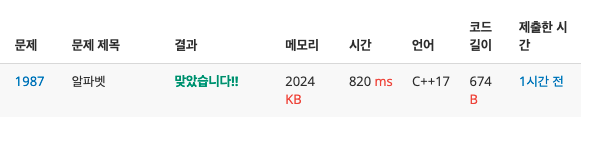
백준 1987 - 알파벳
문제 출처: 백준 1987
중복된 알파벳을 밟지 않으면서 최대 이동할 수 있는 거리를 구해야 한다. 말은 가장 좌측 상단부터 시작해서 현재 위치의 상하좌우로 인접한 칸으로 이동이 가능하다.
풀이 및 코드
문제에서 (0,0)에서 시작한다고 주어졌다. 방문한 칸에 있는 알파벳은 방문했다고 체크 해주어 중복으로 방문하지 않도록 해 주면 된다. 현재 좌표를 기준으로 상하좌우의 좌표와 현재까지 지나온 칸의 개수를 dfs로 넘겨준다. 주어진 좌표값을 이미 방문 했다면 더이상 갈 수 없으므로 뒤로 돌아간다. 돌아가기 전 지나온 칸의개수가 최댓값보다 크면 최댓값에 할당해준다.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int r,c;
vector<string> board;
int alphabet[26];
int max_cnt=0;
int dx[4]={1,0,-1,0};
int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
void DFS(int x,int y,int cnt){
if(alphabet[board[x][y]-'A']==1){
if(max_cnt<cnt) max_cnt=cnt;
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx=x+dx[i];
int ny=y+dy[i];
if(nx<0||ny<0||nx>=r||ny>=c) continue;
alphabet[board[x][y]-'A']=1;
DFS(nx,ny,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[x][y]-'A']=0;
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>r>>c;
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){
string tmp;
cin>>tmp;
board.push_back(tmp);
}
alphabet[board[0][0]-'A']=1;
DFS(0,1,1);
DFS(1,0,1);
cout<<max_cnt;
return 0;
}속도 개선
제한시간이 2초인데 1초 언저리의 시간이 걸렸다. 속도가 느린듯 하여 빠른 속도의 풀이와 비교해보고 다시 수정하였다.
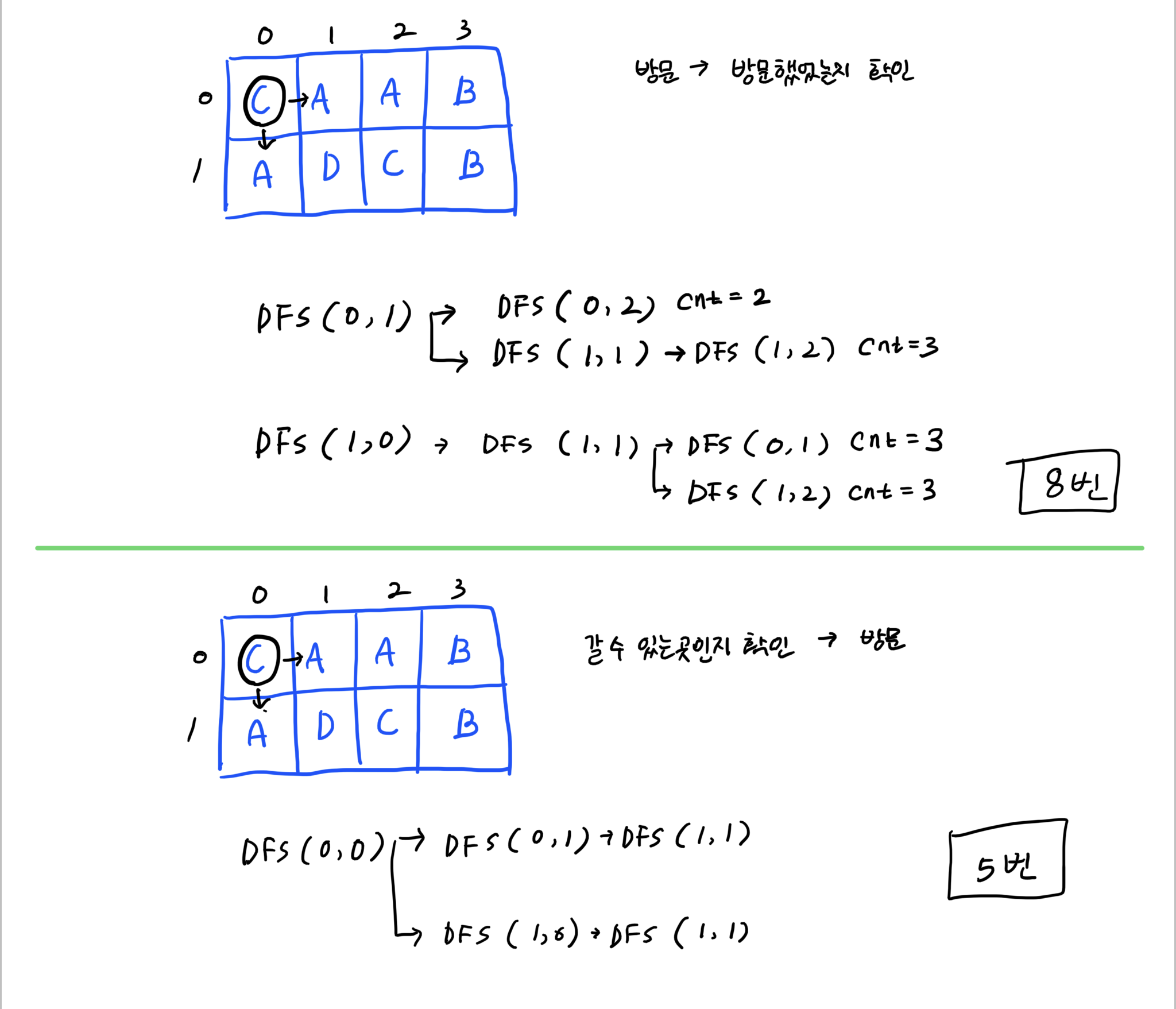
원래 내가 짠 코드는 상,하,좌,우를 모두 방문(=dfs 호출) -> 방문한 알파벳인지 확인 이었는데
이렇게 하면 이미 방문한 알파벳임에도 함수를 호출해야 한다.
그래서 방문하기 전에 미리 방문한 알파벳인지 아닌지 확인하고 아닌 경우에만 함수를 호출하도록 수정했다.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int r,c;
vector<string> board;
int alphabet[26];
int max_cnt=0;
int dx[4]={1,0,-1,0};
int dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
