스택
스택(Stack)은 후입선출(LIFO, Last In First Out)의 원칙을 따르는 자료구조로, 데이터의 삽입과 삭제가 한쪽 끝에서만 이루어지는 구조이다.
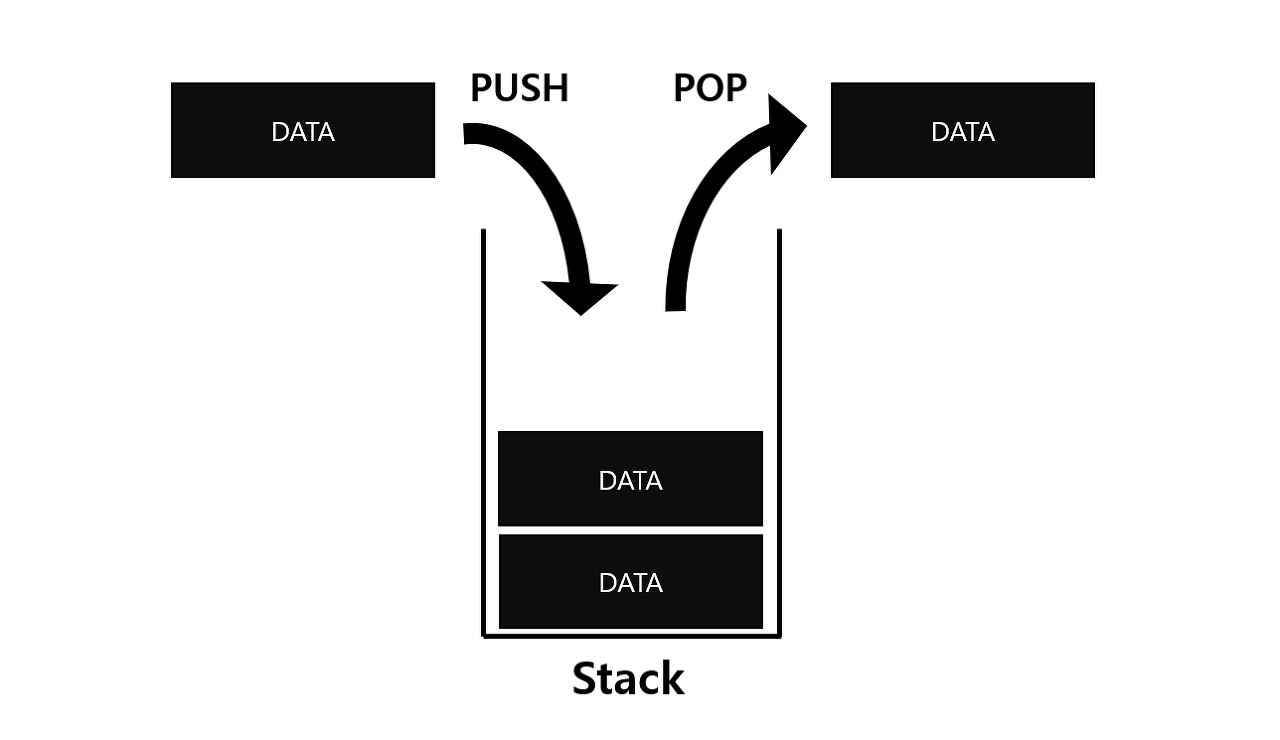
스택의 특징
- LIFO (Last In First Out) : 가장 최근에 삽입된 요소가 가장 먼저 삭제된다.
- 데이터의 삽입(push), 삭제(pop)가 한쪽 끝에서만 이루어짐
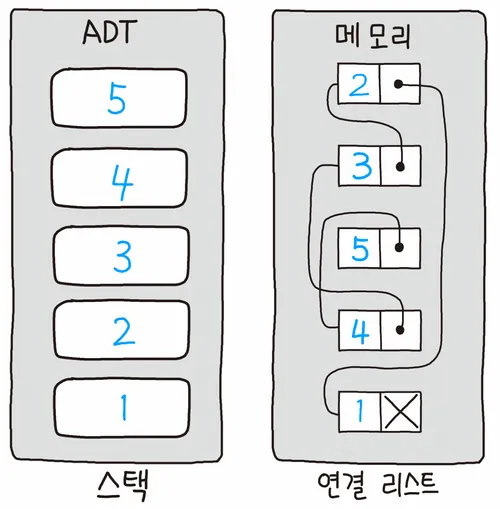
스택의 구현
스택은 배열(Array) 또는 연결 리스트(Linked List)를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다.
