BehaviorTree_EnemyAttack_02
이전 글에서 만들어 둔 MainEnemy를 토대로 자식 클래스를 만들고자 한다.
- 클래스 생성
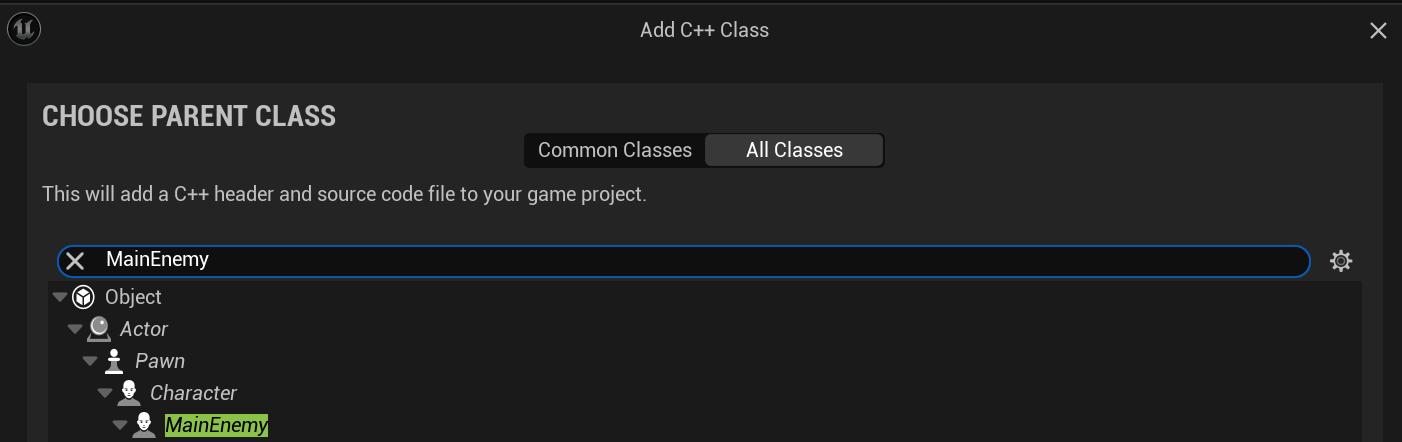
CPP 파일을 생성할 때, 부모클래스를 MainEnemy로 지정한다.
- MainEnemy_Bear.h
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "MainEnemy.h"
#include "MainEnemy_Bear.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class THELASTSURVIVOR_API AMainEnemy_Bear : public AMainEnemy
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
AMainEnemy_Bear();
virtual float TakeDamage(float DamageAmount, FDamageEvent const& DamageEvent, AController* EventInstigator, AActor* DamageCauser) override;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category = BearState)
bool bBearDie = false;
private:
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere, Category = BearState)
float bearHP = 100;
float damage = 30;
virtual void OnAttackMontageEnded(UAnimMontage* Montage, bool bInterrupted) override;
virtual void Attack() override;
virtual void AttackCheckOverlap(UPrimitiveComponent* OverlapComp, AActor* OtherActor, UPrimitiveComponent* OtherComp, int32 OtherBodyIndex, bool bFromSweep, const FHitResult& SweepResult) override;
virtual void EnemyDie() override;
virtual void DestroyEnemy() override;
virtual void OnCollStart() override;
virtual void OnCollEnd() override;
};헤더파일에서는 MainEnemy에서 오버라이드를 하여 사용하기 위해 만들어 둔 함수를 선언하고, 각각의 객체마다 가져야 할 변수를 선언한다.
- MainEnemy_Bear.CPP
#include "MainEnemy_Bear.h"
#include "BearAnim.h"
#include "GameFramework/CharacterMovementComponent.h"
#include "Components/BoxComponent.h"
#include "Components/CapsuleComponent.h"
#include "Kismet/GameplayStatics.h"
AMainEnemy_Bear::AMainEnemy_Bear()
{
static ConstructorHelpers::FObjectFinder<USkeletalMesh>
BearMesh(TEXT("SkeletalMesh'/Game/TheGuardian/Blueprints/Enemy/Bear/Enemy_Bear.Enemy_Bear'"));
if (BearMesh.Succeeded()) {
GetMesh()->SetSkeletalMesh(BearMesh.Object);
}
static ConstructorHelpers::FClassFinder<UAnimInstance>
AnimInstance(TEXT("/Game/TheGuardian/Blueprints/Enemy/Bear/ABP_Bear.ABP_Bear_C"));
if (AnimInstance.Succeeded()) {
GetMesh()->SetAnimInstanceClass(AnimInstance.Class);
}
static ConstructorHelpers::FObjectFinder<USoundBase>
BearDieSound(TEXT("/Script/Engine.SoundWave'/Game/TheGuardian/Sounds/bossDieSound.bossDieSound'"));
if (BearDieSound.Succeeded()) {
DieSound = BearDieSound.Object;
}
LHCollision->SetBoxExtent(FVector(35, 35, 35));
RHCollision->SetBoxExtent(FVector(35, 35, 35));
GetCapsuleComponent()->InitCapsuleSize(90.0f, 90.0f);
}
float AMainEnemy_Bear::TakeDamage(float DamageAmount, FDamageEvent const& DamageEvent, AController* EventInstigator, AActor* DamageCauser)
{
float ActualDamage = Super::TakeDamage(DamageAmount, DamageEvent, EventInstigator, DamageCauser);
if (ActualDamage > 0.f && !bBearDie) {
bearHP -= ActualDamage;
if (bearHP <= 0.f) EnemyDie();
}
return ActualDamage;
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::OnAttackMontageEnded(UAnimMontage* Montage, bool bInterrupted)
{
Super::OnAttackMontageEnded(Montage, bInterrupted);
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::Attack()
{
Super::Attack();
auto AnimInstance = Cast<UBearAnim>(GetMesh()->GetAnimInstance());
