- python3
- review : 240701
문제
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Merge nums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
계획
첫 방식
- nums1 앞부분 복사한 array 생성
- 순서를 알려줄 check 각각 생성
- check로 한 칸씩 나아가면서 크기 비교 후 넣기
- 남은 숫자를 전부 넣기
- 시간 복잡도 : O(m+n) : m번, n번 이동하여 삽입하는 방식이므로 시간 복잡도는 O(1)에 가깝다.
- 공간 복잡도 : O(2(m+n)) : 첫 방식에서는 공간을 두 배로 사용한다.
두 번째 방식
- nums1의 필요없는 뒷부분을 날린다
- nums2와 합친다
- 내장함수 sort를 활용한다
- 시간 복잡도 : O((m+n)log(m+n)) : python에서 sort()를 이용한 배열의 정렬은 O(NlogN) 의 시간 복잡도를 가진다. 따라서 nums1의 요소의 개수 + nums2의 요소의 개수를 합한 m+n개 만큼의 시간 복잡도를 가지게 된다.
- 공간 복잡도 : O(1) : 공간을 따로 사용하지 않는다.
세번째 방식
two pointers and move from the end because it is a non-decreasing array.
코드
1. 첫번째 방식
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: List[int], m: int, nums2: List[int], n: int) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
# 0. nums1 앞부분 복사한 array 생성
arr = copy.deepcopy(nums1[0:m])
# 1. 순서 알려줄 check 생성
check_1 = 0
check_2 = 0
i = 0
# 2. check로 크기 비교하여 넣기
while check_1 < m and check_2 < n:
if arr[check_1] >= nums2[check_2]:
nums1[i] = nums2[check_2]
check_2 = check_2 + 1
i = i + 1
else:
nums1[i] = arr[check_1]
check_1 = check_1 + 1
i = i + 1
# 3. 남은 숫자 넣기
if check_1 < m:
for j in range(check_1, m):
nums1[i] = arr[j]
i = i + 1
if check_2 < n:
for j in range(check_2, n):
nums1[i] = nums2[j]
i = i + 12. 두번째 방식
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: List[int], m: int, nums2: List[int], n: int) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
del nums1[m:]
nums1 += nums2
nums1.sort()결과
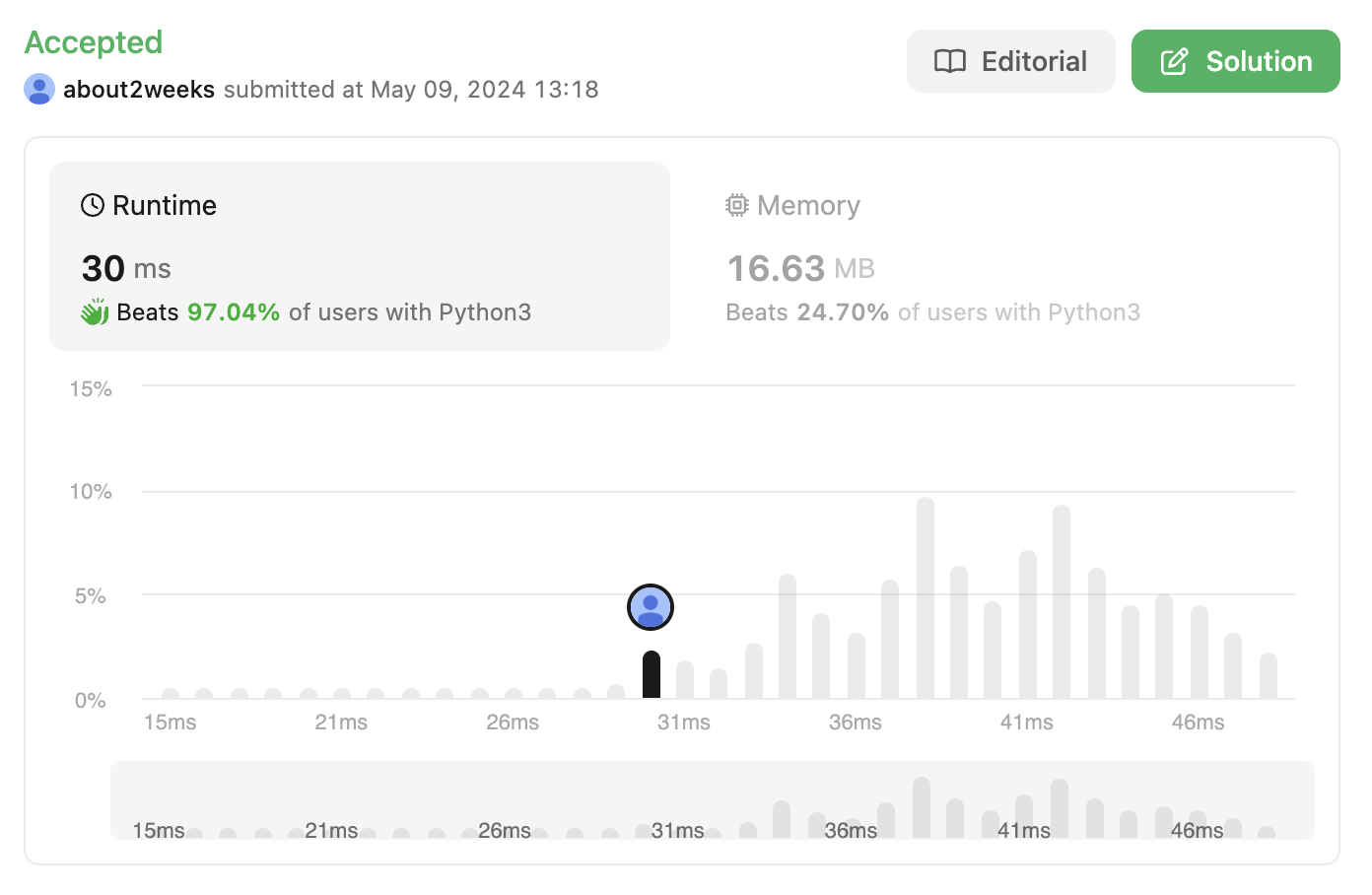
1. 첫번째 방식
2. 두번째 방식
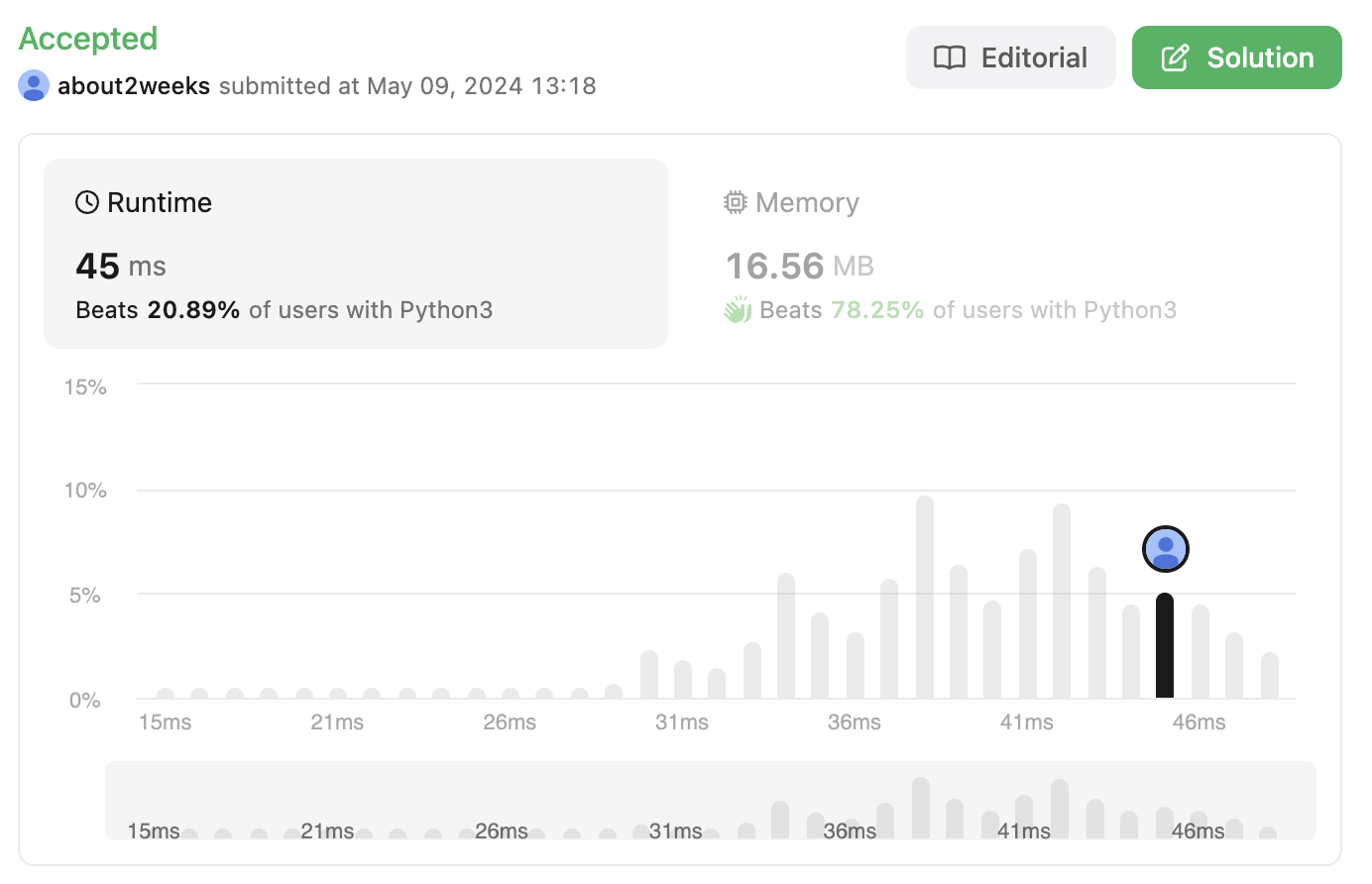
첫번째 방식이 시간은 덜 사용하지만 메모리를 조금 더 쓰고, 두번째 방식이 런타임이 더 오래 걸리는 것을 알 수 있다.
