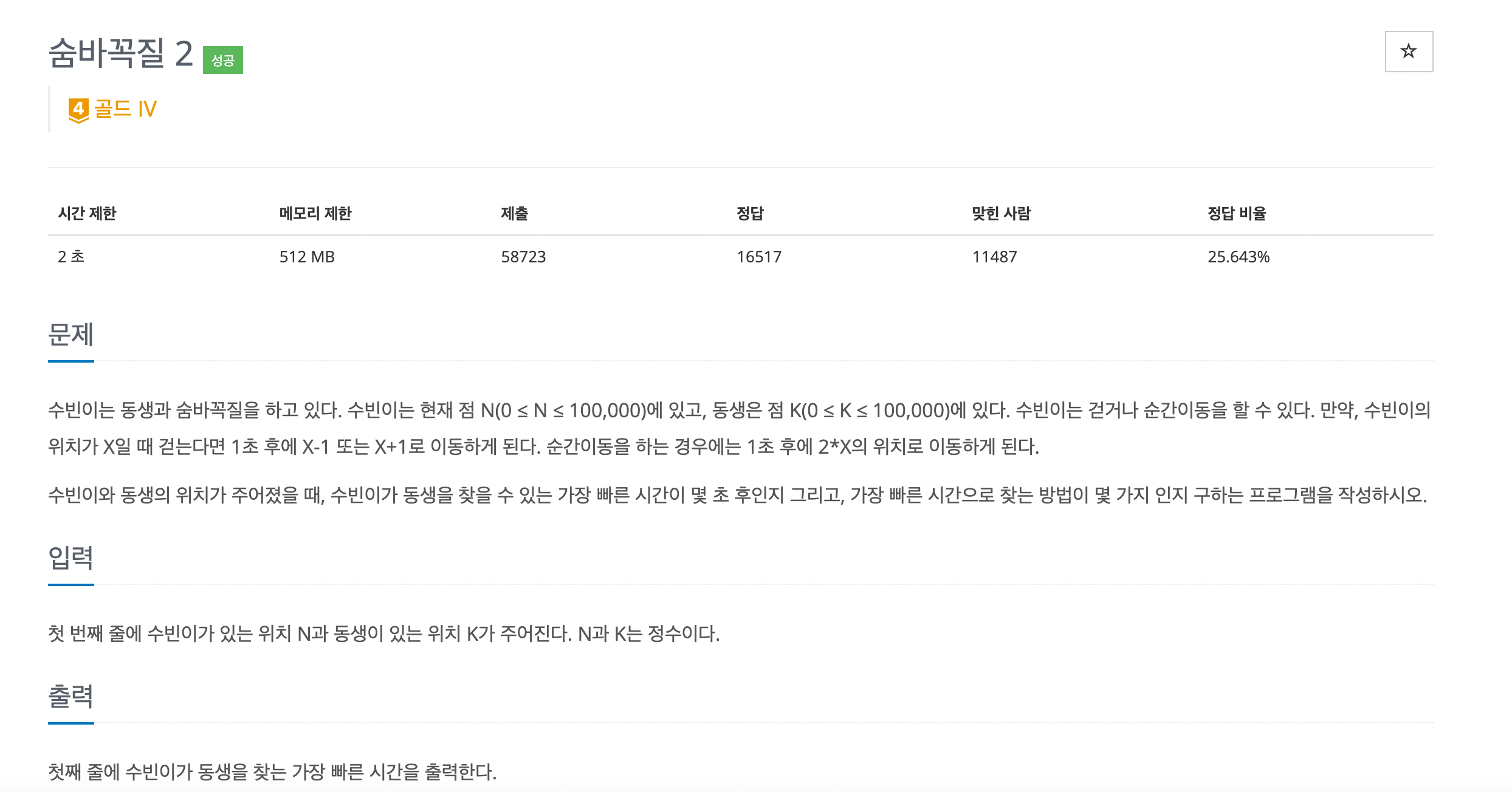
- 예시 입력이 5 17이다. 이를 그려보자.
5
4 6 10 ... (time=1)
3 8 7 12 9 11 20 ...(time=2)
2 16 14 11 13 24 18 22 19 21 40 ...(time=3)
정답은 time=4에서 17이 두개가 나온다. 이를 통해 알 수 있는 점은 과정을 거치며 중복이 많다는 것
BFS를 활용해서 3개씩 증식될 때 이전 레벨에서 존재했던 번호라면 채택하지 않는다.
BFS의 특성상(큐 이용) 예를 들어 time=2의 요소들이 먼저 들어가면 무조건 time=3의 요소들은 time=2 요소들 뒤에 위치할 것이다.
그렇게 17이 발견되면 while을 멈추게하면 된다. 다만 해당 레벨은 모두 검색하고 끝내야 한다.
그렇게 하기 위해 17(목표값)이 발견되면 바로 음수로 설정된 finish를 멈출 time으로 설정한다(time=4는 모두 보아야하기 때문에 finish의 경우는 발견된 위치값 + 1을 했다.
그리고 큐에서 나온 time값이 finish면 break한다.(처음엔 음수니까 계속 돌아간다)
또한 생겨난 정수가 목표값(동생 숫자)보다 +1이상 크다면 목표값으로 갈 수 없다. deque나 visited작업을 해줄 필요가 없다.(메모리 손해)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] siblings = br.readLine().split(" ");
int me = Integer.parseInt(siblings[0]);
int brother = Integer.parseInt(siblings[1]);
List<Integer> result = BFS(me, brother);
System.out.println(result.get(1));
System.out.println(result.get(0));
}
public static List<Integer> BFS(int startInt, int targetInt) {
int finish = -1;
int count = 0;
Deque<int []> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
deque.offer(new int[] {startInt,0});
visited.add(startInt);
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
int[] poll = deque.poll();
visited.add(poll[0]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(poll));
if (poll[1] == finish) {
break;
}
if (poll[0] != targetInt) {
if (!visited.contains(poll[0]-1) && poll[0]-1 >= 0) {
deque.offer(new int[] {poll[0]-1, poll[1]+1});
}
if (!visited.contains(poll[0]+1) && poll[0]+1 < targetInt + 2) {
deque.offer(new int[] {poll[0]+1, poll[1]+1});
}
if (!visited.contains(poll[0]*2) && poll[0]*2 >= 0 && poll[0]*2 < targetInt + 2) {
deque.offer(new int[] {poll[0]*2, poll[1]+1});
}
} else {
finish = poll[1] + 1;
count++;
}
}
return List.of(count, finish - 1);
}
}