if (AnimInstance == nullptr) return;
AnimInstance->Attack();
AnimInstance->OnMontageEnded.RemoveDynamic(this, &AMainEnemy_Bear::OnAttackMontageEnded);
AnimInstance->OnMontageEnded.AddDynamic(this, &AMainEnemy_Bear::OnAttackMontageEnded);
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::AttackCheckOverlap(UPrimitiveComponent* OverlapComp, AActor* OtherActor, UPrimitiveComponent* OtherComp, int32 OtherBodyIndex, bool bFromSweep, const FHitResult& SweepResult)
{
UGameplayStatics::ApplyDamage(OtherActor, damage, GetController(), nullptr, NULL);
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::EnemyDie()
{
Super::EnemyDie();
bBearDie = true;
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), DieSound);
GetWorld()->GetTimerManager().SetTimer(DieTimerHandle, this, &AMainEnemy_Bear::DestroyEnemy, dieDelay, false);
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::DestroyEnemy()
{
Super::Destroy();
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::OnCollStart()
{
Super::OnCollStart();
}
void AMainEnemy_Bear::OnCollEnd()
{
Super::OnCollEnd();
}
생성자에서는 SkeletalMesh, AnimInstance, Sound 등 클래스가 생성될 때 기본적으로 가져야 할 Component를 생성한다. 이외에도 Collision의 크기는 각각의 개체마다 다르기에 이에 맞게 지정해주었다.
MainEnemy에서 오버라이드한 함수들 또한 각각의 객체마다 값을 다르게 갖는 것들은 따로 정의를 해주고, 이외에는 부모의 클래스에 정의되어 있는 함수를 그대로 사용하기 위해 Super 키워드를 통해 부모 클래스의 함수를 호출해주었다.
이와같이 생성했을 때, AI Controller의 있는 값들 또한 만들어지는 클래스에 따라 가변적인 값들이 존재할 수도 있다.
- BTDecorator_IsInAttackRange.CPP
#include "BTDecorator_IsInAttackRange.h"
#include "MainAIController.h"
#include "PlayerCharacter.h"
#include "BehaviorTree/BlackboardComponent.h"
#include "MainEnemy_Bear.h"
#include "MainEnemy_Grunt.h"
#include "MainEnemy_Troll.h"
#include "MainEnemy_Spider.h"
UBTDecorator_IsInAttackRange::UBTDecorator_IsInAttackRange()
{
NodeName = TEXT("CanAttack");
}
bool UBTDecorator_IsInAttackRange::CalculateRawConditionValue(UBehaviorTreeComponent& OwnerComp, uint8* NodeMemory) const
{
bool bResult = Super::CalculateRawConditionValue(OwnerComp, NodeMemory);
auto ControllingPawn = OwnerComp.GetAIOwner()->GetPawn();
if (ControllingPawn == nullptr) return false;
auto Target = Cast<APlayerCharacter>(OwnerComp.GetBlackboardComponent()->GetValueAsObject(AMainAIController::TargetKey));
if (Target == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if (ControllingPawn->IsA(AMainEnemy_Bear::StaticClass()))
{
bResult = (Target->GetDistanceTo(ControllingPawn) <= 300.0f);
}
else if (ControllingPawn->IsA(AMainEnemy_Grunt::StaticClass()))
{
bResult = (Target->GetDistanceTo(ControllingPawn) <= 250.0f);
}
else if (ControllingPawn->IsA(AMainEnemy_Troll::StaticClass()))
{
bResult = (Target->GetDistanceTo(ControllingPawn) <= 250.0f);
}
else if (ControllingPawn->IsA(AMainEnemy_Spider::StaticClass()))
{
bResult = (Target->GetDistanceTo(ControllingPawn) <= 350.0f);
}
return bResult;
}위 코드는 AI Controller를 통해 움직이는 객체와 Target으로 지정된 즉, Player와의 공격범위를 측정하여 범위 안에 Player가 들어왔을 경우, True값을 반환하여 AI에게 공격지시를 내리는 코드이다.
각각의 AI 클래스는 크기가 다르기에 해당 범위가 모두 같다면 AI가 Player에게 공격할 수 있도록 이동하였으나 범위에 닿지 않아 공격을 하지않는 상태가 될 수 있다.
이를 해결하기 위해 Controller를 갖고 있는 AI가 누구인지 저장하는 ControllingPawn 변수의 클래스 정보를 가져와서 각각의 공격 허용 범위를 지정해주었다.