문제 링크
풀이
첫 시도는 bfs를 이용해 destination 으로부터 얼마나 떨어져 있는가를 확인해 보았다.
function solution(n, roads, sources, destination) {
var answer = [];
const graph = new Array(n+1).fill(0).map(()=> new Array(n+1).fill(false))
const value = new Array(n+1).fill(0);
const visited = new Array(n+1).fill(false);
const queue = [[destination, 0]]
for(let i=0; i< roads.length; i++){
const [start, end] = roads[i];
graph[start][end] = true;
graph[end][start] = true;
}
while(queue.length > 0){
const [curNode , curCost] = queue.shift();
// 종료조건
// 방문한 node인 경우 바로 종료
if(visited[curNode]){
continue;
}
else{
visited[curNode] = true;
value[curNode] = curCost
}
// 다음조건
// 그래프와 연결이 되면서 방문한 노드가 아닌경우 추가
for(let nextNode=0; nextNode <=n; nextNode++){
if(graph[curNode][nextNode]){
if(!visited[nextNode]){
queue.push([nextNode, curCost+1])
}
}
}
}
for(let i=0; i< sources.length; i++){
if(value[sources[i]] >0){
answer.push(value[sources[i]])
}else if(sources[i] === destination){
answer.push(0)
}else{
answer.push(-1)
}
}
return answer;
}
// 복귀가 불가능한 경우가 있다.
// 복귀가 가능한 시간은 1이다.
// 복귀가 불가능한 경우 최단시간은 -1이다.
// destination 부터 연결된 모든 노드에 계층을 부여하자. 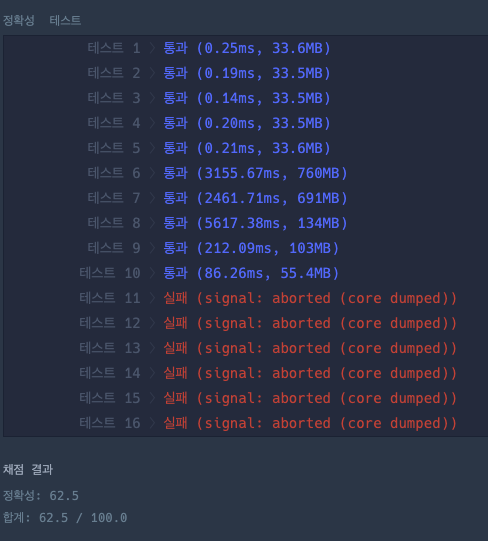
하지만 coredumped가 발생하며, 공간복잡도 상에서 문제가 발생했다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
그 다음 풀이는 그래프를 이용하여 모든 노드간의 연결을 진행하였다.
function solution(n, roads, sources, destination) {
var answer = [];
const graph = new Array(n+1).fill(0).map(()=> new Array(n+1).fill(Infinity))
for(let i=0; i< roads.length; i++){
const [start, end] = roads[i];
graph[start][end] = 1;
graph[end][start] = 1;
graph[i][i] = 0;
}
graph[n][n] = 0
// mid, str. end 순서를 정해보자
for(let mid = 1; mid <=n; mid++){
for(let start = 1; start <=n; start++){
for(let end = 1; end <=n; end++){
if(graph[start][mid] !== Infinity && graph[mid][end] !==Infinity){
graph[start][end] = Math.min(graph[start][mid]+graph[mid][end], graph[start][end])
}
}
}
}
console.log(graph)
for(let i=0; i< sources.length; i++){
const cur = sources[i]
if(cur === destination){
answer.push(0)
}else if(graph[destination][cur] > 0 && graph[destination][cur] !==Infinity){
answer.push(graph[destination][cur])
}else{
answer.push(-1)
}
}
return answer
}
하지만 이 역시 실패하게 되었는데
다시 bfs 방법으로 돌아갔다.
function solution(n, roads, sources, destination) {
var answer = [];
const value = new Array(n+1).fill(Infinity);
const visited = new Array(n+1).fill(false);
const queue = [[destination, 0]]
const temp = new Array(n+1).fill(0).map(() => new Array()) // 정석처럼 만들것
// const temp = new Array(n+1).fill([])
for(let i=0; i< roads.length; i++){
const [start, end] = roads[i];
temp[start].push(end)
temp[end].push(start)
}
while(queue.length > 0){
const [curNode , curCost] = queue.shift();
// 종료조건
// 방문한 node인 경우 바로 종료
if(visited[curNode]){
continue;
}
else{
visited[curNode] = true;
value[curNode] = curCost
}
// 다음조건
// 그래프와 연결이 되면서 방문한 노드가 아닌경우 추가
for(let i=0; i< temp[curNode].length; i++){
const nextNode = temp[curNode][i]
if(!visited[nextNode] && curCost +1 < value[nextNode]){ // 이 부분을 수정해주엇다.
queue.push([nextNode, curCost+1])
}
}
}
return sources.map(v=>{
if(value[v] === Infinity) return -1;
else return value[v];
});
}
문제였던 coredumped는 배열의 크기가 커서 발생하는 문제였으며,
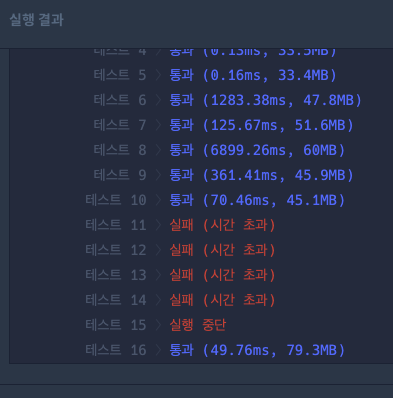
지우고 다시 temp를 통해서 수정하자 시간초과가 발생했다.
코드
function solution(n, roads, sources, destination) {
var answer = [];
const value = new Array(n+1).fill(Infinity);
const visited = new Array(n+1).fill(false);
const queue = [[destination, 0]]
const graph = new Array(n+1).fill(0).map(() => new Array()) // 정석처럼 만들것
// const temp = new Array(n+1).fill([])
for(let i=0; i< roads.length; i++){
const [start, end] = roads[i];
graph[start].push(end)
graph[end].push(start)
}
value[destination] = 0
while(queue.length > 0){
const [curNode , curCost] = queue.shift();
// 종료조건
// 방문한 node인 경우 바로 종료
// 중복되는 로직을 제거해줌, 지금까지는 그냥 혹시 몰라서 추가했으나, 여기서 확인하는 로직 때문에 아주 미세하게
// 실패하게 되는것을 확인
// 다음조건
// 그래프와 연결이 되면서 방문한 노드가 아닌경우 추가
for(let i=0; i< graph[curNode].length; i++){
const nextNode = graph[curNode][i]
if(!visited[nextNode]){
value[nextNode] = curCost+1
visited[nextNode] = true
queue.push([nextNode, curCost+1])
}
}
}
value[destination] = 0
return sources.map(v=>{
if(value[v] === Infinity) return -1;
else return value[v];
});
}
// 복귀가 불가능한 경우가 있다.
// 복귀가 가능한 시간은 1이다.
// 복귀가 불가능한 경우 최단시간은 -1이다.
// destination 부터 연결된 모든 노드에 계층을 부여하자. 