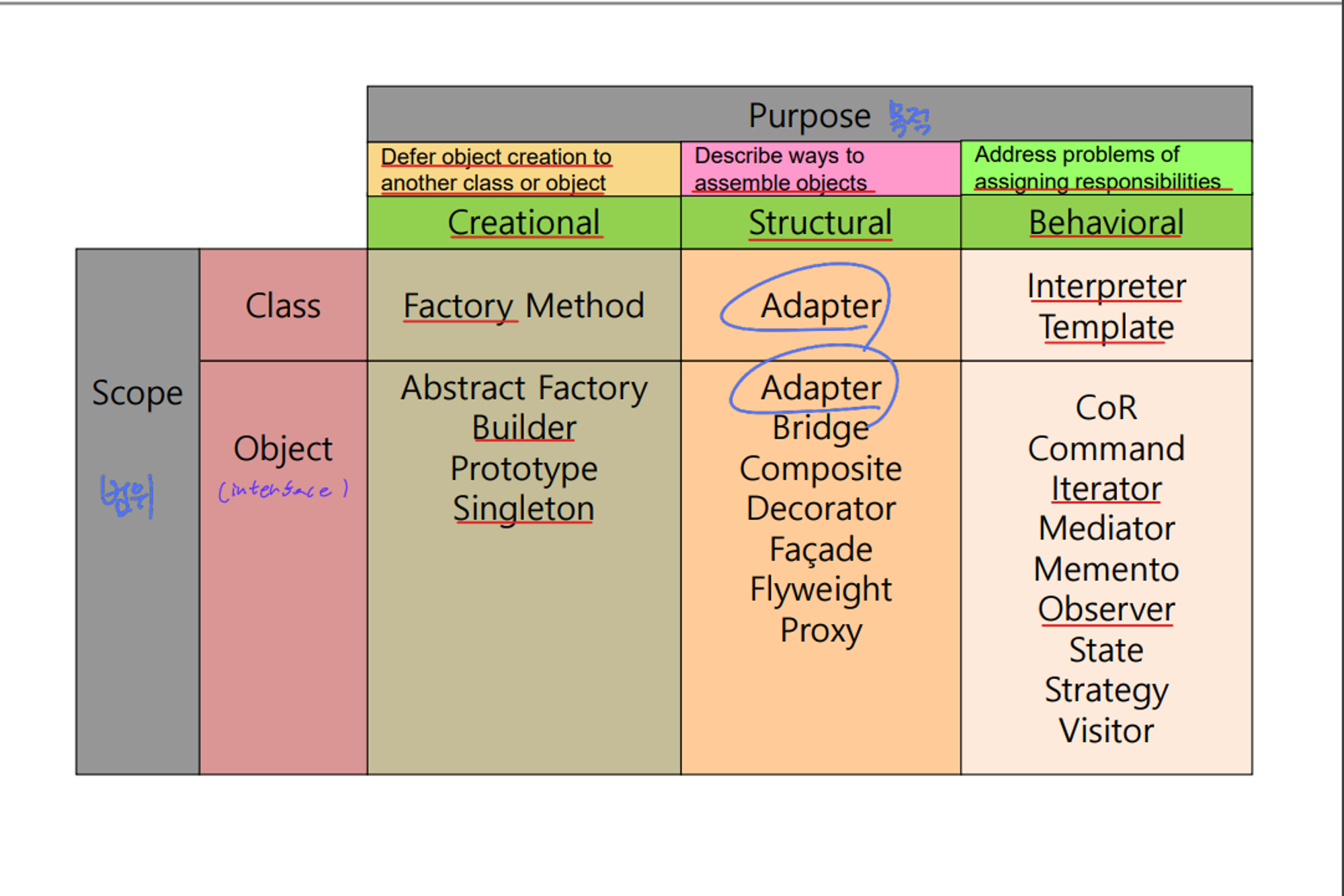
category of GoF Patterns
- purpose:
- Creational: related to address creating object or class
- Structural: related to construct of relation(class and object)
- Behavioral: related to responsibilities and communication
- Scope:
- Class: related to class and usely solve problem with inheritance
- Object: related to instance and usely solve porblem with “composition”
- composition: one class has another classes in body and delegate some functions to them
design pattern’s key feature(7 keywords)
- Bridge
keyword: intent, problem, solution, participants and collaborators, consequence, implementation, generic structure
- intent: purpose
- problem: pattern trying to solve
- solution: not absstract description, emphasizes component’s relationship, responsibilities and collaborations
- participants and collaborators: entities involved in the pattern
- consequences: pros and cons of using pattern in point of reusability, portability, extensibility
- implementation: how pattern can be implemented
- it should not be considered as the pattern itself, it was just concrete manifestations of the pattern
- generic structure: standard diagram
component: service unit, have some feature
- independent, minimize dependency, interface, reuse, looe coupling
hierarchy of pattern knowledge
-
basic: basic concept or knowledge about software
ex: abstraction, inheritance, oop concept
-
principles: guildline or general rule of design
ex: soild(SRP, OCP, LSP, ISP, DIP) principle, DRY(Don't Repeat Yourself) principle, SRP
-
pattern: Strategy pattern, a solution to a problem in a context, based on principles and basic, used to improve design of software
level of patterns[POSA - pattern oriented software archtecture]
-
Architectural pattern
- overall based structure and organization
- provide predefined subsystem, define their responsibility, rules and guildlines for organizing relationshiip between them
- pattern for system structure
ex. MVC pattern
-
Design pattern
- refine subsystem or components or relationships between them
- not affect to overall structure, pattern for component that in the system.
ex. observer pattern
-
Coding pattern
- specific to a programming language
- how to implement particular aspect of components or relationship in given language
summary
Software pattern and pattern history
Design pattern categories
- creational, structural, behavior
Benefit of patterns
- reusable
- communication
Levels of pattern
- Architectural, design, coding
