해시테이블
해시테이블은 (key, value)를 저장하는 자료구조로, 빠른 탐색을 원할때 쓰는 자료구조다. 주로 문자열을 탐색할때 사용된다.(정수 기반 탐색은 인덱싱이 가능한 배열/리스트를 이용하면 된다)
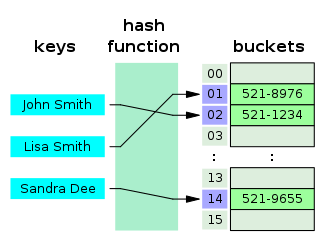
아래 이미지는 사람 이름을 검색하면 전화번호부를 찾는 해시테이블이다. (이미지: 위키백과)
빠른 탐색이 가능하기 때문에, 집합처럼 쓰이기도 한다(key가 없으면 집합의 원소가 아니다라고 판단)
space-time trade-off 관계가 있다. 테이블을 크게 만들면 빠른 탐색이 가능하지만 그만큼 메모리를 많이 사용해야한다. 메모리를 적게 사용하기 위해 테이블을 작게하면 해시충돌이 자주 일어나 탐색 속도가 느리게 되고, 최악의 경우 이 될 수 있다. (정렬되어있다면 이진탐색과 비슷한 수준이 될 것이다)
평가 지표
load factor는 로 구하고
은 해시테이블의 entry 개수, 는 bucket의 개수다.
면 괜찮은 성능이라고 한다.
프로그래밍 언어에서의 구현
C++: unordered_map
Java: HashSet, HashMap, LinkedHashSet, LinkedHashMap
Python: dict
해시함수
해시테이블의 크기가 이라면, 해시함수는 반드시 의 값으로 매핑해야한다. 대표적으로 의 형태로 해시함수를 구성하고, 을 빠르게 계산하고 테이블에 잘 분산되도록 하는 것이 좋은 해시함수다.
해시함수 소스코드
unsigned long hash_func(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381; // 2^n과 거리가 먼 소수일 수록 좋다
int c;
while (*str++) {
c = *str;
hash = (((hash << 5) + hash) + c) % MAX_TABLE;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;해시충돌
해시테이블의 제한된 크기 때문에, 많은 key가 존재하면 반드시 해시값이 중복되는 경우가 생긴다. 이를 해결하는 방법은 여러가지 있다. 이중 대표적으로 2가지 방법만 소개한다.
Seperate Chaining
링크드 리스트로 구현하여 뒤에 새로운 데이터를 추가하는 방법이다.
아래 그림에서 Sandra Dee의 해시값(152)이 John Smith와 충돌하여, John Smith의 노드의 뒤에 연결하여 저장하였다.
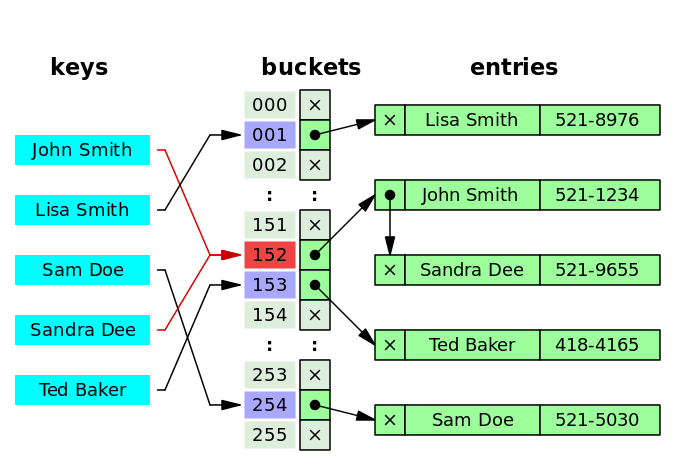
단점으로는 링크드리스트를 이용하기 때문에 캐시 효율성이 떨어진다.(링크드리스트의 노드는 메모리 내에 흩어져 있기 때문) 이를 방지하기 위해 동적배열을 사용하기도 한다고 한다.
Open Adressing
probing을 통해 비어있는 bucket에 데이터를 저장하는 방식이다. linear probing, quadratic probing, double hasing 방법이 있다.
