앞서 이 전 포스트와 이어지는 코드를 담고 있습니다.
앞의 포스트 보러가기
🎇 this
저번 코드를 보시면 알 수 있듯,
메서드에서도 이름, id 가 나오고 , 생성자에서도 이름, id 가 나오고 class 내부에서도 나오는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
코딩을 할 때 변수의 이름은 직관적인 것이 좋습니다.
때문에 name 과 id 에서 많이 동떨어진 이름을 짓기 어렵습니다.
이럴때는 어떻게 해야할까요?
바로 this 를 사용하는 것 입니다.
this 는 객체 자신을 참조하는 키워드 입니다.
예시를 들어 자세히 알아봅시다.
🎇 E.g.
첫 번째 코드는 this 를 사용하였고, 두 번째는 저번 포스트에서 나온 코드입니다.
// USE this
public class Student {
String name;
int studentId;
//method has return type
public void func1(){
String resultName = this.name.toLowerCase();
String resultId = "10"+Integer.toString(this.studentId);
System.out.println(resultName + " "+ resultId);
}
// Constructor has no return type
// if you want to use in the Class StudentExam
// you have to write down the name of student
public Student(String name, int studentId){
//value n pass on to the value name above
this.name = name;
this.studentId = studentId;
}
}
func1 의 매개변수가 없어졌습니다.
또한 생성자에서 직관적이지 않은 변수이름을 바꾸었습니다.
생성자 name 을 객체의 name 에다가 저장할 것이기 때문에 this 를 써주었습니다.
func1 은 매개변수를 받았습니다.
사용자가 직접 입력을 하게 되면 생성자를 만들 때 한 번, 메서드를 호출 할 때 한 번
각각 두 번씩을 써야하기 때문에 번거롭습니다.
어차피 생성자를 입력할 때 this 로 객체에 저장해두었기 때문에
func1 은 매개변수를 없애고 객체에서 참조하는 this 를 사용하였습니다.
// NOT USE this
public class Student {
String name;
int studentId;
//method has return type
public void func1(String name, int id){
String resultName = name.toLowerCase();
String resultId = "10"+Integer.toString(studentId);
System.out.println(resultName + " "+ resultId);
}
// Constructor has no return type
// if you want to use in the Class StudentExam
// you have to write down the name of student
public Student(String n, int id){
//value n pass on to the value name above
name = n;
studentId = id;
}
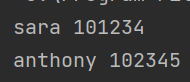
}Student class 를 실행하는 main class 입니다.
public class StudentExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student st1 = new Student("SARA",1234);
Student st2 = new Student("ANTHONY", 2345);
st1.func1();
st2.func1();
}
}