클래스와 객체
- 클래스 : 객체 모양을 선언한 틀
- 객체 : 클래스의 설계대로 생성된 실체(instance)
⏹ 생성자
- 객체가 생성될 때 필드들의 초기화를 위해 실행되는 메소드
- 특징
- 클래스 이름과 동일
- new 를 통해 객체를 생성할 때만 호출
- 생성자도 오버로딩 가능
- 생성자는 리턴 타입을 지정할 수 없다. (void 쓰면 안됨)
- 생성자는 하나 이상 선언되어야함
- 기본 생성자
- 클래스에 생성자가 하나도 선언되지 않을 경우만, 컴파일러에 의해 자동으로 기본 생성자가 생성됨
- 초기화를 하지 않아도 해당 데이터 타입에 맞는 특정 값을 그 생성자가 받는 값으로 자동 초기화 해준다.
⏹ this : 참조(레퍼런스)
- 객체 자신에 대한 레퍼런스
- 컴파일러에 의해 자동 관리
- this.멤버 형태로 멤버 사용
- this 의 필요성
- 객체의 멤버 변수와 메소드 변수의 이름이 같은 경우
- 다른 메소드 호출 시 객체 자신의 레퍼런스를 전달할 때
- 메소드가 객체 자신의 레퍼런스를 반환할 때
- this 가 있을 떄
// 매개변수와 멤버함수가 이름이 같을때 this 가 없으면 구별할 수 없다. 따라서 this 를 사용하여 // 매개변수의 radius 값을 현재 활성화 된 인스턴스(객체) 자신에 대한 레퍼런스인 // this 의 radius 로 값을 할당시켜준다. public class Circle { int radius; public Circle(int radius) { //생성자 this.radius = radius; } // 매개변수와 멤버함수가 이름이 같을때 this 가 없으면 구별할 수 없다. public void set(int radius) { this.radius = radius; //현재 활성화된 인스턴스 } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //객체 생성 Circle ob1 = new Circle(1); Circle ob2 = new Circle(2); System.out.println("ob1 : " + ob1.radius); //객체의 필드를 초기화하기 위해 set 메소드 호출 ob1.set(4); // -> ob1.set(ob1, 4) 로 변환이 됨. -> ob1 을 this 로 접근할수있도록 생성이 된다. ob2.set(5); System.out.println("ob1 : " + ob1.radius); } } //reuslt //ob1 : 1 //ob1 : 4 - this 가 없을 때
// 결과값이 0이 나오는 이유? // ob1 이라는 참조변수가 Circle 메모리 영역에 대한 정보를 가지고 있는데 // this 가 없기 때문에, 객체 자신인 ob1 의 radius 를 1로 업데이트 시켜주지 못한다. // 따라서, 지역변수이자 매개변수인 int radius 로 멤버변수인 radius 를 1로 업데이트 시켜주는 것이고 // 다시 멤버 변수 radius 는 기본 생성자에 의해서 다시 0 으로 초기화 되기 떄문에 모두 0으로 출력되는 것이다. public class Circle { int radius; public Circle(int radius) { radius = radius; } public void set(int radius) { radius = radius; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Circle ob1 = new Circle(1); Circle ob2 = new Circle(2); System.out.println("ob1 : " + ob1.radius); ob1.set(4); ob2.set(5); System.out.println("ob1 : " + ob1.radius); } } //result //ob1 : 0 //ob2 : 0
⏹ this() : 메소드
- this() 로 클래스 내 다른 생성자 호출하는 특별한 메소드
- 생성자 내에서만 사용 가능
- 반드시 생성자 코드의 제일 처음에 수행
public class Modi_Book { String title; String author; void show() {System.out.println(title + ", " + author);} //show 함수는 메개변수가 없기 떄문에 굳이 this.title 이라고 쓰지 않고 생략해도 됨. public Modi_Book() { this("None"); //this() 라는 메소드 사용 -> 매개변수 하나짜리 생성자 호출 System.out.println("Contstructor is called"); } public Modi_Book(String title) { //멤버하고 똑같기 때문에 정확하게 구분하기 위해 this 로 멤버변수와 매개변수 구분 this(title, "The author is unknown"); // 매개변수 2개 짜리 생성자 호출 } public Modi_Book(String title, String author) { //title, author라는 멤버변수가 매개변수의 이름과 똑같음 따라서 this 사용 this.title = title; this.author = author; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Modi_Book littlePrince = new Modi_Book("The Little Prince", "Saint-Exupery"); //객체 생성시 초기값 2개 제공 -> 인자 2개 짜리 생성자 호출 Modi_Book loveStory = new Modi_Book("Chunhyang-jeon"); //객체 생성시 초기값 1개 제공 -> 인자 1개 짜리 생성자 호출 Modi_Book emptyBook = new Modi_Book(); //객체 생성시 초기값 제공x -> 기본 생성자 호출 //emptyBook.show(); loveStory.show(); //show 함수는 메개변수가 없기 떄문에 굳이 this,title 이라고 쓰지 않고 생략해도 됨. } } //result //Contstructor is called //Chunhyang-jeon, The author is unknown
⏹ 객체의 치환
- 객체의 치환은 객체가 복사되는 것이 아니며 참조값을 복사하는 것이다.
