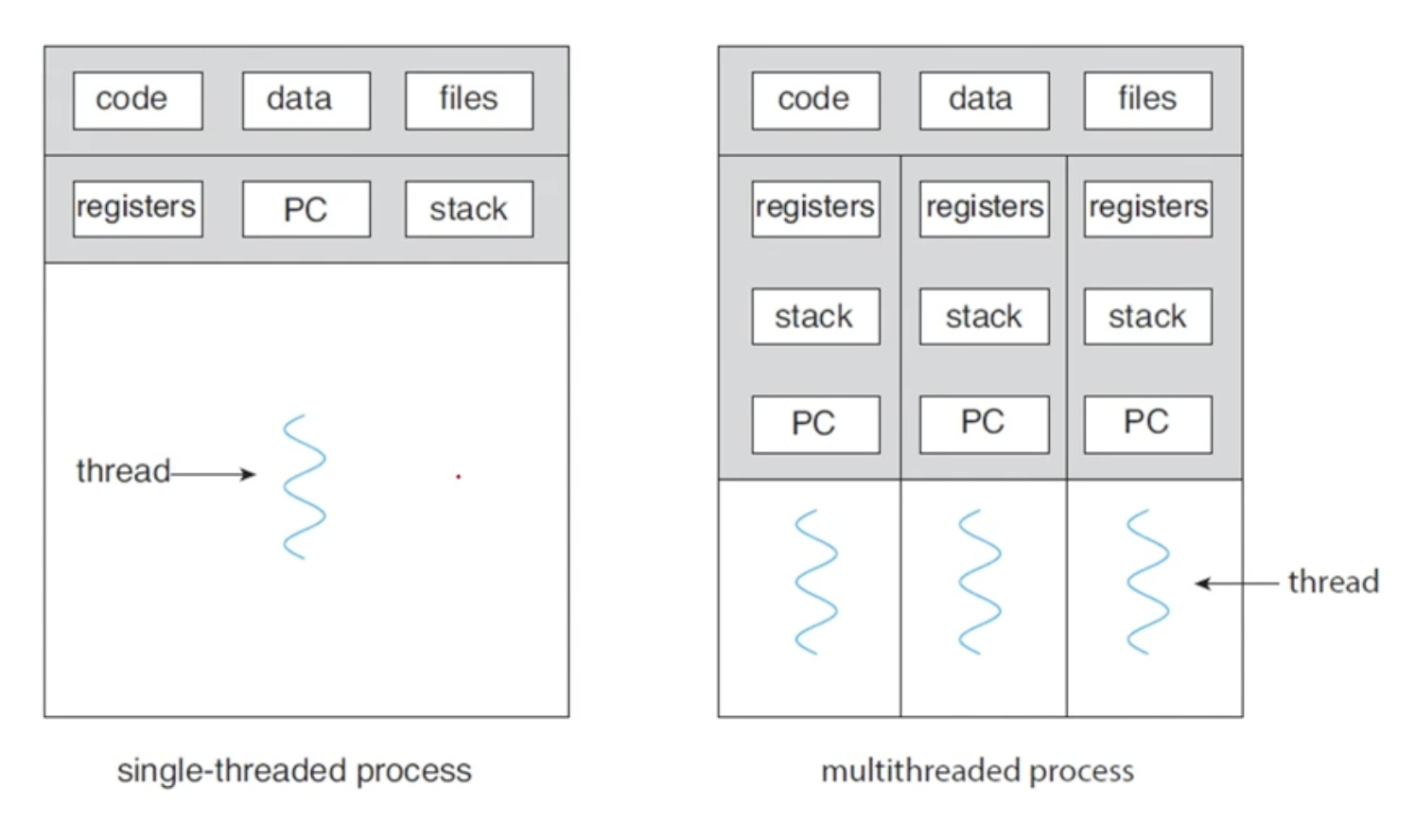
Thread?
- 하나의 프로세스는 여러개의 쓰레드를 가질 수 있다.
- a lightweight process
- CPU를 점유하는 기본 단위
- program counter, register set, stack 도 쓰레드 단위로 가진다. (code, data, files는 공유한다.)
MutiThreading의 이점
- Responsiveness
- server는 client의 요청처리를 thread에 맡기고, non-blocking으로 계속해서(thread의 개수 만큼) client의 요청을 받는다.