아래 그림에서 linear probing(interval=1)로 충돌하는 데이터인 Sandra Dee를 153에 삽입하였다.
linear probing을 적용할 경우, 캐시 효율성을 활용할 수 있다.
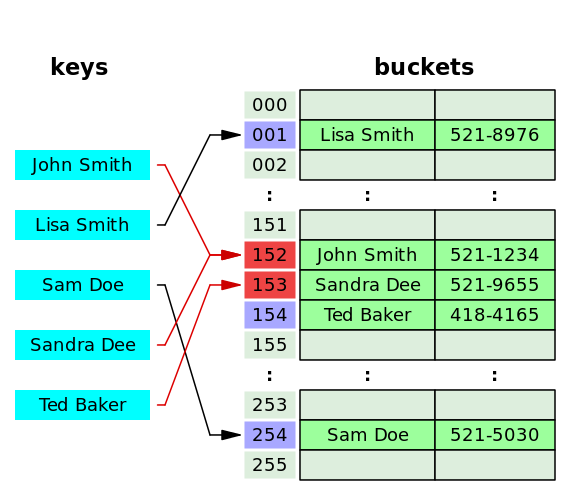
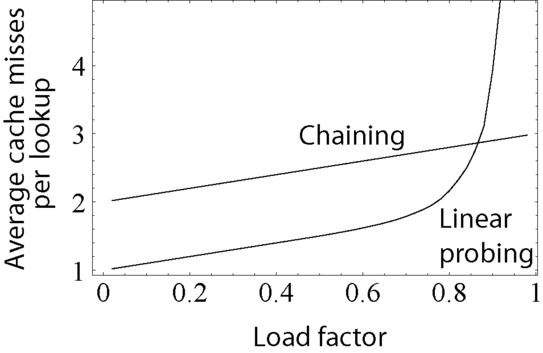
캐시 효율성
테이블이 가득 찰 경우, linear probing의 성능은 급격하게 나빠지는 것을 알 수 있다.
예제 코드 [BOJ 1620]
포켓몬의 이름을 key, 포켓몬의 번호를 value로 하는 해시테이블을 구현한다. (포켓몬 번호가 들어왔을때, 포켓몬의 이름을 찾는 것은 배열로 구현한다)
원래 문제를 변형하여 맨 마지막에는 delete와 display도 추가하였다.
코딩하는거니 님의 유튜브를 참고했습니다
Data Types
// 해시테이블의 크기
#define MAX_TABLE 100007
// 포켓몬 데이터를 저장하는 노드
typedef struct node {
char name[30];
int id;
struct node* next;
}Node;
// 해시테이블 엔트리를 구성하는 버켓
typedef struct bucket {
Node* head;
int count;
}Bucket;utils
// 해시함수 정의
unsigned long hash_func(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while (*str++) {
c = *str;
hash = (((hash << 5) + hash) + c) % MAX_TABLE;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}// 노드 초기화
Node* make_node(const char* name, int id) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// set (key, value) = (name, id)
strcpy(node->name, name);
node->id = id;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// 해시테이블 초기화
Bucket* init_hashTable() {
Bucket* hashTable = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket) * MAX_TABLE);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; i++) {
hashTable[i].head = NULL;
hashTable[i].count = 0;
}
return hashTable;
}insert
- 해시함수를 이용하여 해시값을 찾는다.
- 해시값에 해당하는 엔트리에 데이터를 저장한다.
2.1 만약 엔트리가 비어있다면 바로 삽입한다
2.2 비어있지 않다면, 체이닝으로 리스트를 연결한다. (구현상의 편의를 위해 정렬하지 않고, 데이터삽입을 head에 삽입했음.)- 해당 엔트리의
count값을 증가한다.
void insert(Bucket* hashTable, const char* name, int id) {
int hash = hash_func(name);
Node* node = make_node(name, id);
// empty bucket
if (hashTable[hash].count == 0) {
hashTable[hash].head = node;
}
// already exist
else {
node->next = hashTable[hash].head;
hashTable[hash].head = node;
}
hashTable[hash].count += 1;
//printf("Insert complete!\n\n");
return;
}
}search
- 성공하면 포케몬의 번호를, 실패하면 -1을 반환
- 해시값에 해당하는 엔트리의
head에 접근한다.
