ConcurrentHashMap이란?
ConcurrentHashMap은 Java 1.5 버전에서 HashTable의 대안으로 처음 소개된 Collection이다.
ConcurrentHashMap이 나오기전까진 multi-thread에서 map을 thread-safe하게 운용하기 위해선 method/block lock을 통해 감싸주던지 HashTable 또는 synchronized map을 사용해야 했다.
하지만, HashTable/synchronized map의 경우 Map 전체에 lock을 걸어 운용하고 있기 때문에 thread-safe 하지만, 성능 오버헤드를 발생시킨다. 하나의 Thread가 lock을 유지하는 동안 다른 모든 Thread는 해당 Map Collection을 사용할 수 없기 때문이다.
그래서 Map의 일부에만 lock을 걸어 운용하는 ConcurrentHashMap이 등장했고 Thread-safe한 다른 Map Collection들 보다 성능 우위를 가질 수 있게 되었다.
그렇다면 ConcurrentHashMap은 어떤 방식으로 성능까지 고려한 Thread-safe 환경을 만들었는지 간략히 살펴보도록 하자.
ConcurrentHashMap 동작 원리
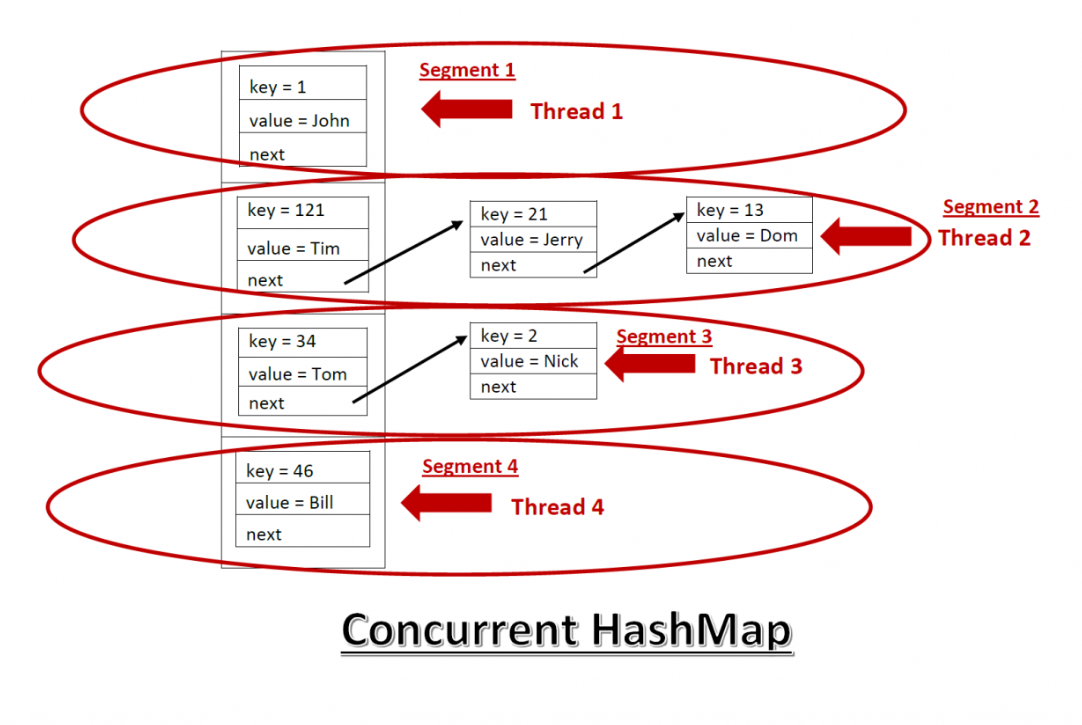
(1) HashMap vs ConcurrentHashMap
우선 HashMap은 동기화 관련 코드가 없기에 Multi-thread 환경에서 사용한다면 다음과 같이 전체에 lock을 걸어야 한다.

하지만, ConcurrentHashMap은 각각의 Bucket 별로 동기화를 진행하기에 다른 Bucket에 속해있을 경우엔 별도의 lock없이 운용한다.
(2) put
Map에 원소를 넣는 put(key, value) 를 호출하면 ConcurrentHashMap 내부적으로 putVal(key, value, onlyIfAbsent)로 연결되는데 이에 대한 전체 소스 코드는 다음과 같다.
이 소스 코드를 대략적으로 살펴보면, method 전체에 synchronized 키워드가 선언되어 있진 않는 것을 볼 수 있다.
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, true);
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; K fk; V fv;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else if (onlyIfAbsent // check first node without acquiring lock
&& fh == hash
&& ((fk = f.key) == key || (fk != null && key.equals(fk)))
&& (fv = f.val) != null)
return fv;
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
else if (f instanceof ReservationNode)
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive update");
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}이제 하나 하나씩 뜯어서 살펴보도록 하자.