void DFS(int x,int y,int cnt){
if(max_cnt<cnt) max_cnt=cnt;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx=x+dx[i];
int ny=y+dy[i];
if(nx<0||ny<0||nx>=r||ny>=c) continue;
if( alphabet[board[nx][ny]-'A']==0){
alphabet[board[nx][ny]-'A']=1;
DFS(nx,ny,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[nx][ny]-'A']=0;
}
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>r>>c;
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){
string tmp;
cin>>tmp;
board.push_back(tmp);
}
alphabet[board[0][0]-'A']=1;
DFS(0,0,1);
cout<<max_cnt;
return 0;
}이렇게 하니 800ms대에서 400ms대까지 시간을 줄일 수 있었다.
그리고 상하좌우 좌표를 구할 때 반복문을 사용하지 않고 4개의 if 문을 사용하면 시간이 조금 더 줄어든다.
...
void DFS(int x,int y,int cnt){
if(max_cnt<cnt) max_cnt=cnt;
if(x-1 >=0 && alphabet[board[x-1][y]-'A'] == 0){
alphabet[board[x-1][y]-'A'] = 1;
DFS( x-1, y,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[x-1][y]-'A'] = 0;
}
if(x+1 <r && alphabet[board[x+1][y]-'A']== 0){
alphabet[board[x+1][y]-'A'] =1;
DFS( x+1, y,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[x+1][y]-'A'] =0;
}
if(y-1 >=0 && alphabet[board[x][y-1]-'A'] ==0){
alphabet[board[x][y-1]-'A'] =1;
DFS( x, y-1,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[x][y-1]-'A'] =0;
}
if(y+1 < c && alphabet[board[x][y+1]-'A'] ==0){
alphabet[board[x][y+1]-'A'] =1;
DFS( x, y+1,cnt+1);
alphabet[board[x][y+1]-'A'] =0;
}
}
...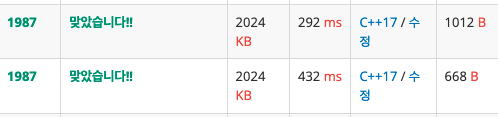
400ms대에서 약 300ms까지 줄일 수 있다.
다만 테스트 통과에는 유의미한 결과를 끼치는건 아닌것 같고 기억 해 뒀다가 적은 시간이라도 단축하고자 할 때 써먹으면 될 듯하다.
이 문제로 간단한 순서의 차이로도 꽤나 큰 차이를 만들어 내는걸 알게 되었다.
재귀함수를 사용할 때 호출을 덜 할수 있는 방법이 더 있는지 한번 더 고민하고 코드를 짜야겠다.