2.1 엔트리가 비어있다면 해당하는key가 없으므로-1반환
2.2 엔트리가 비어있지 않다면, 선형탐색을 통해key가 같은 노드를 찾는다. 먼저 찾으면 해당 포켓몬 번호를 반환한다. (포켓몬번호는 고유하다고 가정한다)
int search(Bucket* hashTable, const char* name) {
int ret_id = -1;
int hash = hash_func(name);
Node* node = hashTable[hash].head;
if (node == NULL) {
return -1;
}
while (node != NULL) {
if (strcmp(node->name, name) == 0) {
ret_id = node->id;
break;
}
node = node->next;
}
return ret_id;
}remove
- 해시값에 해당하는 엔트리의 헤드를 찾는다. 헤드가 비어있다면 없는것이다
search와 유사하게 선형탐색을 하여 해당 노드를 찾는다.- 해당 노드를 삭제하고 엔트리 개수를 1 감소한다.
3.1 삭제할 노드가 헤드라면,next가 새로운 헤드가 된다
3.2 중간 노드를 삭제할 때 이전 노드와 연결해야 한다는 것에 주의.trace활용
void remove(Bucket* hashTable, const char* target) {
int hash = hash_func(target);
Node* node;
Node* trace;
node = hashTable[hash].head;
if (node == NULL) {
printf("No key found: %s\n", target);
return;
}
while (node != NULL) {
if (strcmp(node->name, target) == 0) {
printf("Remove Key: %s\n", target);
if (node == hashTable[hash].head) {
hashTable[hash].head = node->next;
}
else {
trace->next = node->next;
}
hashTable[hash].count -= 1;
free(node);
return;
}
trace = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf("No key found: %s\n", target);
return;
}display
엔트리가 비어있는 경우는 출력하지 않는다
엔트리가 비어있지 않다면 -> 를 이용하여 계속 출력한다.
void display(Bucket* hashTable) {
printf("\n\n===============Display Start===============\n");
Node* node;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; i++) {
if (hashTable[i].count == 0) continue;
printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i);
node = hashTable[i].head;
for (int j = 0; j < hashTable[i].count - 1; j++) {
printf("(%s, %d) -> ", node->name, node->id);
node = node->next;
}
printf("(%s, %d)\n", node->name, node->id);
}
printf("===============End of Display===============\n\n");
}전체 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_TABLE 10 //100007
typedef struct node {
char name[30];
int id;
struct node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct bucket {
Node* head;
int count;
}Bucket;
Node* make_node(const char* name, int id) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
// set (key, value) = (name, id)
strcpy(node->name, name);
node->id = id;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
unsigned long hash_func(const char* str) {
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while (*str++) {
c = *str;
hash = (((hash << 5) + hash) + c) % MAX_TABLE;
}
return hash % MAX_TABLE;
}
Bucket* init_hashTable() {
Bucket* hashTable = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket) * MAX_TABLE);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; i++) {
hashTable[i].head = NULL;
hashTable[i].count = 0;
}
return hashTable;
}
void insert(Bucket* hashTable, const char* name, int id) {
