📌들어가기에 앞서
해당 포스트는 React를 학습한 내용을 일부 정리한 내용입니다.
📖 props drilling
🔎 요약
React에서 "props drilling"은 컴포넌트 계층 구조에서 props를 상위 컴포넌트로 전달하면서 여러 계층을 거쳐야하는 문제를 의미합니다.
React 애플리케이션에서 데이터는 주로 상위 컴포넌트에서 하위 컴포넌트로 전달됩니다. 그러나 여러 계층을 거치면서 props를 전달하다 보면 코드가 복잡해지고 유지보수가 어려워집니다. 이를 "props drilling"이라고 합니다.
예를 들어, 상위 컴포넌트에서 데이터를 가져와 하위 컴포넌트까지 전달해야하는 경우가 있습니다. 그러나 중간에 위치한 컴포넌트들은 이 데이터를 사용하지 않고 그냥 전달만 하기 때문에 불필요한 코드가 생길 수 있습니다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해서는 과도한 props drilling을 방지해야합니다. 컴포넌트와 관련있는 state는 될 수 있으면 가까이 유지하는 방법, childreun을 이용한 방법, 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하는 방법이 있습니다. 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하게 되면 전역으로 관리하는 저장소에서 직접 state를 꺼내쓸 수 있기 때문에 Props Drilling을 방지하기에 매우 효과적입니다.
이를 통해 props drilling을 최소화하고 코드의 가독성과 유지보수성을 높일 수 있습니다.
📖 props drilling
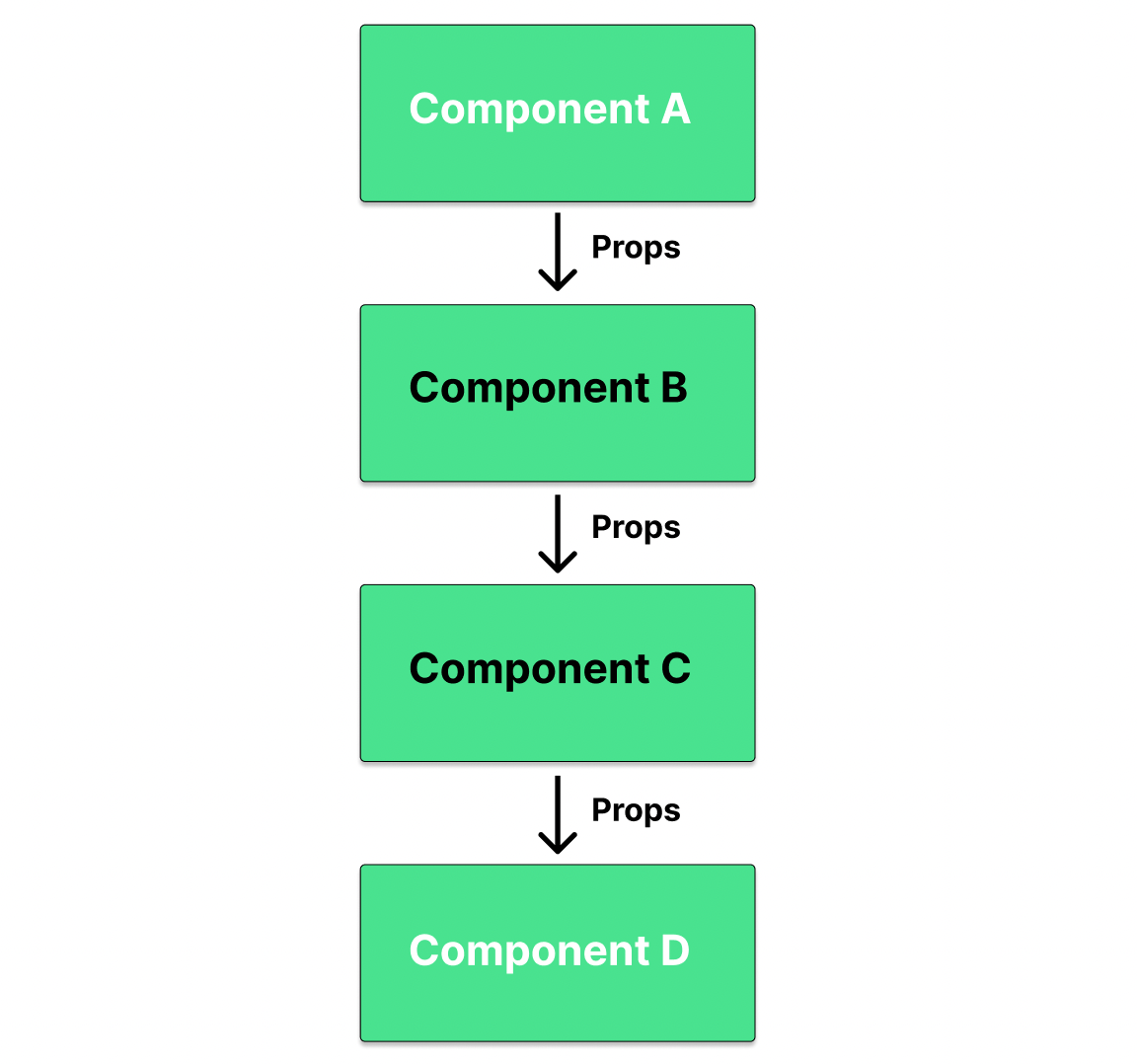
Props Drilling은 상위 컴포넌트의 state를 props를 통해 전달하고자 하는 컴포넌트로 전달하기 위해 그 사이는 props를 전달하는 용도로만 쓰이는 컴포넌트들을 거치면서 데이터를 전달하는 현상을 의미합니다. 위 그림처럼 컴포넌트 A의 state를 컴포넌트 D로 전달하기 위해선 사이에 있는 컴포넌트 B, C를 거쳐야합니다.
🔎 Props Drilling 예시
예시 1
아래의 예시는 props를 제일 깊은 컴포넌트까지 내려주어야 제대로 작동합니다. 지금도 코드를 작성하는게 번거롭고 복잡한데 이보다 더 깊은 컴포넌트와 복잡한 구조가 있다고 생각해보세요. 생각만 해도 끔찍합니다.
function Child1({
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
plusNum,
minusNum,
}) {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 1 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child2 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child2({
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
plusNum,
minusNum,
}) {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 2 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child3 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child3({
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
plusNum,
minusNum,
}) {
