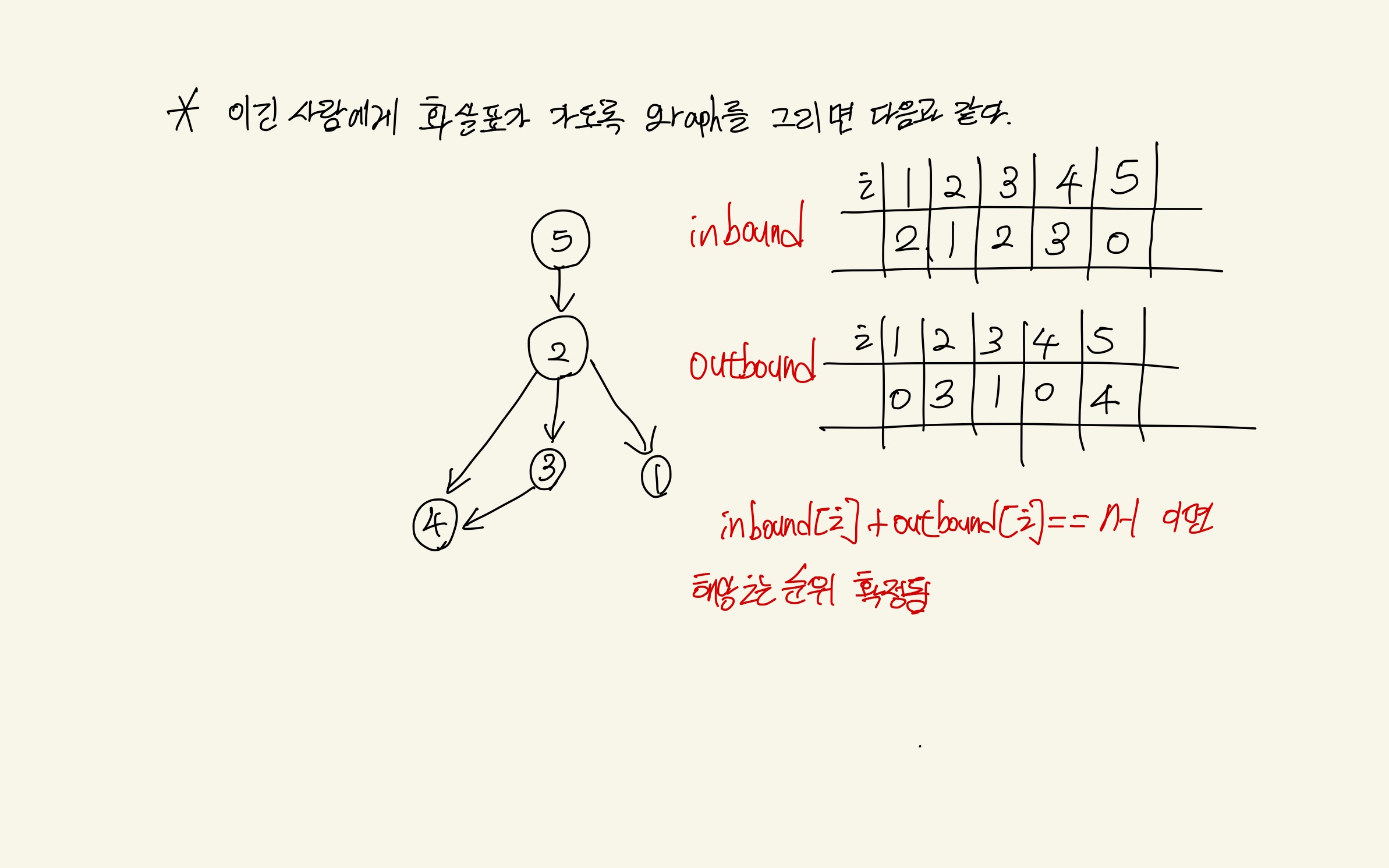
위 문제는 플로이드 와샬로도 풀이가 가능하지만 특정 노드의 inbound 와 outbound 개수를 파악해도 문제 풀이가 가능하다
이때, inbound 란 해당 노드로 올 수 있는 모든 노드의 개수이고 outbound 란 해당 노드에서 갈 수 있는 모든 노드 개수이다.
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static int[] inbound;
static int[] outbound;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] isVisited;
static int count;
public int solution(int n, int[][] results) {
// 그래프 초기화
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] result : results) {
int s = result[1];
int e = result[0];
graph.get(s).add(e);
}
// 매 정점마다 dfs
inbound = new int[n+1];
outbound = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<n+1; i++) {
isVisited = new boolean[n+1];
count = 0;
dfs(i);
outbound[i] = count;
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i=1; i<n+1; i++) {
if(inbound[i] + outbound[i] == n-1) answer++;
}
return answer;
}
public static void dfs(int start) {
// 체크인
isVisited[start] = true;
// 연결된 곳 순회
for(int next : graph.get(start)) {
// 갈 수 있는가?
if(!isVisited[next]) {
dfs(next);
inbound[next]++;
count++;
}
}
}
}