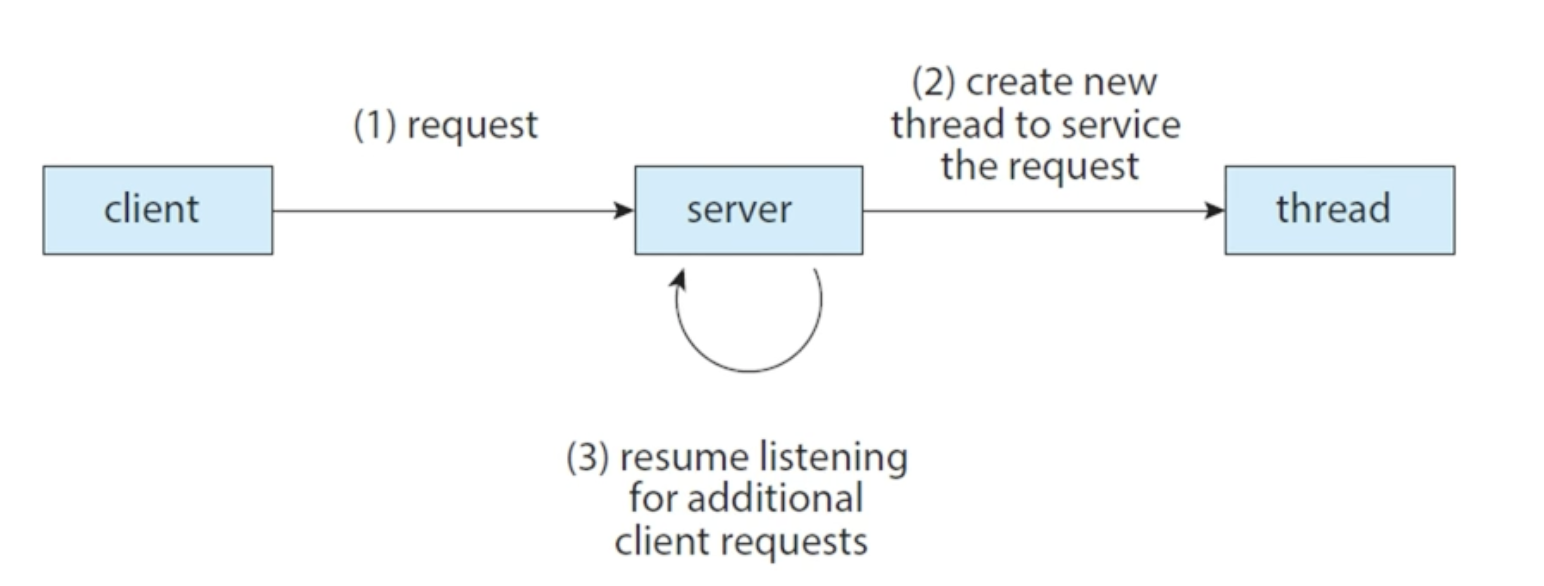
- server는 client의 요청처리를 thread에 맡기고, non-blocking으로 계속해서(thread의 개수 만큼) client의 요청을 받는다.
- Resource Sharing : 자원의 공유 (data영역을 공유 한다.)
- Economy : 프로세스를 생성/context-switching 보다 thread의 경우가 비용이 더 적다.
- Scalability : 확장성. 병렬처리 가능
Thread in Java
- Java는 Thread의 기반으로 만들어졌다.
1. Thread사용 in Java
Thread 클래스 상속Runnable 인터페이스 구현Lamda 표현식으로 Runnable 인터페이스 구현
→ public voud run() 메서드 override
public class ThreadExample1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Thread 클래스 상속
MyThread1 myThread = new MyThread1();
myThread.start();
System.out.println("Hello, My Child!");
// 2. Runnable 인터페이스 구현
Thread thread = new Thread(new MyThread2());
thread.start();
System.out.println("Hello, My Runnable Child!");
// 3. Lambda로 Runnable 인터페이스 구현
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello, Lambda Runnable!");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
System.out.println("I'm interrupted");
}
};
System.out.println("Hello, My Lambda Child!");
}
}
class MyThread1 extends Thread{
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello, Thread!");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
System.out.println("I'm interrupted");
}
}
}
class MyThread2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello, Runnable!");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
System.out.println("I'm interrupted");
}
}
}OUTPUT (1. Thread 클래스 상속)
Hello, My Child!
Hello, Thread!
Hello, Thread!
Hello, Thread!
Hello, Thread!
Hello, Thread!
Hello, Thread!➡️ main thread 에서 MyThread1 생성 → start() → run()
: start() 시점에 아직 contextx-switching이 발생하지 않았으므로 main thread의 Hello, My Child!를 먼저 출력해준다. 이후 contextx-switching으로 MyThread1의 Hello, Thread!를 출력해준다.
2. 부모 쓰레드의 대기 : join
- 프로세스에서의 wait 개념
public class ThreadExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello, Lambda Runnable!");
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
thread.start();
try {
thread.join(); // 이때 돌고 있는건 main
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
System.out.println("Parent thread is interrupted");
}
System.out.println("Hello, My Joined Child!");
}
}OUTPUT
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, My Joined Child!➡️ main thread 에서 MyThread1 생성 → start() → run() → join()
: join()에 돌고 있는 main thread가 대기 상태로 들어간다. start()된 task thread가 모두 실행후 main thread의 Hello, My Joined Child!가 출력된다.
3. 쓰레드의 종류 : interrupt
- stop의 deprecated됨
public class ThreadExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello, Lambda Runnable!");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
System.out.println("I'm interrupted");
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("Hello, My Interrupted Child!");
}
}OUTPUT
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
Hello, Lambda Runnable!