//ob2 라고 하는 객체의 참조값이 ob1 과 s 라는 참조변수에게 복사되어 //ob1, s 모두 radius=2 로 설정된 객체의 메모리 영역에 접근할 수 있다. public class Circle { int radius; public Circle(int radius) { this.radius = radius; } public void set(int radius) { this.radius = radius; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Circle ob1 = new Circle(1); Circle ob2 = new Circle(2); //Circle ob3 = new Circle(3); Circle s; //참조변수만 선언 s = ob2; ob1 = ob2; //객체 치환 System.out.println("ob1 radius: " + ob1.radius); //ob1.set(4); //ob2.set(5); //ob3.set(6); System.out.println("ob2 radius: " + ob2.radius); } } //result //ob1 radius: 2 //ob2 radius: 2
⏹ 객체 배열
-
배열 관리를 위한 레퍼런스 선언
-
해당 레퍼런스에 동적 배열 공간 5개를 연결 시킨다.
class Circle{ int radius; public Circle(int radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getArea() { return 3.14*radius*radius; } } public class CircleArray {] public static void main(String[] args) { Circle [] c; //Circle 배열에 대한 레퍼런스 변수 c 선언 c = new Circle[5]; //크기가 5인 레퍼런스 배열 생성 for(int i=0; i<c.length; i++) //c.length 는 배열 c의 크기로서 5 c[i] = new Circle(i); //초기값 i 를 가진 배열의 각 원소 객체 5개 생성 for(int i=0; i<c.length; i++) // 배열에 있는 모든 Circle 객체의 면적 출력 System.out.print((int)(c[i].getArea() + " ")) // 배열의 원소 객체 사용 } } //result //0 3 12 ...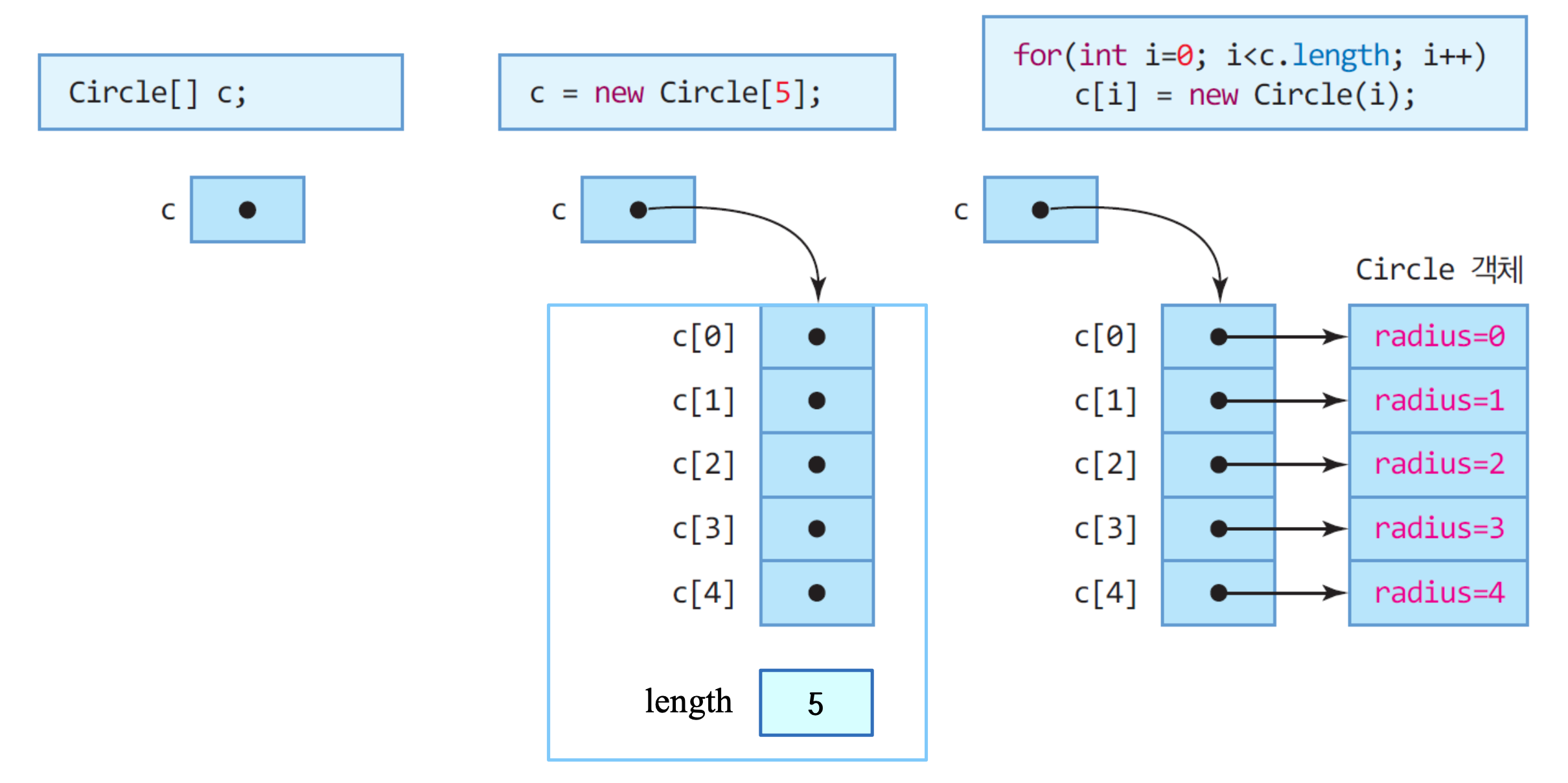
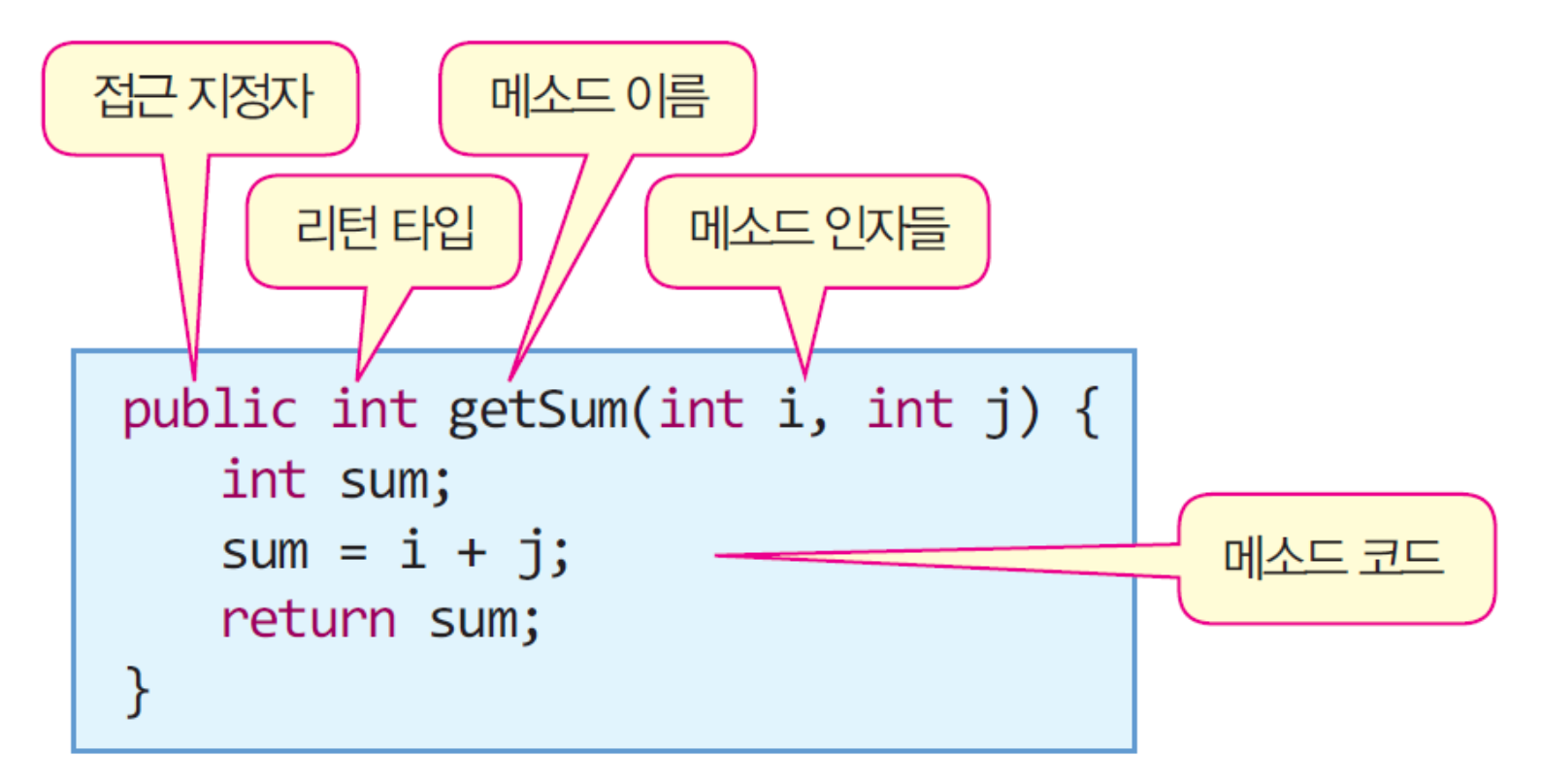
⏹ 메소드 형식
- 메소드 - 모든 메소드는 반드시 클래스 안에 있어야 함(캡슐화의 원칙)
자바의 인자 전달 방식
⏹ Call by value
: 기본 타입의 값 전달하는 경우
- 호출자가 건네는 값이 매개변수에 복사되어 전달
- 매개 변수 값이 변경되어도 호출한 실 인자 값은 변경되지 않는다.
