
백준 2667 단지번호붙이기
🔍 문제 설명
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2667
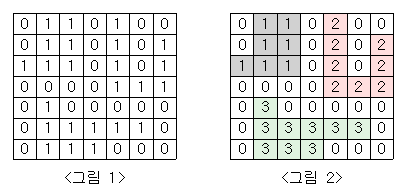
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
✔ 입력
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형이므로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
✔ 출력
첫 번째 줄에는 총 단지수를 출력하시오. 그리고 각 단지내 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 한 줄에 하나씩 출력하시오.
💡 풀이
- 격자형 그래프 탐색 이용
- 격자형 그래프 탐색에서 상,하,좌,우 에서 유효성 체크, 범위 확인 할 것
- DFS 이용
📝 소스코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static FastReader scan = new FastReader();
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static int N; // 지도의 크기
static String[] a; // 그래프 가지고 있을 배열
static boolean[][] visit;
static int[][] dir = {{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}}; // 4개 방향을 표시하기 위한 배열
static ArrayList<Integer> group; // 단지 갯수를 저장하고 있는 배열
static int group_cnt = 0;
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
group_cnt++;
visit[x][y] = true;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = x + dir[i][0], ny = y + dir[i][1];
// 유효한지 아닌지 체크
if(nx >= N || ny >= N || nx < 0 || ny < 0) continue;
if(visit[nx][ny]) continue;
if(a[nx].charAt(ny)== '0') continue;
dfs(nx,ny);
}
}
static void pro() {
group = new ArrayList<>();
// 아직 방문하지 않은 집 방문
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
if(a[i].charAt(j) == '0' || visit[i][j]) continue;
group_cnt = 0;
dfs(i,j);
// 탐색을 하고 나서
group.add(group_cnt);
}
}
Collections.sort(group);
sb.append(group.size()).append('\n');
for(int ans : group) sb.append(ans).append('\n');
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
input();
pro();
}
static void input() {
N = scan.nextInt();
a = new String[N];
visit = new boolean[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
a[i] = scan.nextLine();
}
}
static class FastReader {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastReader() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public FastReader(String s) throws FileNotFoundException {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s));
}
String next() {
while(st == null || !st.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
Integer nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
Double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
Long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
}