1. use strict 선언
'use strict';
console.log('hello world')js는 유연한 언어이다. -> 위험!
use strcit는 ECMAScript 5에 포함되어 있다.
선언되지 않은 변수를 사용하면 error가 뜬다.
2. Variable
👉 let(added in ES6)
let name = 'jiwon';
console.log(name);
name='kim ji won';
console.log(name);block scope
let globalName = 'global name';
{
let name = 'jiwon';
console.log(name);
name='kim ji won';
console.log(name);
}- block 밖에서는 block 안에 있는 내용을 볼 수 없다.
- block 밖에서 name을 접근하게되면 아무값도 나오지 않는다.
- block을 쓰지 않고 파일 안에다가 바로 정의해서 쓰는 변수들을
global scope이라고 한다. global 변수들은 어느 곳에서나 접근 가능!- global한 변수들은 어플리케이션이 실행되는 순간부터 끝날 때까지 항상 메모리에 탑재되므로 최소한으로 쓰는 것이 좋다.
👉 var
선언도 하기 전에 값을 할당할 수 있다.
사용하지 않는 것이 좋음
var hosting
어디에 선언했냐에 상관없이 항상 선언을 젤 위로 끌어올려주는 것
선언하기 전에 변수를 console.log 찍어보면 undefined가 나온다.
'use strict';
console.log(age);
//undefiend
// var age 선언이 파일 제일 위로
//올라가서 undefined 나옴 (hosting)
age = 4;
var age;
console.log(age);
//4has no block scope
{
age = 4;
var age;
console.log(age);
//4
}
console.log(age);
//4블럭안에다 선언해도 어디에서나 불러올수 있다.
3. constants
한번 할당하면 값이 절대 바뀌지 않는 아이
값이 계속 변경 될수 있는 것을 Mutable 데이터 type이라고 한다.
(ex. let)
constants는 변경이 불가능 하기 때문에 Immutable 데이터 type이라고 불린다.
왠만하면 값을 할당한 다음에 변경하지 않는 데이터 타입을 사용하자!
const daysInWeek = 7;
const maxNumber = 5;Note!!
- Immutable data types:
- ex) primitive types, frozen objects(i.e. object.freeze())
- primitive type 같은 경우에는 한번 ellie라는 string을 정의하게 되면
ellie를 통채로 메모리에 올렸다가 다른 string으로 변경이 가능하지
ellie라는 string 자체를 i를 빼고 e로 바꾼다던지 data 자체를 바꾸는 것은 불가능
- Mutable data types:
- ex) all objects by default are mutable in JS
- 변경이 가능한 data type은 object!
ellie object 안에 있는 name이나 age가 변경 가능하므로 object는 mutable
이유
- securtiy
해커들이 코드를 삽입해서 값을 변경해 나갈 수 있는데 Immutable 데이터 타입은 이를 방지 할수 있다. - thread safety
여러 쓰레드들이 동시에 그 값에 접근해 값을 변경할 수 있다.
동시에 값을 변경한다는 것은 위험! - reduce human mistakes
4. Variable types
- primitive :
- 더 이상 작은 단위로 나눠질 수 없는 한가지의 아이템
- ex) number, string, boolean, null, undefined, symbol
- object
- 싱글 아이템들을 묶어서 한 단위로, 한 박스로 관리할 수 있게 해주는 것
- function, first-class function
(function도 변수에 할당이 가능하고, 파라미터로 전달도 가능하고, return 타입으로도 가능한 것을 의미)
자바스크립트는 integer나 decimal number 상관없이 모두 number!
const count = 17; //integer
const size = 17.1; //decimal number
console.log(`value: ${count}, type: ${typeof count}`);
console.log(`value: ${size}, type: ${typeof size}`);
//value: 17, type: number
//value: 17.1, type: number
👉 number - speical numberic values: infinity, -infinity, NaN
const infinity = 1/0;
const negativeInfinity = -1/0;
const nAn = 'not a number' / 2;
console.log(infinity); //Infinity
console.log(negativeInfinity); //-Infinity
console.log(nAn); //NaN 👉 bigInt (fairly new, don't use it yet)
chorme이랑 firefox에서만 지원
javascript의 number는 (-2**53) ~ 2**53 범위의 숫자만 표현이 가능하다.
