GraphTraversal_쉬운 최단거리(14940)
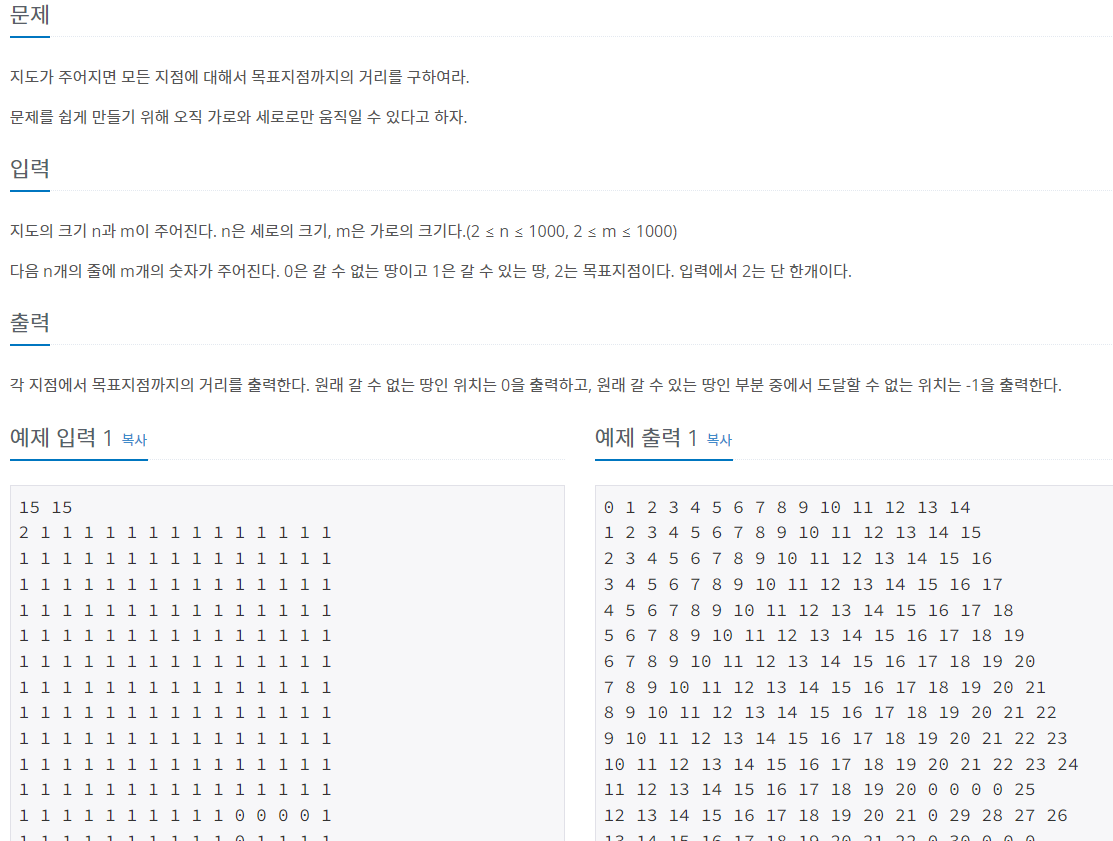
문제
풀이
- BFS 이용
- visited 이차원 배열, board 이차원 배열 사용
- 상,하,좌,우 탐색(dy,dx 만들어 for문 돌릴 수 있으니 시간 줄이기 위해 그냥 if문 4개 사용)
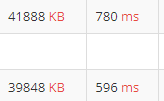
그럼 메모리와 시간 차이 조금 있다..
코드
from collections import deque
import sys
sys.stdin = open("input.txt", "rt")
def BFS(destination):
queue = deque([destination])
while queue:
pos = queue.popleft()
if pos[0] - 1 >= 0 and board[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]] == 1 and not visited[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]]:
board[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]] = board[pos[0]][pos[1]] + 1
queue.append((pos[0] - 1, pos[1]))
visited[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]] = True
if pos[0] + 1 < N and board[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]] == 1 and not visited[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]]:
board[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]] = board[pos[0]][pos[1]] + 1
queue.append((pos[0] + 1, pos[1]))
visited[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]] = True
if pos[1] - 1 >= 0 and board[pos[0]][pos[1] -1] == 1 and not visited[pos[0]][pos[1] - 1]:
board[pos[0]][pos[1] - 1] = board[pos[0]][pos[1]] + 1
queue.append((pos[0], pos[1] - 1))
visited[pos[0]][pos[1] - 1] = True
if pos[1] + 1 < M and board[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1] == 1 and not visited[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1]:
board[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1] = board[pos[0]][pos[1]] + 1
queue.append((pos[0], pos[1] + 1))
visited[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1] = True
if __name__ == "__main__":
N, M = map(int, input().split())
board = []
visited = []
destination = (0, 0)
for i in range(N):
board.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
visited.append([False]*M)
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if board[i][j] == 2:
board[i][j] = 0
visited[i][j] = True
destination = (i, j)
BFS(destination)
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if board[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:
board[i][j] = -1
for i in board:
print(*i)
느낀점
- 무난 했다. 이제 그래프 탐색 골드 문제 풀러 간다..!
정말 알고리즘 1년정도 장난식으로 공부 했는데 이렇게 그래프 탐색 이해한 적은 처음이다. 새삼 머리가 많이 좋지 않다고 느낀다..
- 면접에서 알고리즘 개념 질문을 받았을 때 아주 개발자스럽지 못하게 대답했던 기억이 난다. 이후 알고리즘 개념에 대해 블로그에 잘 정리해야겠다..