인자 전달 : 기본 타입의 값이 전달되는 경우
int n=10; static void increase(int m) { increase(n); ---> m = m + 1; //increase 함수를 호출! }호출을 통해 관련 메소드로 가 m 이라는 공간에 n = 10 이라는 실 인자의 값을 건네어 리턴값 명시 없이 되돌아오더라도 increase 함수의 매개변수 m = 10 으로 복사만 할뿐 n = 10 은 변하지 않는다.
⏹ Call by reference
: 객체 혹은 배열을 전달하는 경우
- 객체나 배열의 레퍼런스(참조값 해시코드) 만 전달
- 갹체 혹은 배열이 통쨰로 복사되어 전달 되는 것이 아닌 참조 변수에 할당된 '해시코드' 가 전달됨
- 메소드의 매개변수와 호출한 실제 인지가 서로 객체 혹은 배열을 공유한다.
인자 전달 : 객체가 전달 되는 경우
CIrcle pizza = new Circle(10); static void increase(Circle m) { increase(pizza); ---> m.radius++; }pizza 라는 참조 변수로 관리하는 Circle 이라는 동적 메모리 영역의 radius = 10 을 참조에 의한 호출과 m 객체의 접근으로 radius = 11 으로 업데이트 해주었다. 같은 참조값을 사용하여 같은 메모리 영역에 접근하기 떄문에 radius 값 공유
인자 전달 : 배열이 전달되는 경우
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; static void increase(int[] array) { ---> for (int i=0; i<array.length; i++) { increase(a); array[i]++; } }배열 레퍼런스만 매개 변수에 전달
배열의 해시코드를 가지는 참조변수 a 로 increase(a) 를 참조의 의한 호출을 하고 a 의 참조값을 int[] array 가 받는다면 같은 메모리 공간을 가리키기 떄문에 정보 업데이트가 가능하다.
- 배열 통쨰로 전달되지 않음
- 객체가 전달되는 경우와 동일
