1) Malware 9 types
Rootkits
IoT Malware
ICS Malware
Trojan
Ransomware
Mobile Malware
Virus
Worm
Exploit Kits
2) Design paradigms
- Encryption with the Decryption (기본 암호학의 성질 & 구조)
encryption이랑 decryption은 기본 inverse로 private key와 중간의 generator key를 안다는 가정하에 그냥 풀림
-
Oligomorphism & Polymorphism
Oligomorphism → n possible way of decrypts , it means that thousand of sample might introduce the detection of virus.
Polymorphism → Whenever create in the machine and recreate or change the file code, the whole system just becomes totally different one. It allows hard to detect the virus. -
Metamorphism
Different body shapes, Pattern detection X work
Heuristic detection or algorithm detection -
Rootkit
Embedded system and keep the stealthy of malware code that can easily track for user to investigate which command or which files are running right now.
1) (Intercept any function call) → Main function of Rootkit.
2) With the true and false based function call, detect whether the user might recognize the malware code file or not. If yes, the Rootkit intercepts the result of function call and hide it. (Rootkit fileter가 하는 역할) -
Fileless Malware
residues in memory during the execution cycle without nay footprint int he file system. (Increase the stealthy) -
Large-Scale Software development model
Plugin-based framework, unique functionality of plugin provides the password stealing and stealthy with long persistence. -
Example) RAT(Remote Access Trojan)
(Infiltraiton methods) Pop-up system, Email
It works as the other system files and it is hard to detect it by using the memory-usage detection model, memory traffic detection model. (Remote control of access needs the large amount of data transfer that is recognized as an abnormal action)
3) APT attack Frameworks
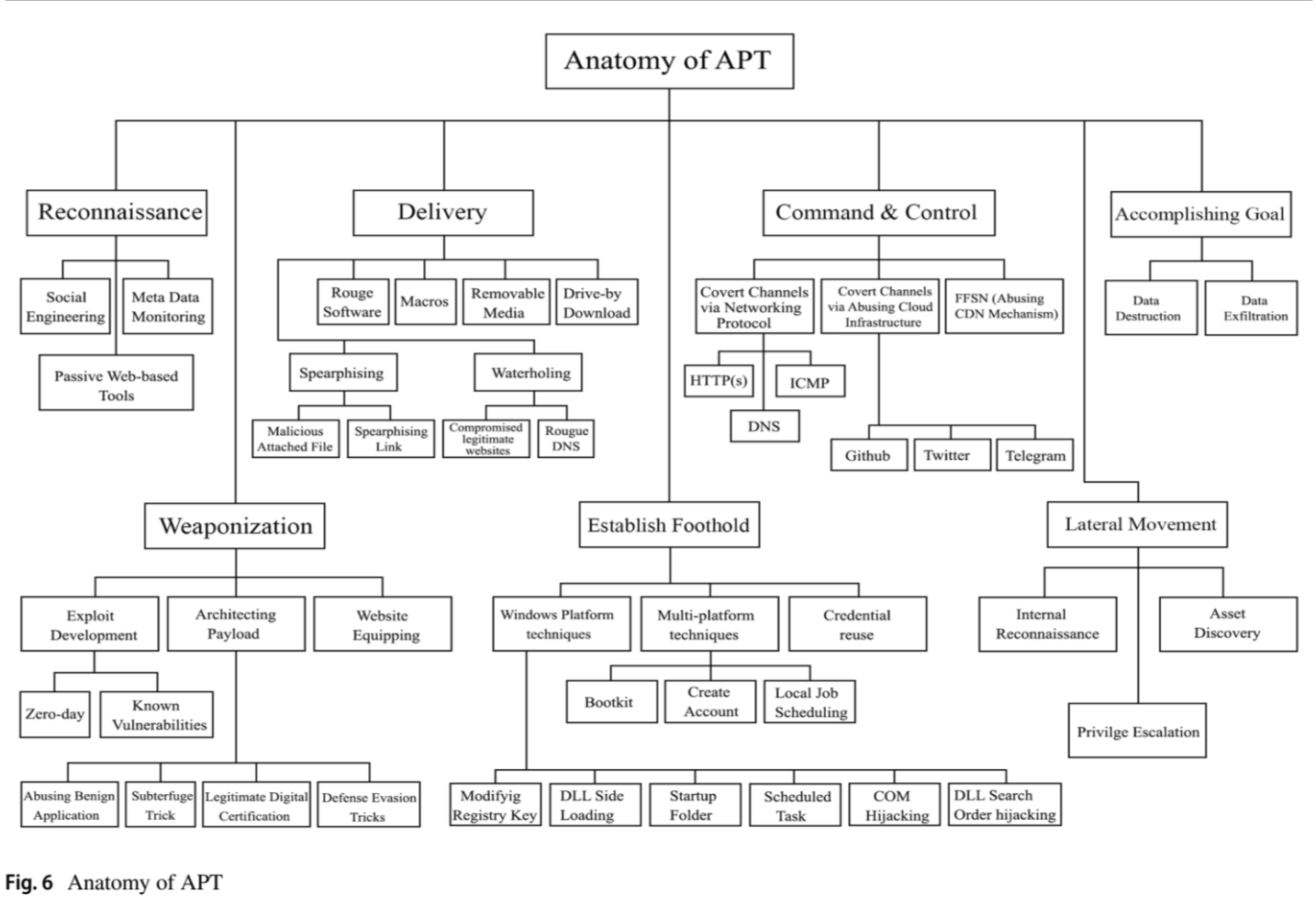
| Name of Phase | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Reconnaissance (정찰) | Familarize before the invasion of system | Social engineering, Passive reconnaissance, and meta-data monitoring |
- Social Engineering
- Human interaction (rely on human trust system) - Meta Data Monitoring
- Active recon technique - Passive reconnaissance
- Information from open-source
| Name of Phase | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Weaponization | create target specific malware | Exploit Component (Zero-day exploit, N-day exploit) , Payload Component (APT payloads); Stealth modules |
- Exploit Component