3. 세번째 방식 - 리뷰1
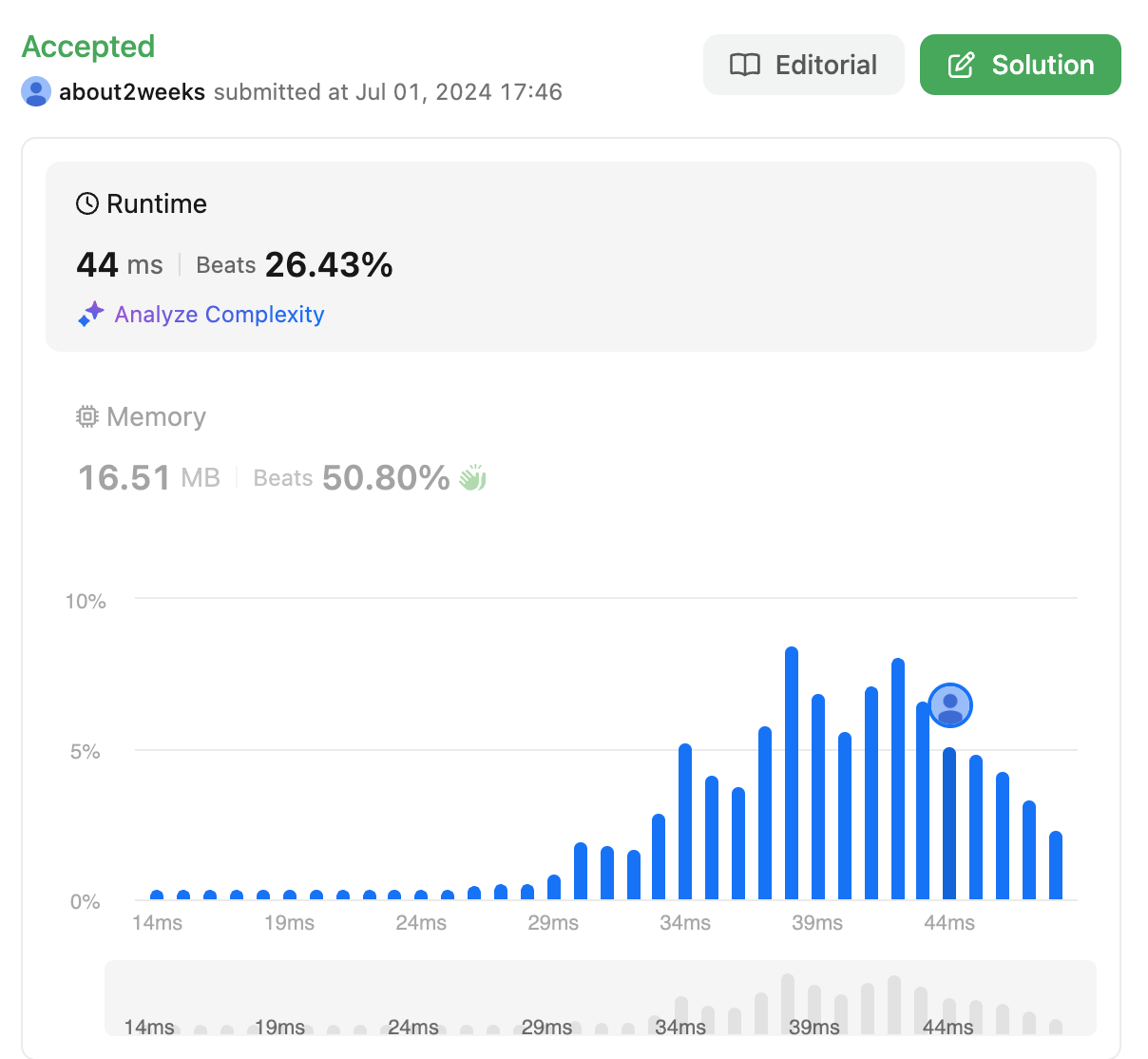
- Time Complexity : O(n)
- Space Complexity : O(1)