- 매개변수가 실제 인자의 배열을 공유
인자로 배열이 전달되는 예
public class ArrayParameter { static void replaceSpace(char a[]) { //c의 해시코드 값을 a로 받는다 for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) if(a[i] == ' ') //스페이스바 인지 확인 a[i] = ','; //그 공간의 정보를 쉼표로 바꾸기 } static void printCharArray(char a[]) { //c의 해시코드 값을 a로 받는다 // c는 배열의 해시값인데 이것을 참조변수 a가 받아 배열 하나하나 접근 for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) System.out.print(a[i]); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub char c[] = {'T','h','i','s',' ','i','s',' ','a',' ','p','e','n','c','i','l','.'}; printCharArray(c); //c를 인자로 제공 replaceSpace(c); //c를 인자로 제공 printCharArray(c); //쉼표로 바뀐 정보를 다시 출력 } } //result //This is a pencil. //This,is,a,pencil.
메소드 오버로딩
⏹ 오버로딩
-
이름이 똑같은 함수가 있는데 제공되는 정보가 2개 3개에 따라 구분이 가능한 것을 메소드 오버로딩이라고 한다.
-
함수의 리턴 데이터 타입은 오버로딩과 무관하다.
//메소드 오버로딩이 성공한 사례 class MethodOverloading { public int getSum(int i, int j) { //정수 2개 return i+j; } public int getSum(int i, int j, int k) { //정수 3개 return i+j+k; } } //메소드 오버로딩이 실패한 사례 class MethodOverloadingFail { public int getSum(int i, int j) { return i + j; } public double getSum(int i, int j) { //오버로딩을 하기 위해서 매개변수의 타입을 double i, double j 로 수정해야함. return (double)(i + j); } } //두 개의 getSum() 메소드는 매개변수의 개수와 타입이 같기 떄문에 오버로딩 실패
객체의 소멸과 가비지
⏹ 객체 소멸
- 객체 소멸 : 객체 메모리를 JVM 의 가용메모리로 돌려주는 행위
- 소멸된 객체 공간은 가용 메모리에 포함
- new 에 의해 생성된 객체 메모리 해지를 JVM 이 적당한 시점에서 자동으로 해준다
⏹ 가비지
- 가리키는 레퍼런스가 하나도 없는 객체
- 누구도 사용할 수 없게 된 메모리
- 가비지 컬렉션
- 자바 가상 기계의 가비지 컬렉터가 자동으로 가비지 수집 반환
- 개발자에 의한 강제 가비지 컬렉션
- System 또는 Runtime 객체의 gc() 메소드 호출
System.gc();
- System 또는 Runtime 객체의 gc() 메소드 호출
- 다음 소스에서 언제 가비지가 발생하는지
public class GarbageEx { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = new String("Good"); String b = new String("Bad"); String c = new String("Normal"); String d,e; a = null; d = c; c = null; } }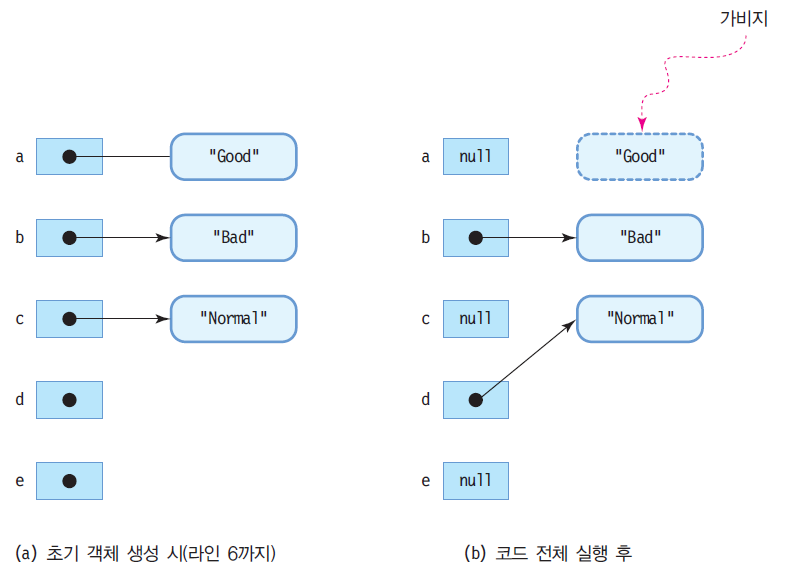
⏹ 접근 지정자
- 자바의 접근 지정자
- 4가지 : private, protected, public, default
- 접근 지정자의 목적
- 클래스나 일부 멤버를 공개하여 다른 클래스에서 접근할도록 허용
- 객체 지향 언어의 캡슐화 정책은 멤버를 보호하는 것
- 접근 지정은 캡슐화에 묶인 보호를 일부 해제할 목적
- 접근 지정자에 따른 클래스나 멤버 공개 범위