Java Stack 클래스 사용
// Stack 선언 및 초기화
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 스택에 요소 추가
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
// 스택의 최상단 요소 확인
System.out.println("Top element: " + stack.peek());
// 스택에서 요소 제거
stack.pop();1. 스택의 정적 구현 (Array)
배열 기반 스택은 고정된 크기를 가진다.
public class ArrayStack {
private int maxSize; // 스택의 최대 크기
private int top; // 스택의 현재 위치 (top)
private int[] stackArray; // 정수형 배열을 사용한 스택
// 생성자
public ArrayStack(int size) {
maxSize = size;
stackArray = new int[maxSize];
top = -1; // 스택이 비어있을 때 top을 -1로 초기화
}
// 스택에 요소 추가 (push)
public void push(int value) {
if (top < maxSize - 1) { // 스택이 가득 찼는지 확인
stackArray[++top] = value;
System.out.println("Pushed: " + value);
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is full. Cannot push " + value);
}
}
// 스택에서 요소 제거 및 반환 (pop)
public int pop() {
if (top >= 0) { // 스택이 비어있는지 확인
int poppedValue = stackArray[top--];
System.out.println("Popped: " + poppedValue);
return poppedValue;
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty. Cannot pop.");
return -1; // 스택이 비어있을 때는 임의의 값(-1) 반환
}
}
// 스택의 현재 최상단 요소 반환 (peek)
public int peek() {
if (top >= 0) {
return stackArray[top];
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
return -1; // 스택이 비어있을 때는 임의의 값(-1) 반환
}
}
// 스택이 비어있는지 여부 반환
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// 스택이 가득 찼는지 여부 반환
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 스택 생성 (최대 크기: 5)
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(5);
// 스택에 요소 추가
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
// 스택의 현재 최상단 요소 확인
System.out.println("Top element: " + stack.peek());
// 스택에서 요소 제거
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
// 스택이 비어있는지 여부 확인
System.out.println("Is stack empty? " + stack.isEmpty());
// 스택에 요소 추가
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6); // 스택이 가득 차서 추가되지 않음
}
}2. 스택의 동적 구현 (Linked List)
연결 리스트 기반 스택은 동적으로 크기가 조절될 수 있으나 구현이 복잡하고, 삽입/삭제 시간이 오래 걸린다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedStack {
private LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
// 스택에 요소 추가
public void push(int item) {
list.addFirst(item);
System.out.println("Pushed: " + item);
}
// 스택에서 요소 제거 및 반환
public int pop() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
int poppedValue = list.removeFirst();
System.out.println("Popped: " + poppedValue);
return poppedValue;
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty. Cannot pop.");
return -1; // 스택이 비어있을 때는 임의의 값(-1) 반환
}
}
// 스택의 현재 최상단 요소 반환
public int peek() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
return list.getFirst();
} else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty.");
return -1; // 스택이 비어있을 때는 임의의 값(-1) 반환
}
}
// 스택이 비어있는지 여부 반환
public boolean isEmpty() {
return list.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 연결 리스트 기반 스택 생성
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack();
// 스택에 요소 추가
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
// 스택의 현재 최상단 요소 확인
System.out.println("Top element: " + stack.peek());
// 스택에서 요소 제거
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
// 스택이 비어있는지 여부 확인
System.out.println("Is stack empty? " + stack.isEmpty());
// 스택에 요소 추가
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
}
}
스택의 활용 예시
1. 실행취소
가장 최근에 실행한 명령어를 취소해야하기 때문에 스택구조가 효율적이다.
2. 재귀 알고리즘
함수가 호출될 때마다 호출된 함수의 정보(매개변수, 지역변수, 반환 주소 등)를 스택에 저장하고, 함수의 실행이 끝날 때 스택에서 해당 정보를 꺼내 복귀한다.
