배열
- 배열의 메모리 할당 (객체 생성)
배열선언
- int num[ ] = int[ ] num
- int[ ] num로 쓰는 것도 가능
정렬하는 방법 : Selection Sort(선택정렬) / Bubble Sort(버블정렬) / Insertion Sort(삽입정렬)
大 [>] 小 = 내림차순(小 -> 大)
小 [>] 大 = 오름차순(大 -> 小)내림차순 정렬방법 (데이터의 처리과정을 가독성 좋게 하기위해)
- Selection Sort = 0,1 / 0,2.. = j , j+1 / j , j+2..(왼쪽부터 채워짐)
- Bubble Sort = 0,1 / 1,2..= j , j+1 / j+1 , j+2.. (오른쪽부터 큰 수 채워짐)
🔎 [Eclipse] - [package] - [class] 생성
📌 Note Code
Test1. 10명 이내의 이름과 점수를 입력받아 점수를 내림차순(큰->작은)으로 출력
💻 입력
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // new가 붙으면 거의 다 메모리 할당
// java langue? - string int class 등 new가 안받는 것도 메모리에 다 올라가있음
// 선언
String[] name; // 조금있다가 밑에서 만들거야
int[] score, rank;
int inwon, i, j, t1, t3; // 인원, 정렬 2개, 점수 temp1
String t2;// 이름 temp2
// 10명을 넘어선 안되고, 값하나는 받아봐야하니
do {
System.out.print("인원수[1~10]?");// 3
inwon = sc.nextInt();
} while (inwon < 1 || inwon > 10);
// 배열의 메모리 할당(name이라는 객체 생성)
name = new String[inwon]; // 인원수만큼
score = new int[inwon];
rank = new int[inwon]; // 사용자에게 받는거 아님 그래서 아래에 안씀 (초기값 0)
for (i = 0; i < inwon; i++) { // 인원수(inwon)까지 배열 반복
System.out.print((i + 1) + "번째 이름?");
name[i] = sc.next();
System.out.print("점수");
score[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 석차 초기화
for (i = 0; i < inwon; i++) { // rank[0] = 0 (초기값 0)
rank[i] = 1;// rank[i]+=1;
}
// 석차만들기
for (i = 0; i < inwon - 1; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < inwon; j++) {
if (score[i] > score[j]) {
rank[j]++;
} else if (score[i] < score[j]) { // else를 쓰면 안되는 이유는 동점일 때 1,2등 승부를 내버림
rank[i]++;
}
}
}
// 점수 내림차순 정렬
// Selection Sort
for (i = 0; i < inwon - 1; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < inwon; j++) { // 공식 : j = i+1
if (score[i] < score[j]) {
t1 = score[i];
score[i] = score[j];
score[j] = t1;
t2 = name[i];
name[i] = name[j];
name[j] = t2;
t3 = rank[i];
rank[i] = rank[j];
rank[j] = t3;
}
}
}
// 출력
// 지금 확장 x - 2개라서 ! 확장 for문 : 하나의 데이터에서 하나의 데이터(name에 있는 값)을 가져와서 순서대로 하겠다
for (i = 0; i < inwon; i++) {
System.out.printf("%6s %4d%4d\n", name[i], score[i], rank[i]);
}
/*
* System.out.print("이름?");//suzi 위에 for문으로 압축 name[0] = sc.next();
*
* System.out.print("점수?");//40 score[0] = sc.nextInt();
*
*
* System.out.print("이름?");//inna name[1] = sc.next();
*
* System.out.print("점수?");//60 score[1] = sc.nextInt();
*
*
* System.out.print("이름?");//edam name[2] = sc.next();
*
* System.out.print("점수?");//90 score[2] = sc.nextInt();
*/
}
}
💡 **출력**
인원수[1~10]?3
1번째 이름?aa
점수70
2번째 이름?bb
점수80
3번째 이름?cc
점수75
bb 80 1
cc 75 2
aa 70 3📌 Note Code
Test2. 1~45까지의 수 중 6개의 난수를 발생시켜 크기순으로 정렬 (로또)
💻 입력
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rd = new Random(); // Random 클래스가 메모리 할당 (객체생성)했다.
int[] num = new int[6];
int i, j, n, temp;
// 랜덤다루는 방법
n = 0; // 0번지~5번지까지 자리값 {0,1,2,3,4,5}
while (n < 6) { // while) 몇번을 반복해야할지 모를 때!! (random이라 반복으로 꺼낼 수도 있기때문에 겹치면 다시 뽑아야함)
num[n] = rd.nextInt(45) + 1; // 0~44까지인데 로또번호는 1~45라서 44번지(45) + 1 =45
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 공식 외우기* - i<n은 i=0처음 이므로 n<0,1,2,3...이므로 x,한번돌고,두번돌고,,,
if (num[i] == num[n]) {
n--;
break;
}
}
n++; // 안해주면 계속 0=>1=>0=>1로 돌기때문에
}
//Bubble Sort (비교가 0,1 / 1,2 /... 오른쪽 가장 큰 값) 뒤에서 부터 값이 채워짐 , , , ,5 -> , , ,4,5
// Selection Sort (비교가 0이 기준- 0,1/0,2/,0,3....)