⏹ 클래스 접근 지정자
- 클래스 접근 지정
- 다른 클래스에서 사용하도록 허용할지 지정
- public 클래스
- 다른 모든 클래스에게 접근 허용
- 디폴트 클래스(접근 지정자 생략)
- package-private 이라고도 함
- 같은 패키지의 클래스에만 접근 허용
⏹ 멤버 접근 지정
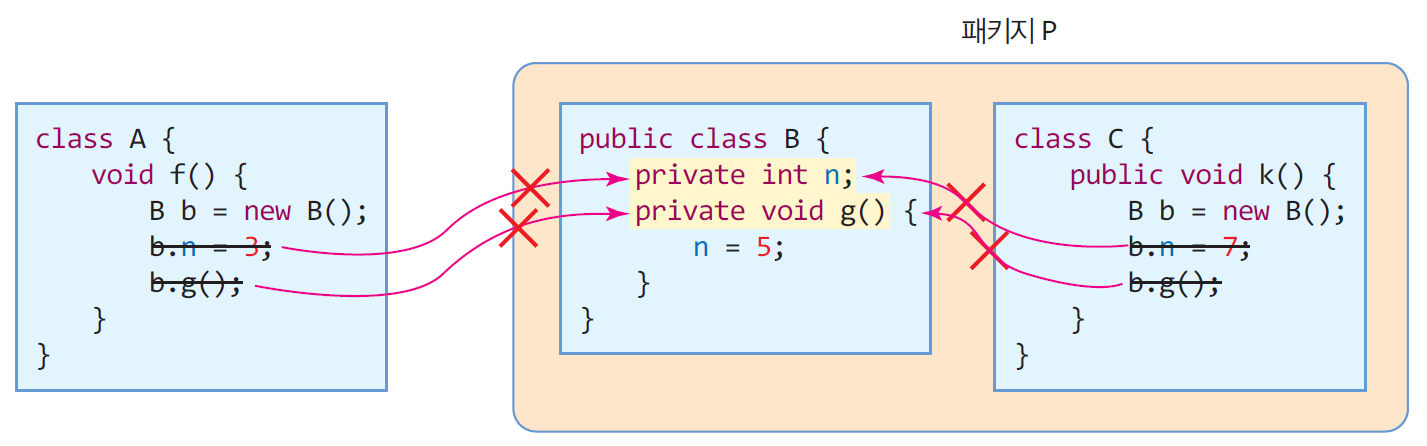
- public 멤버
- 패키지에 관계 없이 모든 클래스에게 접근 허용
- private 멤버
- 동일 클래스 내에만 접근 허용
- 상속 받은 서브 클래스에서 접근 불가
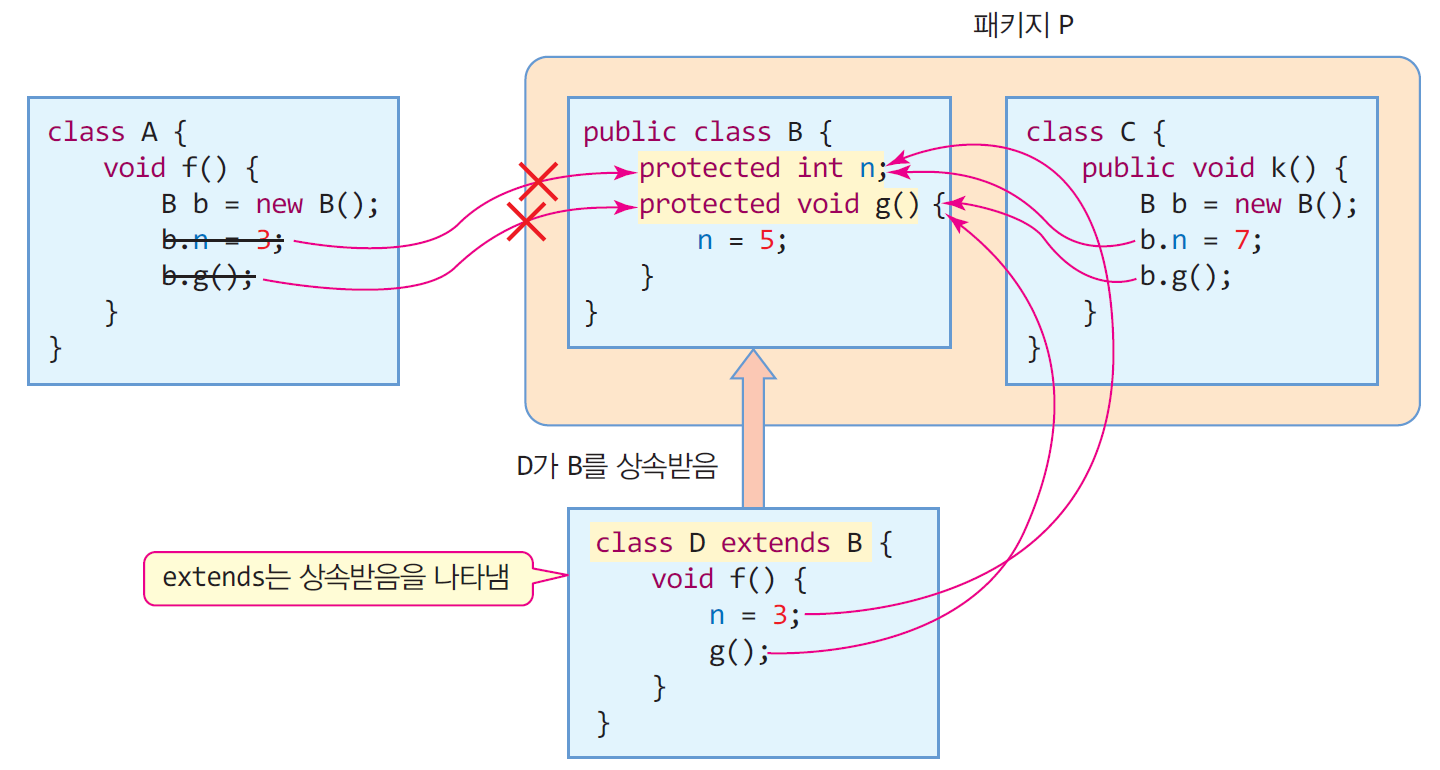
- protected 멤버 (자식, 동일 패키지)
- 같은 패키지 내의 다른 모든 클래스에게 접근 허용
- 상속 받은 서브 클래스는 다른 패키지에 있어도 접근 가능
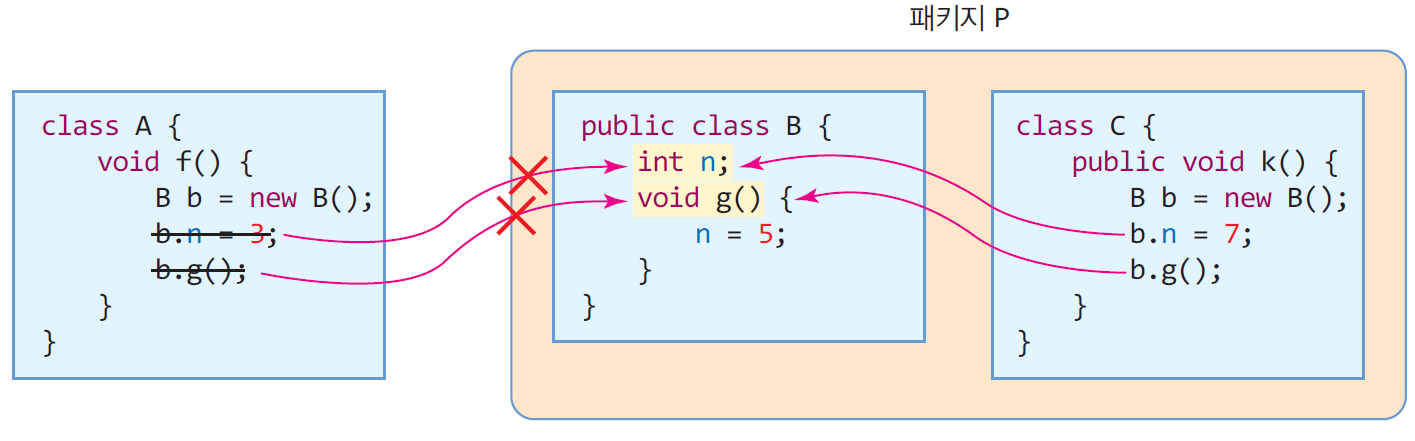
- default 멤버
- 같은 패키지 내의 다른 클래스에게만 접근 허용
-
멤버에 접근하는 클래스 private default protected public 같은 패키지의 클래스 다른 패키지의 클래스 접근 가능 영역 클래스 내 동일 패키지 내 동일 패키지와 자식 클래스 모든 클래스
- public 접근 지정 사례
- private 접근 지정 사례
- default 접근 지정 사례
- protected 접근 지정 사례
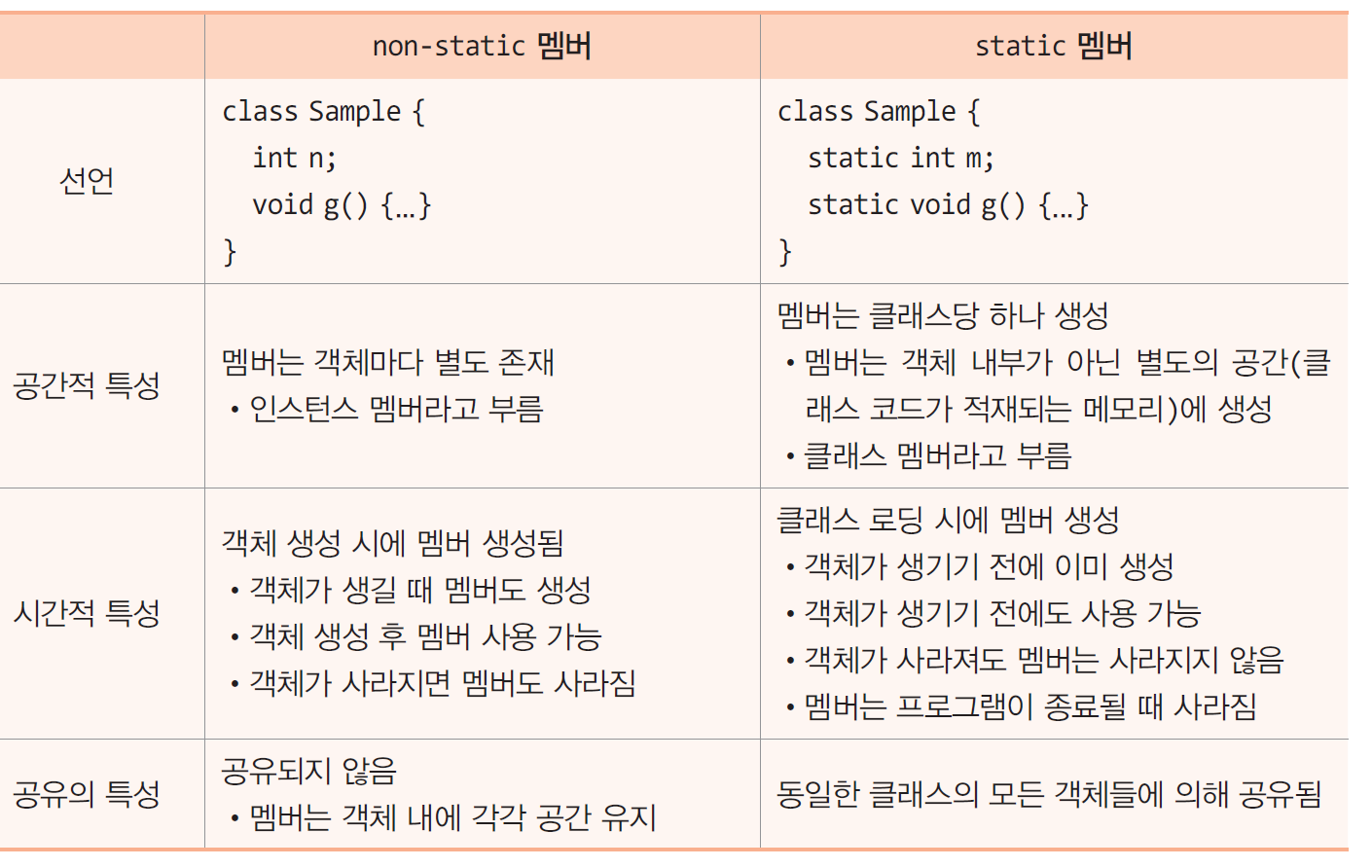
⏹ static 멤버와 non static 멤버
- non static 멤버의 특성
- 공간적 - 멤버들은 객체마다 독립적으로 별도 존재
- 인스턴스 멤버(인스턴스 변수, 인스턴스 메소드)라고도 부름
- 시간적 - 필드와 메소드는 객체 생성 후 비로소 사용 가능
- 비공유의 특성 - 멤버들은 여러 객체에 의해 공유되지 않고 베타적

- 공간적 - 멤버들은 객체마다 독립적으로 별도 존재
- static 멤버란?
- 객체를 생성하지 않고 사용 가능
- 객체 마다 생기는 것이 아님.