이를 넘는 큰 숫자는 숫자 뒤에 n 을 붙혀 bigInt type으로 만들면 된다.
const bigInt = 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890n;
console.log(`value: ${bigInt}, type: ${typeof bigInt}`);
//value: 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890,
//type: bigint👉 string
javascript에서는 한 가지의 글자든 여러개의 글자든 모두 string
const char = 'c';
const brendan = 'brendan';
const greeting = 'hello' + brendan;
console.log(`value: ${greeting}, type: ${typeof greeting}`);template literals
`을 이용하여 string을 만들 수 있다.
const helloBob = `hi ${brendan}!`;
//template literals (string)
console.log(`value: ${helloBob}, type: ${typeof helloBob}`);👉 boolean
- false: 0, null, undefined, NaN, ''
- true: any other value
const canRead = true;
const test = 3 < 1; //false
console.log(`value: ${canRead}, type: ${canRead}`);
console.log(`value: ${test}, type: ${typeof test}`);👉 null
비어있는 empty값이야 라고 지정
let nothing = null;
console.log(`value: ${nothing}, type: ${typeof nothing}`);👉 undefined
선언은 되었지만 값이 지정되어 있지 않음
let x;
console.log(`value: ${x}, type: ${typeof x}`);👉 Symbol
create unique identifiers for objects
- map이나 자료구조에서 고유한 식별자가 필요할때
- 동시에 다발적으로 일어날수 있는 그런 코드에서 우선순위를 주고 싶을 때
- 정말 고유한 식별자가 필요할 때 쓰여짐
동일한 string을 작성했어도 다른 symbol로 만들어지기 때문에 주어진 string에 상관없이 고유한 식별자를 만들 때 사용
const symbol1 = Symbol('id');
const symbol2 = Symbol('id');
console.log(symbol1 === symbol2);
//false
const gSymbol1 = Symbol.for('id');
const gSymbol2 = Symbol.for('id');
console.log(gSymbol1 === gSymbol2);
//true
//그냥 ${symbol1} 이라고 출력하면 error
//.description을 붙혀서 string으로 변환해서 출력해야함
console.log(`value: ${symbol1.description}, type: ${typeof symbol1}`);👉 object, real-life object, data structure
const me = {name:'jiwon', age: 25};
me.age = 20;object를 가르키는 reference가 메모리에 저장된다.
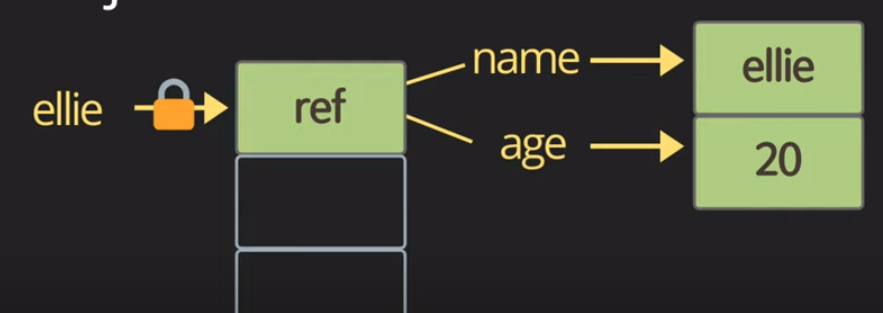
5. Dynamic typing: dynamically typed language
선언할 때 어떤 타입인지 선언하지 않고
runtime 때 즉 프로그램이 동작할 때 할당된 값에 따라서 type이 변경될 수 있다.
let text = 'hello';
console.log(text.charAt(0)); //h
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
//value: hello, type: string
text = 1;
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
//value: 1, type: number
text = '7'+5;
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
//value: 75, type: string
text = '8'/'2';
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
//value: 4, type: number
console.log(text.charAt(0));
//string-> number로 바뀌었는데 charAt을 물어봐서 error
//runtime error