다형성의 실세계 비유
대부분의 승용차는 국가에서 공인한 운전면허증만 있다면, 특별한 경우가 아닐시 어떤 종류의 자동차든 운전할 수 있다. 이는 모든 자동차에서 엑셀, 브레이크, 핸들링이라는 기본 기능이 동일하게 동작하기 때문이다. 다형적 설계의 핵심은 이러한 역할과 구현을 명확히 분리하는 데 있다.
운전에는 두 가지 역할이 존재한다. 운전자의 역할은 엑셀을 밟는 것과 같은 동작이고, 자동차의 역할은 엑셀을 밟으면 앞으로 나아가는 것이다. 반면, 자동차의 구현은 "앞으로 나아가는 것"에 대한 세부적인 로직이다. 예를 들어, 전기차와 디젤차는 엑셀을 밟았을 때 앞으로 나아가는 세부적인 기계공학적 로직은 다르지만, 운전자는 이러한 세부 구현을 알 필요 없이 엑셀을 밟는다는 동일한 방식으로 자동차를 운전할 수 있다.
따라서 기계공학자들은 디젤 자동차에 익숙한 운전자도 전기 자동차를 쉽게 운전할 수 있도록 설계해야 한다. 이는 전기 자동차가 "자동차"라는 인터페이스에 맞추어 설계되었기 때문이다. 즉, 역할과 구현을 분리함으로써 다양한 자동차 간의 일관성을 유지할 수 있다.
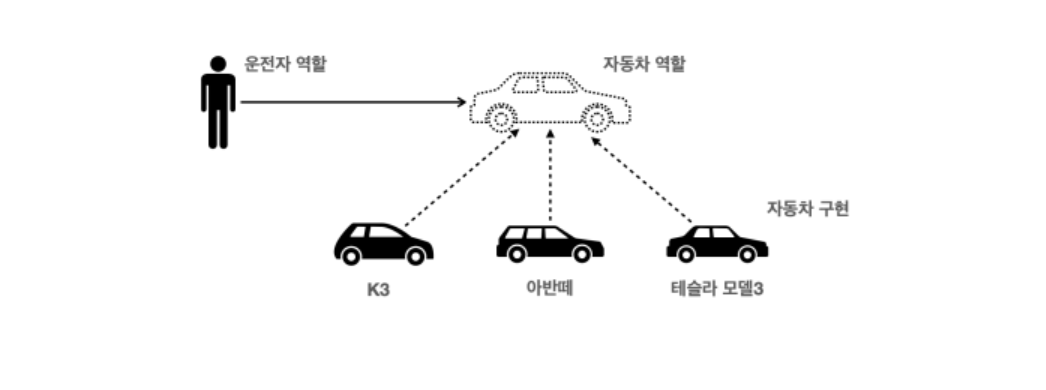
- 클라이언트는 인터페이스(역할)만 알면 된다.
- 클라이언트는 구현의 내부 구조를 몰라도 된다.
- 클라이언트는 구현의 내부 구조가 변경되어도 영향을 받지 않는다.
- 클라이언트는 구현 대상 자체를 바꾸어도(전기차 -> 디젤엔진차) 영향을 받지 않는다.
OCP(Open-Closed Principle)
OCP (Open/Closed Principle)란, 소프트웨어는 새로운 기능을 추가하거나 변경할 때 확장에는 열려(Open) 있어야 하고, 기존 코드의 수정에는 닫혀(Closed) 있어야 한다는 설계 원칙이다.
이 말이 처음에는 모순처럼 들릴 수 있지만, 핵심은 변경이 필요한 부분(구현)과 변경이 필요하지 않은 부분(인터페이스 또는 클라이언트 코드)을 명확히 분리하는 것이다. 이를 통해 새로운 요구사항이 추가되더라도 기존 코드를 수정하지 않고 기능을 확장할 수 있다.
아래는 OCP를 위반한 예제 코드이다. 새로운 기능이 추가될 때마다 기존 코드가 수정되어야 한다.
class NotificationService {
public void sendNotification(String type, String message) {
if (type.equals("Email")) {
System.out.println("Sending Email: " + message);
} else if (type.equals("SMS")) {
System.out.println("Sending SMS: " + message);
} else if (type.equals("Push")) {
System.out.println("Sending Push Notification: " + message);
}
}
}
문제점
- 새로운 알림 방식(예: Slack)을 추가하려면 sendNotification 메서드에 else if 조건을 추가해야 한다.
- 기존 코드를 계속 수정하게 되므로 OCP를 위반한다.
이 문제를 해결하려면 확장 가능하고 변경에는 닫힌 구조를 만들어야 한다. 이를 위해 인터페이스와 다형성을 활용한다.
// Notification 인터페이스: 공통 동작 정의
interface Notification {
void send(String message);
}
// EmailNotification 구현
class EmailNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void send(String message) {
System.out.println("Sending Email: " + message);
}
}
// SMSNotification 구현
class SMSNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void send(String message) {
System.out.println("Sending SMS: " + message);
}
}
// PushNotification 구현
class PushNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void send(String message) {
System.out.println("Sending Push Notification: " + message);
}
}
// NotificationService 클래스: 클라이언트 코드
class NotificationService {
private final List<Notification> notifications = new ArrayList<>();
// 알림 방식을 추가하는 메서드
public void addNotification(Notification notification) {
notifications.add(notification);
}
// 알림 전송
public void notifyAll(String message) {
for (Notification notification : notifications) {
notification.send(message);
}
}
}
// 클라이언트 코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NotificationService service = new NotificationService();
// 알림 방식 추가 (확장)
service.addNotification(new EmailNotification());
service.addNotification(new SMSNotification());
service.addNotification(new PushNotification());
// 모든 알림 전송
service.notifyAll("Hello, World!");
}
}
OCP 준수
- 새로운 알림 방식(Slack, WhatsApp 등)을 추가하려면 새로운 클래스만 추가하면 된다.
- 기존의 NotificationService 클래스나 기존 알림 클래스는 수정할 필요가 없다.
OCP는 코드를 확장 가능하도록 설계하고, 기존 코드를 안정적으로 유지하는 원칙이다. 인터페이스와 다형성을 활용하여 변화에 유연한 설계를 하면, 새로운 기능을 추가할 때 기존 코드를 변경하지 않고도 확장할 수 있다. 이를 통해 코드의 유지보수성을 높일 수 있다.