2-1) 빈 Hash Bucket에 노드를 삽입하는 경우 Compare and Swap을 이용하여 lock을 사용하지 않고 새로운 Node를 Hash Bucket에 삽입한다.
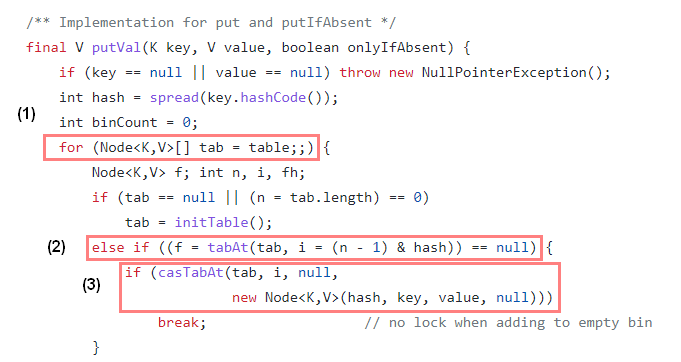
(1) table은 ConcurrentHashMap에서 내부적으로 관리하는 Node의 가변 Array이며, 무한 loop를 통해 삽입될 bucket를 확인한다.
(2) 새로운 Node를 삽입하기 위해, tabAt()을 통해 해당 bucket을 가져오고 bucket == null로 비어 있는지 확인한다.
(3) bucket이 비어 있는 경우 casTabAt()을 통해 Node를 담고 있는 volatile 변수에 접근하고 Node와 기대값 null 을 비교하여 같으면 Node를 생성해 넣고, 아니면 (1)번으로 돌아가 재시도 한다.
그리고 tabAt() 과 casTabAt() 은 다음과 같고 직접 memory를 Handling 하는 UnSafe 를 이용하고 있다.
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>) U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long) i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long) i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
static {
try {
U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
...
}
} 2-2) 이미 Bucket에 Node가 존재 하는 경우 synchronized를 이용해 하나의 thread만 접근할 수 있도록 제어하며, 서로 다른 thread가 같은 Hash Bucket에 접근할 때만 해당 block이 잠기게 된다.

(1) f는 비어있지 않은 Node<K,V> type의 hash bucket을 의미하고 이것을 통해 동기화를 한다.
(2) 같은 Key 값이 들어올 경우 새로운 Node로 교체하고, putIfAbsent(key, value) 일 경우엔 값을 변경하지 않는다.
(3) Hash type fh 값이 양수이고 Hash 충돌일 경우엔 Seperate Chaining에 추가한다.
(4) Hash type fh 값이 음수일 경우엔 Tree에 추가한다.
(5) Hash bucket의 수 binCount에 따라 Linked List로 운용할지 Tree로 운용할지 정한다.
특히, (3), (4)에선 Separate Chaining에 추가 하거나 Tree에 추가하는 것을 알 수 있는데 이는 HashMap의 내부 구현과 같으며
- bucket의 크기가
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8값보다 큰 경우 Linked List 대신 Tree로 운용하는 조건이 만족된다. - bucket의 크기가
UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6보다 작아지면 Tree 대신 다시 Linked List로 운용된다.
[Hash Type]
/*
* Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
*/
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
[Bucket Threshold]
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2, and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
[HashMap Tree Threshold]
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* The value should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid
* conflicts between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
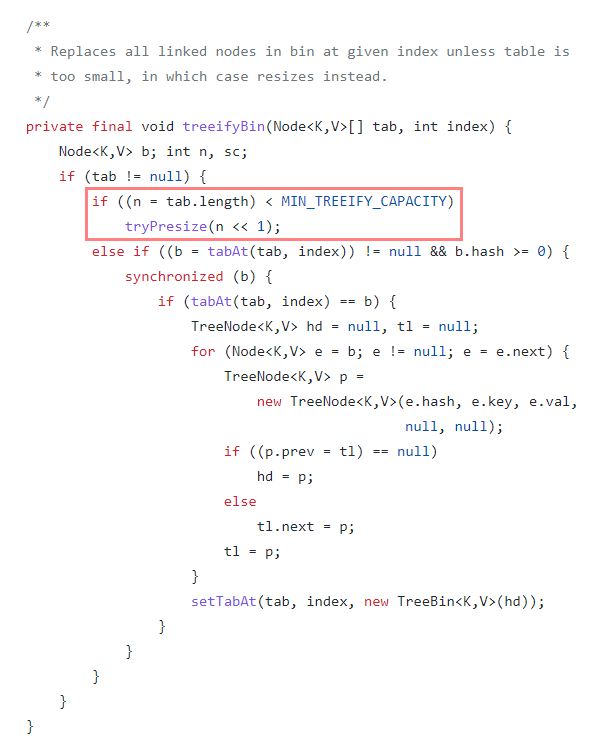
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;여기서 좀 더 자세히 들어가면, bucket의 수가 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8 일 경우 treeifyBin()을 통해 Tree 구조로 변경되는 것을 봤다.
