State
State는 컴포넌트의 내부에서 변경 가능한 데이터를 관리
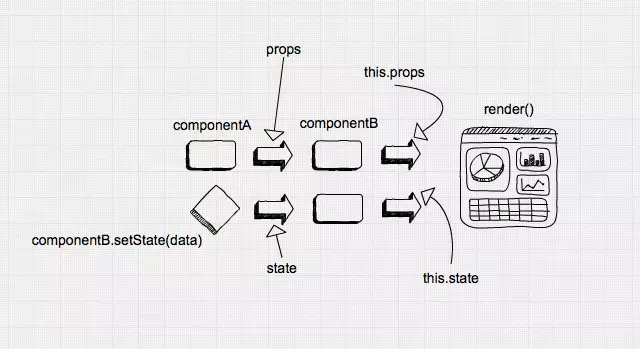
State는 컴포넌트의 내부에서 동적으로 데이터를 관리하기 위해 사용한다.
이전 포스팅에서 설명했던 Props는 컴포넌트 내부에서 값을 바꿀 수 없기 때문에 정적으로 데이터를 관리했다.
그래서 이러한 단점을 해결하기 위해 State를 사용하여 값을 저장하거나 변경이 불가능한 객체를 이벤트와 함께 사용하여 동적으로 데이터의 값을 변경한다.
Props와 State의 가장 큰 차이점은 Props는 함수의 매개변수처럼 컴포넌트에 전달되고 State는 함수 내에 선언된 변수처럼 컴포넌트 안에서 관리된다는 점이다.
Class Components에 로컬 State 추가
아래 코드는 Props를 통해 다음과 같은 화면을 출력한다.
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
class PrintFruit extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Delicious!! {this.props.date}.</h1>
<button>Change Fruit</button>
</div>
);
}
}
function tick() {
root.render(<PrintFruit date='apple' />);
}
tick();
다음과 같은 순서로 위 클래스 컴포넌트에 State를 추가하여 동적으로 데이터를 변경할 수 있다.
render()메서드 안에 있는this.props.date를this.state.date로 변경한다.
class PrintFruit extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Delicious!! {this.state.date}.</h1>
<button>Change Fruit</button>
</div>
);
}
}- 클래스에
생성자(constructor)를 추가하여 초기this.state를 지정한다.
class PrintFruit extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props); // 클래스 컴포넌트는 항상 props로 기본 constructor를 호출
this.state = {date: 'apple'};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Delicious!! {this.state.date}.</h1>
<button>Change Fruit</button>
</div>
);
}
}<PrintFruit />요소에서 date prop을 삭제한다.
ReactDOM.render(
<PrintFruit />,
document.getElementById('root')
);State를 추가하여 수정한 코드의 결과는 다음과 같이 동일한 것을 확인할 수 있다.

setState
setState()메서드는 로컬 state의 값을 업데이트할 때 사용한다.
state값이 업데이트되면 클래스 컴포넌트에서는 코드전체가 아닌 render() 함수만 재실행된다는 점을 주의해야한다.
또한 setState() 함수가 연달아 실행되면 그때마다 실행되는 것이 아닌 실행된 setState() 함수를 모아서 한번에 랜더링한다.
아래 코드는 해당 메서드를 통해 버튼을 클릭하면 state값을 변경하여 화면에 출력한다.
class PrintFruit extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: 'apple'};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Delicious!! {this.state.date}.</h1>
<button onClick= {() => { this.setState({ date: 'banana' })}}>Change Fruit</button>
</div>
);
}
}

prevState
prevState()메서드는 이전의 state값을 참조하여 새로운 state를 생성한다.
prevState는 setState에 매개변수로 할당되고 그 안에서 새로운 state를 return하여 사용한다.
class PrintFruit extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: 'apple'};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Delicious!! {this.state.date}.</h1>
<button onClick= {() => {
this.setState((prevState) => {
return {
// prevState에는 이전 state인 apple이 할당
data: prevState.data + 'and Banana'
}})}>
Change Fruit
</button>
</div>
);
}
}Lifecycle
Lifecycle은React에서 특정 상황에 발생하는 이벤트를 의미
React에서 컴포넌트가 실행, 업데이트 또는 제거될 때, 특정한 이벤트들이 발생하는데 이를 컴포넌트 생명 주기 또는 라이프사이클(Life cycle)이라고 표현한다.