for (i = 0; i < num.length - 1; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < num.length; j++) { // j = i+1
if (num[i] > num[j]) {
temp = num[i];
num[i] = num[j];
num[j] = temp;
}
}
}
// 출력***
for (int su : num) {
System.out.printf("%4d", su);
}
}
}
💡 **출력**
//Random
10 20 25 31 40 45📌 Note Code
Test3. 주어진 배열을 오름차순으로 정렬하여라
💻 입력
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num[] = { 28, 65, 7, 4, 10 };
int i, j, temp;
System.out.print("Source Data : ");
for (i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%4d", num[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// Bubble Sort
for (i = 1; i < num.length; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < num.length - i; j++) {
if (num[j] > num[j + 1]) { // 0,1/1,2/2,3 ... = j,j+1/j+1,j+2....
temp = num[j];
num[j] = num[j + 1];
num[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.print("Sorted Data : ");
for (i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%4d", num[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
💡 **출력**
Source Data : 28 65 7 4 10
Sorted Data : 4 7 10 28 65📌 Note Code
Test4. 주민번호 검사기
💻 입력
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String jumin;
int[] chk = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,2,3,4,5};
int i,tot,su;
System.out.print("주민번호[xxxxxx-xxxxxxx]?");
jumin = sc.next();
if(jumin.length()!=14) { //배열의 length는 괄호 x , 나머지 length (= 개수)는 괄호 O
System.out.print("입력오류!!");
return; // = stop (아래코딩 실행하지마 -> 프로그램 종료) , return(값) = 값 돌려주기
}
tot = 0; //(쓰레기값이기때문에 초기화하고 시작한다)
//index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3
//jumin: 9 4 1 0 1 0 - 2 0 8 7 6 5 4
//chk :{2,3,4,5,6,7 8,9,2,3,4,5};
for(i=0;i<12;i++) { // 12인이유 : -랑 맨마지막 부호비트 빼서 12 - 0~11까지 12번 돎
if(i>=6) { //주민번호 뒷자리
tot+=chk[i] * Integer.parseInt(jumin.substring(i+1, i+2));
}else {//주민번호 앞자리
tot+=chk[i] * Integer.parseInt(jumin.substring(i, i+1));
}
}
su = 11 -tot%11;
su = su%10;//[0~9]
if(su==Integer.parseInt(jumin.substring(13))) {
System.out.println("정확한 주민번호!");
}else {
System.out.println("틀린 주민번호!");
}
}
}
//Example
//856131-2123215
//234567 892345
/*
합 = (8*2)+(5*3)...
합 = 11 - (합%11) : 11-나머지(1~10)
합 = 합%10 = 맨마지막 식별숫자 5
*/
/*
String str = "seoul korea";
//index : 01234564789
//-> 고유인덱스 번호 부여 / 특정값을 찾을 때 없으면 -1 (0부터 시작해서 없기 때문에)!!!
//문자 추출 (str.substring) - 0부터인거 까먹지 말기
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 3));//seo [0에서부터2(항상 마지막 숫자 endIndex - 1)까지]
System.out.println(str.substring(6, 8));//ko
System.out.println(str.substring(6));//korea [6번째 자리부터 끝까지]
*/💡 **출력**
주민번호[xxxxxx-xxxxxxx]?111111-1111118
정확한 주민번호!📌 Note Code
Test5. 배열의 배열 (6*6표)
💻 입력
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] [] arr = new int[6][6]; // 실행하는 순간 몽땅 0
int i,j,n;
n=0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {//(i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++)
for(j=0;j<5;j++) {
//System.out.println(i+":"+j);
n++; // 1이 먼저 들어가게
arr[i][j] = n;
arr[5][j] += n;
arr[i][5] += n;
arr[5][5] += n;
/*
0.5
1.5
2.5
-------
[i][5] += n -> 5고정 +=누적
*/
}
}
//표 모두 출력해야하므로 최대값에 개수(변수.length) 넣기
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
for(j=0;j<arr.length;j++) {
System.out.printf("%4d",arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
💡 **출력**
1 2 3 4 5 15
6 7 8 9 10 40
11 12 13 14 15 65
16 17 18 19 20 90
21 22 23 24 25 115
55 60 65 70 75 325
📌 Note Code
- 2차원 배열이란 ?
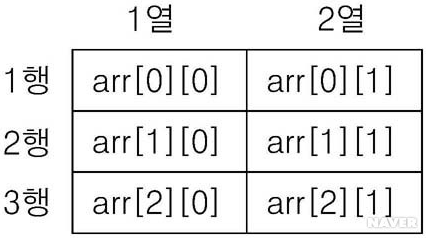
[3행 2열의 요소를 갖는 배열 arr]
출처 : 컴퓨터 개론
Test6. 2차원 배열
💻 입력
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = {{5,6,7},{3,4,5},{7,8,9}};
int[][] b = {{6,7,8},{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
int[][] sum = new int[3][3];
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
for(j=0;j<a.length;j++) {
sum[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j];
System.out.printf("%4d",sum[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
💡 **출력**
11 13 15
4 6 8
11 13 15
