.png)
✔ BOJ_21918

풀이과정
내 제출현황
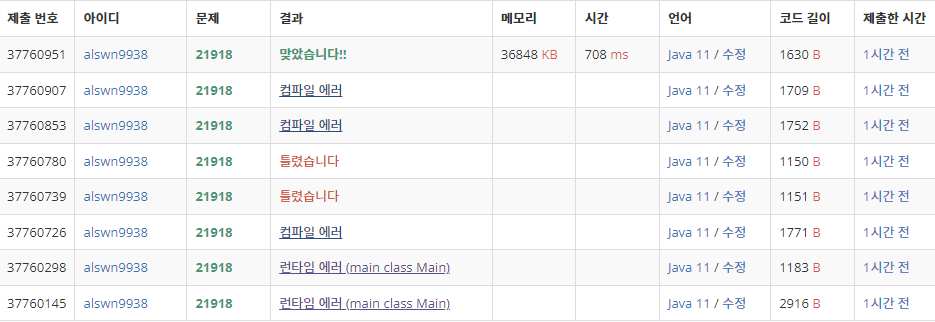
런타임에러 컴파일에러난건 클래스 이름 잘못적거나, 패키지를 잘못 선언해서.. 생긴거고
틀렸습니다는 아직도 잘 모르겠다 ㅠ BufferedReader 사용한건 틀렸다고 나오는데 똑같은 코드 Scanner 쓰면 맞았다고 나옴..
✏ BR 쓴 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// String 읽기
String s = br.readLine();
// 공백 단위로 데이터를 가공하고자 StringTokenizer 사용한다.
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s);
// N개의 전구
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// M개의 명령
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 상태
int[] status = new int[N];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i< N; i++){
status[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
// 명령
int[][] command = new int[M][3];
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=0; j<3; j++){
command[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
}
public static int turn(int s){
if(s==0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
}
✏ SC 쓴 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int[] status = new int[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
status[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int[][] command = new int[M][3];
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
command[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 1 i x : i번째 전구의 상태를 x로 변경
// 2 l r : l~r 번째까지의 전구의 상태를 변경한다
// 3 l r : l~r 번째까지의 전구를 끈다.
//4 l r : l~r번째까지의 전구를 킨다.
int index = 0;
while(true){
if(index >=M) break;
switch(command[index][0]){
case 1:
status[command[index][1]-1] = command[index][2];
break;
case 2:
for(int i=command[index][1]-1; i<=command[index][2]-1;i++){
status[i] = turn(status[i]);
}
break;
case 3:
for(int i=command[index][1]-1; i<=command[index][2]-1;i++){
status[i] = 0;
}
break;
case 4:
for(int i=command[index][1]-1; i<=command[index][2]-1;i++){
status[i]=1;
}
break;
}
index ++;
}
for(int i=0; i< status.length; i++){
System.out.print(status[i]+" ");
}
}
public static int turn(int s){
if(s==0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
}
대단한 알고리즘없이 문제 그대로 따라서 작성했다. 명령을 command라는 배열에 입력하고 command[][0]에 있는 숫자를 이용해서 switch-case문으로 명령을 수행했다. 0과 1을 바꾸는 방식은 turn이라는 함수를 따로 선언해서 수행했다.
아쉬운건 코드 실행 시간 ㅠㅠ 줄이고싶은데 방법을 찾아봐도 잘 안나와서 문제..