I'm interrupted
Hello, My Interrupted Child!Multithreading in a Muiticore system
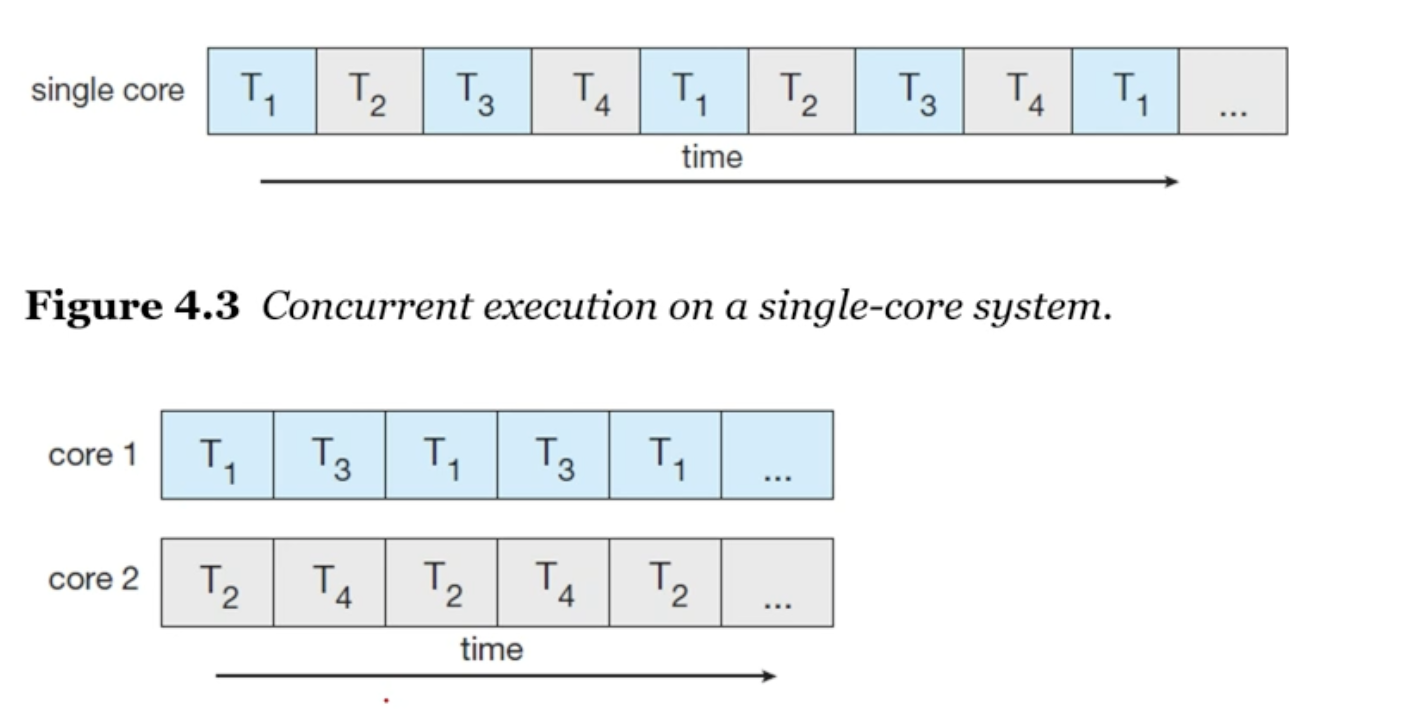
- concurrency(병렬처리)의 향상
- 4개의 thread가 있을때,
- 싱글코어 : 시간별로 interleaving 된다. (시분할=time-sharing)
*interleaving : 끼워서 처리된다. - 멀티코어 : 코어의 수만큼 병렬처리 된다.
- 싱글코어 : 시간별로 interleaving 된다. (시분할=time-sharing)
멀티코어에 따른 고려사항
- Identifying tasks : 분리된 task를 분리할줄 알아야한다.
- 1~50 까지 더할때, 1~25더한것과 26~50까지 더한것을 합치면됨 → 완전한 병렬작업가능
- 소팅시, 1~25소팅한것과 26~50까지 소팅한것은 완전한 병렬작업이라고 할 수 없음
- Balance : 동일한 작업량을 분배
- Data Splitting
- Data dependency : 데이터의 의존성을 관리 해준다. 예를들어 위의 머지소팅의 경우 각 그룹의 결과를 어떤 그룹과 비교할지와 같은 결정을 잘해주어야 한다.
- Testing and debugging : 단일 스레드 환경보다 테스트/디버깅이 어려움
병렬처리 방법
- data parallelism
- task parallelism
→ 최근엔 분산처리 환경이 가능해지며, 단일 컴퓨팅 환경이 아닌 수많은 컴퓨팅, 디스크 자원을 활용 함으로서 위 병렬처리 방법에 대한 구분이 무의미해짐
Amdahl's Law
- CPU코어가 많다고 무조건 속도가 향상되지는 않는다.
- serial(직렬) 처리되는 작업의 양에 따른 적정 코어수가 존재한다.