- 클래스당 하나만 생성됨
- 클래스 멤버라고도 부름
- 특성
- 공간적 특성 - static 멤버들은 클래스 당 하나만 생성
- 시간적 특성 - static 멤버들은 클래스가 로딩될 때 공간 할당
- 공유의 특성 - static 멤버들은 동일한 클래스의 몯느 객체에 의해 공유
- non-static 멤버와 static 멤버의 차이
⏹ static 실습
-
m 필드와 f 메소드는 static 공간에 미리 메모리 확보
class StaticSample { public int n; public static int m; public void g() { m = 20;} public void h() { m = 30;} public static void f() { m = 5; // n = 10; 오류가 난다 // -> nonstatic 이라고 선언한 n 이라는 변수의 공간을 찾을 수 없기 때문에 오류 } } public class Ex { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //<!-- static 멤버를 클래스의 이름으로 접근하는 사례 -->// System.out.println(StaticSample.m); //객체 생성 전 클래스 이름으로 static 멤버 접근 StaticSample.m = 10; //클래스 이름으로 static 멤버 접근 //<!-- static 멤버를 객체의 멤버로 접근하는 사례 -->// StaticSample s1; s1 = new StaticSample(); //m, f 는이미 공용으로 사용하는 static 공간에 있기 때문에 굳이 추가를 안해주고 //int n, g, h 등 non static 만 등록된다. s1.n = 5; s1.g(); // m = 20 업데이트 System.out.println(s1.m) s1.m = 50; //static 멤버를 객체의 멤버로 접근 System.out.println(s1.m) } } //result //0 //20 //50
⏹ static 활용
- 전역 변수와 전역 함수를 만들때 활용
- 전역 변수나 전역 함수는 static 으로 클래스에 작성
- static 멤버를 가진 클래스 사례
- Calc 클래스 : java.lang.Math
// 모든 필드와 메소드가 public static 으로 선언 // 다른 모든 클래스에 사용할 수 있음. class Calc { public static int abs(int a) {return a>0?a:-a} public static int max(int a, int b) {return (a>b)?a:b} public static int min(int a, int b) {return (a>b)?b:a} } public class CalcEx { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Calc.abs(-5)); System.out.println(Calc.max(10,8); System.out.println(Calc.min(-3, -8)); } } //result //5 //10 //-8// 잘못된 사용법 Calc m = new Calc; int n = m.abs(-5); // 바른 사용법 : 객체를 사용하지 않고, 클래스 이름으로 해당 static 메소드 사용 int n = Calc.abs(-5);
- Calc 클래스 : java.lang.Math
- 공유 멤버를 작성할 때
- static 필드나 메소드는 하나만 생성
- 같은 인스턴스(객체) 변수에서 클래스의 static 객체들 공유
⏹ static 메소드의 제약조건
-
static 메소드는 non-static 멤버는 접근할 수 없다.
- 객체가 생성되지 않은 상황에서도 static 메소드는 실행될 수 있기 때문에, non-static 메소드와 필드 사용 불가
- 반대로, non-static 메소드는 static 멤버 사용 가능
class StaticMethod { int n; void f1(int x) { n = x; } // 정상 void f2(int x) { m = x; } // 정상 static m; static void s1(int x) { n = x; } //컴파일 오류. static 메소드는 non-static 필드 사용 불가. static void s2(int x) { f1(3); } //컴파일 오류. static 메소드는 non-static 필드 사용 불가. static void s3(int x) { m = x; } //정상. static 메소드는 static 필드 사용 가능 static void s4(int x) { m = x; } //정상. static 메소드는 static 필드 사용 가능
-
static 메소드는 this 를 사용할 수 없다.
- static 메소드는 객체가 생성되지 않은 상황에서도 호출이 가능하기 떄문에, 현재 실행 중인 객체를 가리키는 this 레퍼런스를 사용할 수 없다
class StaticAndThis { int n; static int m; void f1(int x) { this.n = x; } void f2(int x) { this.m = x; } //non-static 메소드에서는 static 멤버 접근 가능 static void s1(int x) { this.n = x; } //컴파일 오류. static 메소드는 this 사용 불가 static void s2(int x) { this.m = x; } //컴파일 오류. static 메소드는 this 사용 불가 }
- static 메소드는 객체가 생성되지 않은 상황에서도 호출이 가능하기 떄문에, 현재 실행 중인 객체를 가리키는 this 레퍼런스를 사용할 수 없다
⏹ final 클래스와 메소드
-
클래스 앞에 final - 상속하지 못하도록 설정
final class FinalClass { //final 클래스 ... } class DerivedClass extends FinalClass { //컴파일 오류. FinalClass 상속 불가 ... } -
클래스 내 메소드 return data 앞에 fianl - 상속 받은 곳에서 오버라이딩 불가
public class SuperClass { protected final int fianlMethod() { ... } //final 메소드 } class DerivedClass extends SuperClass { protected int finalMethod() { ... } //컴파일 오류. 오버라이딩 불가. }⏹ final 필드
-
final 필드, 상수 정의
- 상수를 정의할 떄 사용 (c언어의 const 와 동일한 개념)
- 상수 필드는 선언 시에 초기 값을 지정하여야 한다.
- 상수 필드는 한 번 정의되면 값을 바꿀 수 없다.
class SharedClass { public static final double PI = 3.141592; } public class FinalFieldClass { final int ROWS = 10; //상수 정의. 이때 초기값 (10) 을 반드시 설정 final int COLS; //컴파일 오류. 초기값을 지정하지 않았다. void f() { int[] intArray = new int [ROWS]; //상수 활용 ROWS = 30; //컴파일 오류. final 필드 값은 변경할 수 없다. } }