console.log('Child3');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 3 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child4 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child4({ plusNum, minusNum }) {
console.log('Child4');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 4 Component]</Text>
<Button onClick={plusNum}>👍</Button>
<Button onClick={minusNum}>👎</Button>
</Container>
);
}
예시 2
import React from "react";
import "./styles.css";
export default function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<FirstComponent content="Who needs me?" />
</div>
);
}
function FirstComponent({ content }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the first component</h3>;
<SecondComponent content={content} />|
</div>
);
}
function SecondComponent({ content }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the second component</h3>;
<ThirdComponent content={content} />
</div>
);
}
function ThirdComponent({ content }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the third component</h3>;
<ComponentNeedingProps content={content} />
</div>
);
}
function ComponentNeedingProps({ content }) {
return <h3>{content}</h3>;
}
content 를 App > First > Second > Third > ComponentNeedingProps 순으로 전달합니다.
ComponentNeedingProps 컴포넌트에서 해당 props를 사용하기 위해 전달하는 과정을 거치게 됩니다.
🔎 Props Drilling의 문제점
props의 전달 횟수가 3 ~ 5회 이내로 많지 않다면 props drilling 은 큰 문제가 되지 않습니다. 하지만 규모가 커지고 구조가 복잡해지면서 props의 전달 과정이 늘어난다면 어떻게 될까요? 당장 생각할 수 있는 문제만해도 아래와 같습니다.
-
코드의 가독성이 매우 나빠지게 됩니다.
-
코드의 유지보수 또한 힘들어지게 됩니다.
-
state변경시props전달 과정에서 불필요하게 관여된 컴포넌트들 또한 리렌더링이 발생합니다. -
따라서, 웹성능에 악영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
🔎 해결 방법
과도한 props drilling을 방지하기 위한 방법으로는 컴포넌트와 관련있는 state는 될 수 있으면 가까이 유지하는 방법, children을 이용한 방법, 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하는 방법이 있습니다. 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하게 되면 전역으로 관리하는 저장소에서 직접 state를 꺼내쓸 수 있기 때문에 Props Drilling을 방지하기에 매우 효과적입니다.