int hash = hash_func(name);
Node* node = make_node(name, id);
// empty bucket
if (hashTable[hash].count == 0) {
hashTable[hash].head = node;
}
// already exist
else {
node->next = hashTable[hash].head;
hashTable[hash].head = node;
}
hashTable[hash].count += 1;
//printf("Insert complete!\n\n");
return;
}
int search(Bucket* hashTable, const char* name) {
int ret_id = -1;
int hash = hash_func(name);
Node* node = hashTable[hash].head;
if (node == NULL) {
return -1;
}
while (node != NULL) {
if (strcmp(node->name, name) == 0) {
ret_id = node->id;
break;
}
node = node->next;
}
return ret_id;
}
void remove(Bucket* hashTable, const char* target) {
int hash = hash_func(target);
Node* node;
Node* trace;
node = hashTable[hash].head;
if (node == NULL) {
printf("No key found: %s\n", target);
return;
}
while (node != NULL) {
if (strcmp(node->name, target) == 0) {
printf("Remove Key: %s\n", target);
if (node == hashTable[hash].head) {
hashTable[hash].head = node->next;
}
else {
trace->next = node->next;
}
hashTable[hash].count -= 1;
free(node);
return;
}
trace = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf("No key found: %s\n", target);
return;
}
void display(Bucket* hashTable) {
printf("\n\n===============Display Start===============\n");
Node* node;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TABLE; i++) {
if (hashTable[i].count == 0) continue;
printf("Bucket[%d]: ", i);
node = hashTable[i].head;
for (int j = 0; j < hashTable[i].count - 1; j++) {
printf("(%s, %d) -> ", node->name, node->id);
node = node->next;
}
printf("(%s, %d)\n", node->name, node->id);
}
printf("===============End of Display===============\n\n");
}
int main() {
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// init hash table
Bucket* hashTable = init_hashTable();
int N, M;
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
Node* id2name = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node) * (N + 1));
char str[30];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
scanf("%s", str);
insert(hashTable, str, i);
strcpy(id2name[i].name, str);
}
int id;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
scanf("%s", str);
if (str[0] >= 'A' && str[0] <= 'Z') {
id = search(hashTable, str);
printf("%d\n", id);
}
else {
id = strtol(str, NULL, 10);
printf("%s\n", id2name[id].name);
}
}
display(hashTable);
if (search(hashTable, "ABCDEFG") == -1) {
printf("ABCDEFG is not in the hashTable\n");
}
remove(hashTable, "Pikachu");
remove(hashTable, "Pidgeot");
remove(hashTable, "Caterpie");
remove(hashTable, "ABCDEFG");
display(hashTable);
return 0;
}출력 결과
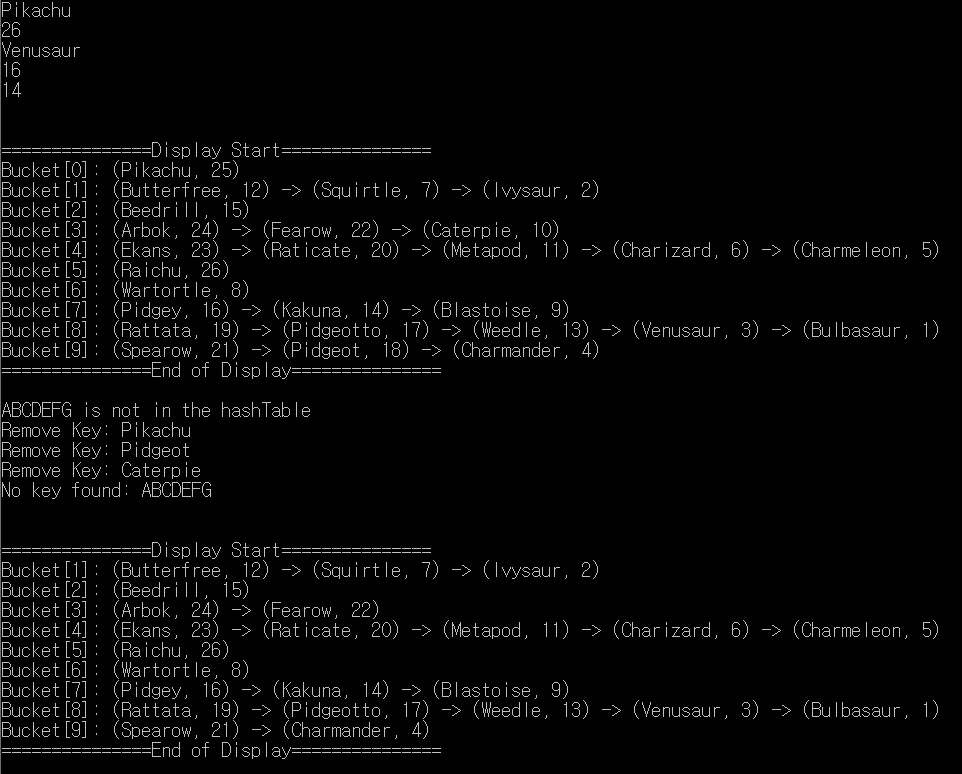
해시테이블 출력을 잘 보기 위해 MAX_TABLE = 10으로 했다.
백준에서 문제를 풀 때는 MAX_TABLE = 100,007로 했다.