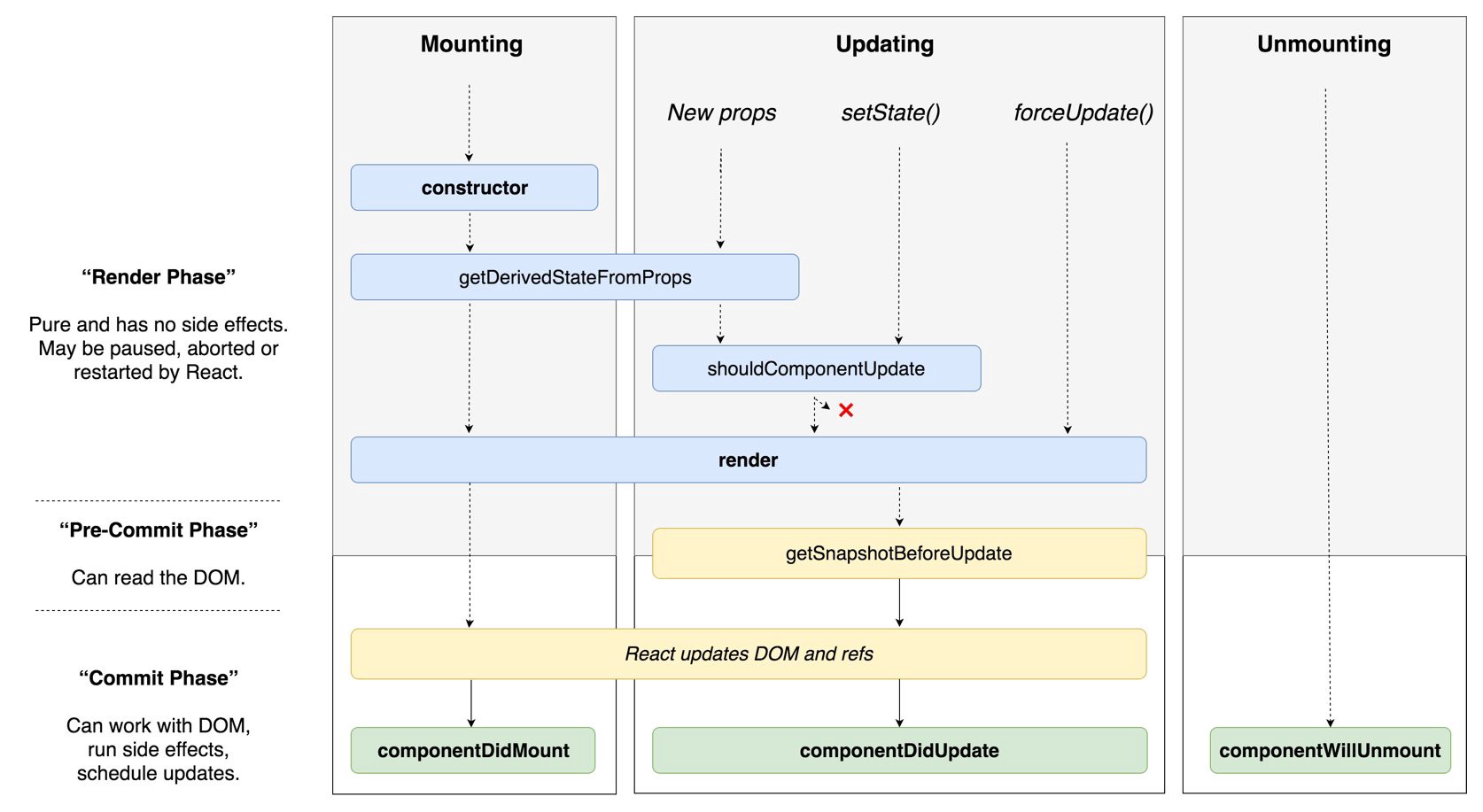
또한 각각의 컴포넌트 생명 주기 상황에서 특별한 메서드를 선언하여 특정 상황이 될 때 일부 코드를 실행할 수 있는데 이를 “생명주기 메서드”라고 불른다.
생명주기 메서드의 종류는 다음과 같다.
componentDidMount
componentDidMount() 메서드는 render() 함수가 처음 실행되고 정상적으로 실행된 후 동작한다.
주로 비동기 요청을 할때 사용되며 state, props의 변화로 render() 함수가 재실행될때는 componentDidMount()는 실행되지 않는다.
즉 처음 render() 함수가 실행될때만 동작하는 메서드이다.
componentDidMount() {
this.runTimeouts = setInterval(
() => this.second(),
1000
);
}componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount() 메서드는 컴포넌트가 제거되기 직전에 실행된다.
주로 componentDidMount()에서 요청한 비동기 처리를 제거하는 용도로 사용되므로 componentDidMount와 짝을 이룬다.
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.runTimeouts);
}componentDidUpdate
componentDidUpdate() 메서드는 render() 함수가 재실행 즉 state, props가 변경되어 랜더함수를 재실행할 때 실행된다.
componentDidUpdate() 메서드는 prevProps, prevState 두 가지 인자를 통해 바뀌기 전과 후의 state값을 참조할 수 있다.
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (this.prevState.num === 1) {
this.runTimeouts();
}
}
