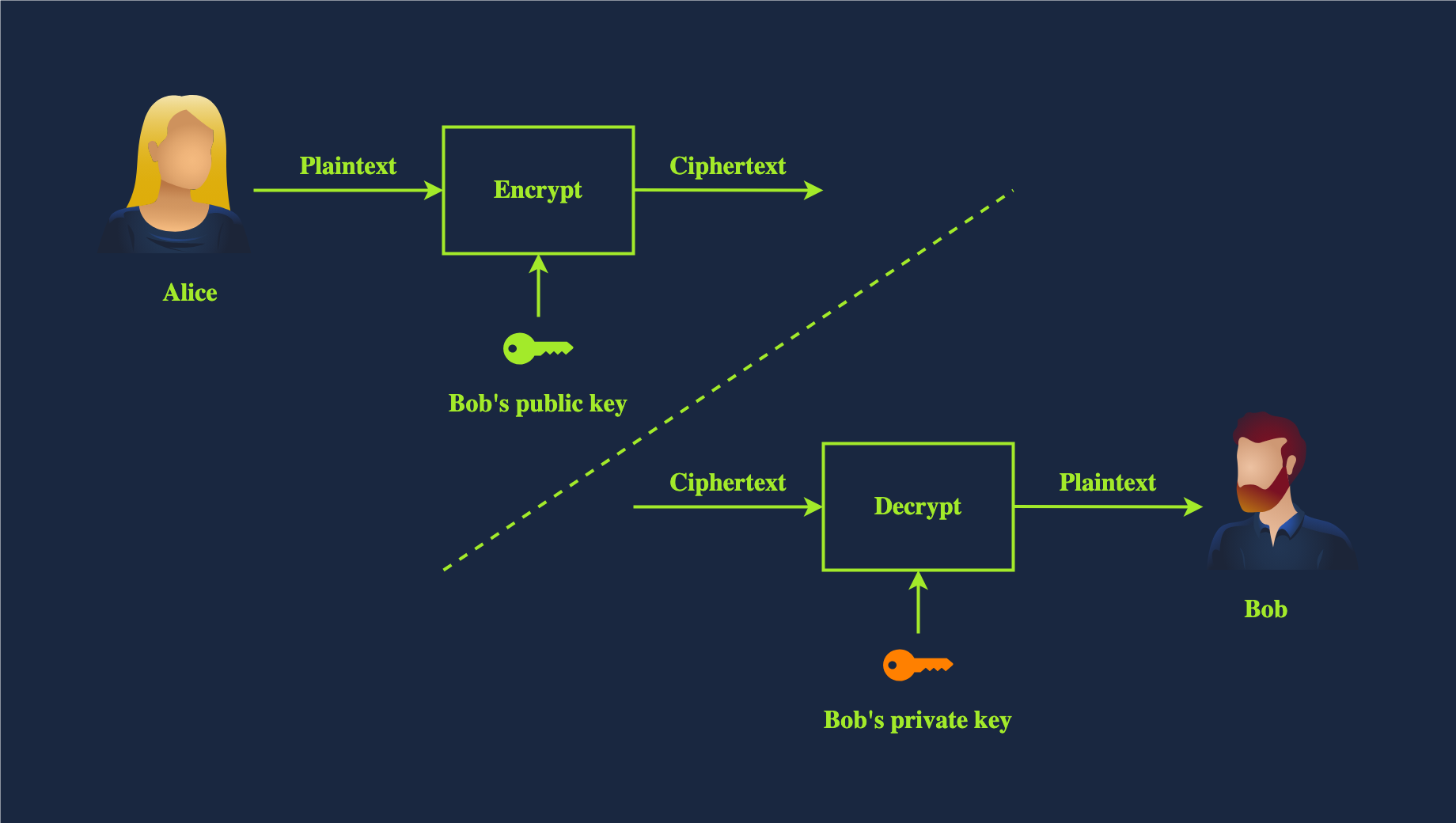
1️⃣ Overview
Asymmetric Encryption (also called public-key cryptography) uses two different keys for encryption and decryption:
- Public Key: Available to anyone; used to encrypt data.
- Private Key: Kept secret by the owner; used to decrypt data.
Unlike symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, asymmetric encryption allows secure key distribution without a shared secret.
2️⃣ Key Characteristics
| Feature | Description | Technical Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Key Pair | Uses Public & Private Keys | Public Key can be shared; Private Key must remain secret |
| Security | Resistant to interception attacks | Data can be encrypted safely without a secure channel |
| Speed | Slower than symmetric encryption | Typically used for key exchange, not bulk data encryption |
| Applications | Digital signatures, authentication, key exchange | TLS/SSL, PGP, SSH, X.509 certificates |
3️⃣ How It Works
① Data Encryption
- Sender A obtains the receiver B’s public key.
- A encrypts the message using B’s public key.
- Encrypted message is sent to B.
- B decrypts the message with their private key.
② Digital Signature
- Sender A creates a hash of the message.
- A encrypts the hash with their private key → digital signature.
- Receiver B verifies the signature using A’s public key.
- Ensures message integrity and sender authentication.
4️⃣ Common Algorithms
- RSA: Most widely used; security increases with key length.
- ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography): Provides same security as RSA with shorter keys; ideal for mobile/IoT.
- DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm): Specifically for digital signatures.
5️⃣ Technical-Level Insights
-
Key Management is Critical
- If the private key is leaked, encryption and digital signatures are compromised.
- Use Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for secure storage.
-
Practical Applications
- Data Transfer: Use asymmetric encryption to exchange session keys; actual data encrypted with symmetric keys.
- Authentication: Public-key certificates (X.509) for TLS or SSH.
- Digital Signatures: Ensure integrity and non-repudiation.
-
Performance Optimization
- Asymmetric encryption is computationally expensive.
- Use hybrid cryptography: asymmetric encryption for key exchange, symmetric encryption (e.g., AES) for bulk data.
6️⃣ Summary
- Definition: Uses two different keys (public/private) for encryption and decryption.
- Advantages: Secure key distribution, authentication, integrity verification.
- Disadvantages: Slower than symmetric encryption → hybrid approach recommended.
- Real-World Use: TLS/SSL, SSH, PGP, digital signatures, certificate-based authentication.