1) A zero-day exploit targets vulnerabilities that are unpatched or unknown to software developers
2) While an N-day exploit targets vulnerabilities that are already known
| Name of Phase | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery | delivers the weapon to target environment | Spear Phishing, Watering hole attack, Removable Media |
- Spear Phishing
1) sent to victim that intrigue target to open or click and allows the hackers to install the weapon in victim's system - Watering hole attack
1) gain access the third part network and wait the victim to access it → This infects all the visitors in the end - Removable Media
1) Air-gapped system, phsycial infecting method of activating malware code
| Name of Phase | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Establish Foothold | maintain persistence with payload, increase the access level of network |
| Name of Phase | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Command & Control | Communication channels, C&C server | DNS as C2, FFSN, Covert Channels |
- DNS as C2
- DNS route를 C2 channel로 사용. DNS 서버는 원래 존재
- FFSN
- The transformation of CDN; Content Delivery Network. CDN uses the cash server that is spread out the world and delivers the website content to nearest server and it allows user to speed up when they open the website with strong security.
- FFSN makes one of C2 servers to points out the several IP address to hide out the real C2 server. The IP address are already virused by attackers so it is hard to figure out which IP attacks the system.
- Convert Channels
1) Authoritaive name server을 hacking을 하면, DNS의 response들은 모두 attacking sign.
| Name of Phase | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Lateral Movement | maintain long-term access to the infrastrucutre(APT objective) |
| Name of Phase | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Accomplishing Goal | Data Exfiltration, Data destruction/ manipulation |
- Data Exfiltration
1) sensitive information (system → C2 server), internal server to external server encryption with SSL/TLS protocols to remain stealthy.
-
SSL protocol (Secure Socket Layer)
client-server handshake , key exchange of encryption RSA ecnrytion scheme.
Collision problem from the hashing function of same encryption key. -
TLS protocol (Transport Layer Security)
client-server handshake , key exchange of encryption RSA ecnrytion scheme.
Collision Resistant
TTP
- MITRE ATT & CK Model
1) The framework that categorizes the cyber threat (APT) in tactics, techniques, procedures.