하지만, treeifyBin()의 내부 구현을 보면 아래와 같이 hashMap 전체 크기가 MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64 미만일 경우엔 tree 대신 HashMap만 n << 1로 2의 거듭제곱만큼 resize만 한다는 것을 알게되었다.
즉, bucket의 수가 8이 넘더라도 전체 HashMap 크기가 64가 넘지 않는다면, Tree 구조로 변경되지 않는다.
(3) get
ConcurrentHashMap에서의 get을 살펴보면, synchroized keyword를 발견할 수 없다는 것을 알 수 있다. 즉, get은 가장 최신의 value 값을 return한다.
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}(4) ConcurrentHashMap 생성자
ConcurrentHashMap는 총 5개 생성자를 가지고 있다.
그 중 default 생성자의 주석을 보면 초기 table size는 16으로 이루어져 있다는 것을 알수 있는데 이는 bucket의 수가 16이고 16개의 thread가 동시 쓰기를 할 수 있다는 것을 의미한다.
그리고 생성자에서 직접 HashTable을 생성하지 않고 첫 Node가 삽입될 때 lazily initialized 된다는 것도 알 수 있다.
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}나머지 4개의 생성자를 살펴보면 생성자의 주요 파라미터는 3가지가 있다.
-
initialCapacity
초기 용량을 결정한다. 구현은 지정된 부하 계수가 주어지면 이 많은 요소를 수용하기 위해 내부 크기 조정을 수행한다. -
loadFactor
초기 hashTable의 크기를 설정하기 위한 용도로 쓰이며, 추후엔 ConcurrentHashMap에서는 이 인자 값과 상관 없이 0.75f로 동작한다.
ex) 초기 hashTable 크기가 16 이면 entry 수가 12개가 될 때 hashTable 사이즈를 16에서 32로 증가시킨다. -
concurrencyLevel
"동시에 업데이트를 수행하는 예상 스레드 수" 라고 주석에 적혀 있지만, 구현시 이 값은 단순히 초기 테이블 크기를 정하는데 힌트로만 사용된다.
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.
*
* @param m the map
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and
* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table
* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently
* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently
* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as
* a sizing hint.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is
* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are
* nonpositive
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}(5) ConcurrentHashMap의 entrySet(), keySet(), values()
내가 이번 포스팅을 하게 된 이유이다.....
ConcurrentHashMap은 다른 HashMap 종류와 달리 자체적인 entrySet(), keySet(), values()을 가지고 있다.
즉, entrySet()에서 remove()가 발생할 경우 CocurrentHashMap에 정의되있는 remove()가 수행되기 때문에 remove()로 인한 동기화 문제는 발생하지 않게된다.
/**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. The set supports element
* removal, which removes the corresponding mapping from the map,
* via the {@code Iterator.remove}, {@code Set.remove},
* {@code removeAll}, {@code retainAll}, and {@code clear}
* operations.
*
* <p>The view's iterators and spliterators are
* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.
*
* <p>The view's {@code spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#CONCURRENT},
* {@link Spliterator#DISTINCT}, and {@link Spliterator#NONNULL}.
*
* @return the set view
*/
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySetView<K,V> es;
return (es = entrySet) != null ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySetView<K,V>(this));
}
public KeySetView<K,V> keySet(V mappedValue) {
if (mappedValue == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new KeySetView<K,V>(this, mappedValue);
}
public Collection<V> values() {
ValuesView<K,V> vs;
return (vs = values) != null ? vs : (values = new ValuesView<K,V>(this));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
*/
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return value != null && replaceNode(key, null, value) != null;
}
==================================================================================
/**
* A view of a ConcurrentHashMap as a {@link Set} of (key, value)
* entries. This class cannot be directly instantiated. See
* {@link #entrySet()}.
*/
static final class EntrySetView<K,V> extends CollectionView<K,V,Map.Entry<K,V>>
implements Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
EntrySetView(ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> map) {
super(map);
}
...
public boolean remove(Object o) {
Object k, v; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
map.remove(k, v));
}
...마무리
ConcurrentHashMap은 각 Table bucket을 독립적으로 잠그는 방식이다.
빈 bucket으로의 노드 삽입은 lock 을 사용하지 않고 단순히 Compare And Swap 만을 이용하고
그 외의 업데이트(삽입, 삭제 및 교체)는 lock을 이용하지만 각 bucket의 첫 번째 Node를 기준으로 부분적인 잠금을 획득하여 thread 경합을 최소화 하고 안전한 업데이트를 한다.
ref)
https://github.com/frohoff/jdk8u-jdk/blob/master/src/share/classes/java/util/concurrent/ConcurrentHashMap.java
https://pplenty.tistory.com/17
http://daplus.net/java-hashmap-java-8-%EA%B5%AC%ED%98%84/