예시1 의 redux를 사용한 방법
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import styled from 'styled-components';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
const Container = styled.div`
border: 5px solid green;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
position: relative;
`;
const Quantity = styled.div`
text-align: center;
color: red;
border: 5px solid red;
padding: 3px;
font-size: 1.2rem;
`;
const Button = styled.button`
margin-right: 5px;
`;
const Text = styled.div`
color: ${(props) => (props.color ? props.color : 'black')};
font-size: ${(props) => (props.size ? props.size : '1rem')};
font-weight: ${(props) => (props.weight ? '700' : 'inherit')};
`;
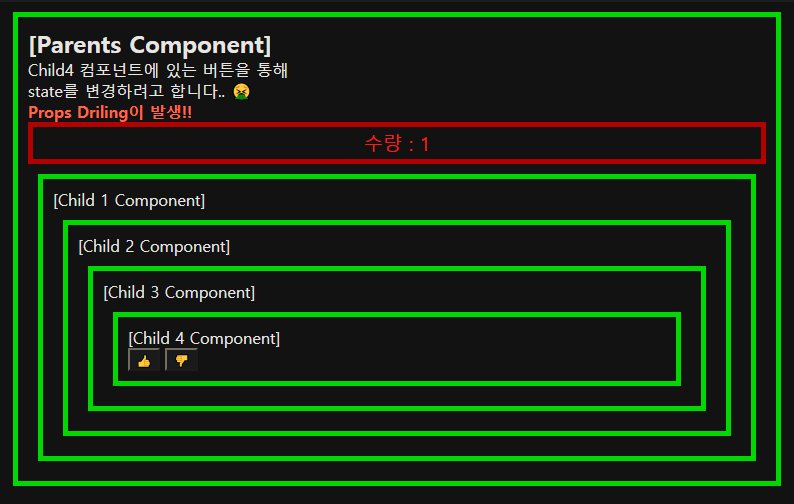
export default function App() {
const number = useSelector((state) => state);
console.log('Parents');
return (
<Container>
<Text weight size="1.5rem">
[Parents Component]
</Text>
<Text>
Child4 컴포넌트에 있는 버튼을 통해 <br /> state를 변경하려고 합니다. ☺️
</Text>
<Text weight color="tomato">
(Redux를 사용하는 경우)
</Text>
<Quantity>{`수량 : ${number}`}</Quantity>
<Child1 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child1() {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 1 Component]</Text>
<Child2 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child2() {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 2 Component]</Text>
<Child3 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child3() {
console.log('Child3');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 3 Component]</Text>
<Child4 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child4() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const plusNum = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'Plus' });
};
const minusNum = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'Minus' });
};
console.log('Child4');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 4 Component]</Text>
<Button onClick={plusNum}>👍</Button>
<Button onClick={minusNum}>👎</Button>
</Container>
);
}
예시 2의 children 사용한 방법
import React from "react";
import "./styles.css";
export default function App() {
const content = "Who needs me?";
return (
<div className="App">
<FirstComponent>
<SecondComponent>
<ThirdComponent>
<ComponentNeedingProps content={content} />
</ThirdComponent>
</SecondComponent>
</FirstComponent>
</div>
);
}
function FirstComponent({ children }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the first component</h3>;
{ children }
</div>
);
}
function SecondComponent({ children }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the second component</h3>;
{children}
</div>
);
}
function ThirdComponent({ children }) {
return (
<div>
<h3>I am the third component</h3>
{children}
</div>
);
}
function ComponentNeedingProps({ content }) {
return <h3>{content}</h3>
}예시 2의 방법처럼 리팩토링을 통해 하나의 컴포넌트에서 값을 관리하고, 그 값을 하위요소로 전달할 때 코드의 추적이 쉬워질 수 있습니다. 또한 전역 상태관리 라이브러리(redux, MobX, recoil) 등을 사용하여 해당 값이 필요한 컴포넌트에서 직접 불러서 사용할 수 있습니다.
🔎 결론
props drilling은 무조건 배제하거나 무조건 사용하기엔 장점도 있고, 단점도 있는 양날의 검과 같습니다. 개발하려는 어플리케이션에 따라 적절한 방법을 선택해야하고 올바르게 사용할 수 있도록 해야 유지보수하기 쉬운 기능이 될 것입니다.
📚 레퍼런스
How To Avoid Prop Drilling in React Using Component Composition