Example of using neural network to investigate APT. (Rosenberg I, Sicard G, David EO (2017) Deepapt: nation-state apt attribution using end-to-end deep neural networks. In International Conference on Artifcial Neural Networks, pages 91–99. Springer) → 94.6% accuracy
Random Forest classifier
SVM classifier
Attack case studies
| Hacker Group Name | Group Explanation |
|---|---|
| APT38-Lazarus Group | North Korea |
| APT41- Double Dragon Group | China |
| Hidden Lynx | considered to be a China-based threat actor |
| WaterBug-Symantec | a notorious espionage group expert in conducting watering hole and spearphishing campaigns |
| APT 28 | attributed to Russian and is responsible for interfering with the United States presidential election |
| Oilrig-Palo Alto | attributed to Iran state-sponsored group, leveraged the trust relationship between organizations and performed supply chain attacks on their primary targets |
| Transparent Tribe-Proofpoint | Pakistan, maliciuos spearphishing email and Remote Access Trojan (RAT) |
| Ke3chang -FireEye | North Korea |
| APT38-Lazarus Group | suspect as a China group |
| BlackOasis-Kaspersky | Middle Eastern, Gamma Group is the client of hacking |
| FIN6-FireEye | stealing payment card data and POS system, trade on the dark web |
| Tick-Symantec | spearphishing emails |
| APT1 | China |
| Sandworm Team-Trend | a Russian cyberespionage group, sabotage and destruction |
Malware Detection Based Approach
1) Static Analysis
- Examined without execution of the malware code
- Basic static analysis
- Static code analysis
2) Dynamic Analysis
- Running malware code in air gapped system
3) Hybrid
- patch the binary with static and extract behavior with dynamic
1) Memory Forensics
- Memory payload
1) Negative Day Malware Alert
-
Signature based detection
- prone to detect meta-morphic and poly-morphic malware and APT malware because of the primitive nature of signature, which can be evaded easily
1) Dyanamic , collect the information and exhibits the program's behavioral pattern
2) Static , PUI to IR and compare PUI and CFG. If both have common def, it is malicious, if not normal.
3) Hybrid -
Behavior based detection (Anomaly detectors)
1) Anomaly based detection
- observes the behavior of PUI along with the host’s behavior
- Dynamic Anomaly based detection
System call frequency - Static Anomaly based detection
File structure characteristics under inspection - Hybrid Anomaly based detection
- inside-the-box approach
- outside-the-box approach
2) Specifcation Based Detection
- Dynamic Anomaly based detection
- estimates the requirement of the application
- Dynamic Specifcation-based detection
- Observe the behavior of runtime/execution for implementation
- Example)
- Trace Rule
- DIFA, a pattern of system method calls
- Stack Smashing attacks of LIFO(Last-In-First-Out), Similar to the buffer overflow problem. This happens when all the space of buffer filled in and there is no more space. Then, the new data memory will cover up to the memory that is already spaced in. This might be the key point of malware as the attackers might redirect the position of that space and convert it as their space. They can take out the sensitive data from the user. The Secure Return Address Stack (SRAS) is solution for stack memory consistency.
- Observe the behavior of runtime/execution for implementation
- Static Specifcation-based Detection
- Dynamic Specifcation-based detection
- Machine learning
- ANN classifier → describe the maliciousness from the accumulated record sample test set
- Q-learning based defense scheme
- Find the best decision making, (The maximum Rewards based on the action)
- Genetic Algorithm based approaches
- used for generating clusters of the malware and produce a lineage graph
- Game Theory based approaches
- Stackelberg game
- The defender sets the finitie source to defense the system
- The attacker investigates the defense strategy and select the attack route
- This game shows the optimal defense strategy considering the expected attacking strategies
- Stackelberg game
Monitoring Based Approach
- DNS logs and events that communicates with the C2 server (C&C)
Moving Target Defense Based Approach
- IP address randomly change, target IP hide from the attacker
Attack Graph Based Approach
- A cost model that describes the impact of each action
- Analyze the attack graph