예제 2 [BOJ 1764] 듣보잡
소스코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
unsigned int hash_func(const char* str, int table_size) {
unsigned int hash = 5381; // 2^n과 거리가 먼 소수일 수록 좋다
int c;
while (*str++) {
c = *str;
hash = (((hash << 5) + hash) + c) % table_size;
}
return hash % table_size;
}
typedef struct entry {
char* key;
int value;
struct entry* next;
}Entry;
typedef struct {
Entry** entries;
int size;
}HashTable;
Entry* createNode(const char* key, int value) {
Entry* entry = (Entry*)malloc(sizeof(Entry));
entry->key = (char*)malloc(sizeof(key) + 1);
strcpy(entry->key, key);
entry->value = value;
entry->next = NULL;
return entry;
}
HashTable* createTable(int size) {
HashTable* table = (HashTable*)malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
table->size = size;
table->entries = (Entry**)malloc(sizeof(Entry*) * table->size);
for (int i = 0; i < table->size; i++) {
table->entries[i] = NULL;
}
return table;
}
void insert(HashTable* table, const char* key, int value) {
unsigned int index = hash_func(key, table->size);
Entry* entry = table->entries[index];
Entry* node = createNode(key, value);
if (entry == NULL) {
table->entries[index] = node;
return;
}
Entry* prev;
while (entry != NULL) {
if (strcmp(entry->key, key) == 0) {
entry->value = value;
return;
}
prev = entry;
entry = prev->next;
}
prev->next = node;
}
int search(HashTable* table, const char* key) {
unsigned int index = hash_func(key, table->size);
Entry* entry = table->entries[index];
if (entry == NULL) return -1;
while (entry != NULL) {
if (strcmp(entry->key, key) == 0) {
return entry->value;
}
entry = entry->next;
}
return -1; // fail to find key
}
void display(HashTable* table) {
printf("\n\n===============Display Start===============\n");
Entry* entry;
for (int i = 0; i < table->size; i++) {
if (table->entries[i] == NULL) continue;
printf("Entry[%d]: ", i);
entry = table->entries[i];
while (entry->next != NULL) {
printf("(%s, %d) -> ", entry->key, entry->value);
entry = entry->next;
}
printf("(%s, %d)\n", entry->key, entry->value);
}
printf("===============End of Display===============\n\n");
}
typedef struct {
char* name;
}Person;
int cmp_person(const void* a, const void* b) {
const Person* pa = (Person*)a;
const Person* pb = (Person*)b;
return strcmp(pa->name, pb->name);
}
int main() {
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
int table_size = 750000;
HashTable* ht1 = createTable(table_size);
HashTable* ht2 = createTable(table_size);
int N, M;
char name[30];
scanf("%d %d", &N, &M);
Person* persons = (Person*)malloc(sizeof(Person) * (N + M));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%s", name);
insert(ht1, name, i);
persons[i].name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(name) + 1);
strcpy(persons[i].name, name);
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
scanf("%s", name);
insert(ht2, name, N + i);
persons[N + i].name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(name) + 1);
strcpy(persons[N + i].name, name);
}
//display(ht1);
//display(ht2);
Person* both = (Person*)malloc(sizeof(Person) * (N + M));
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (search(ht1, persons[i].name) != -1 &&
search(ht2, persons[i].name) != -1) {
both[count].name = (char*)malloc(sizeof(persons[i].name) + 1);
strcpy(both[count].name, persons[i].name);
//printf("%s %s\n", both[count].name, persons[i].name);
count += 1;
}
}
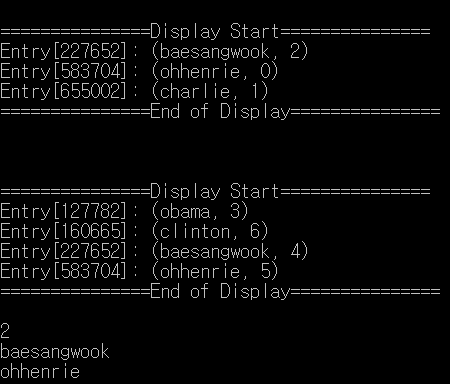
printf("%d\n", count);
qsort(both, count, sizeof(Person), cmp_person);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("%s\n", both[i].name);
}
return 0;
}예제 출력(display)