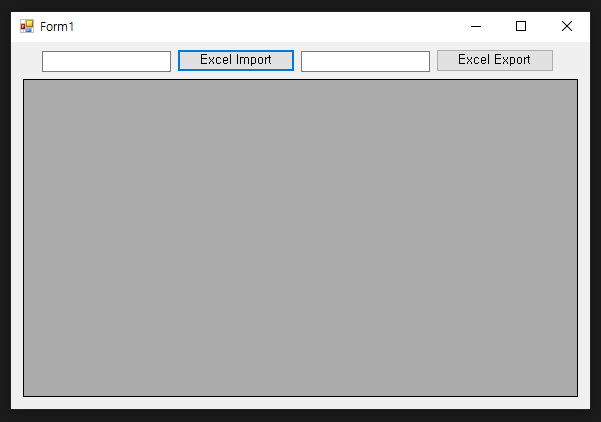
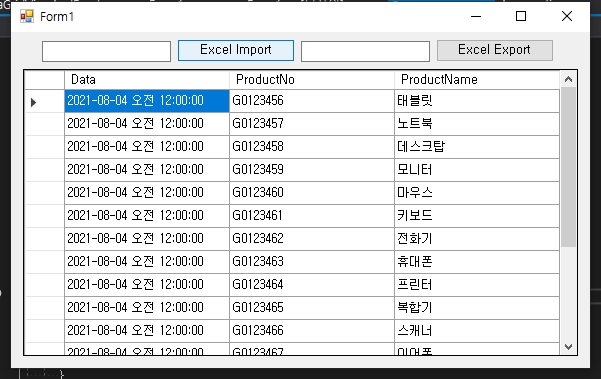
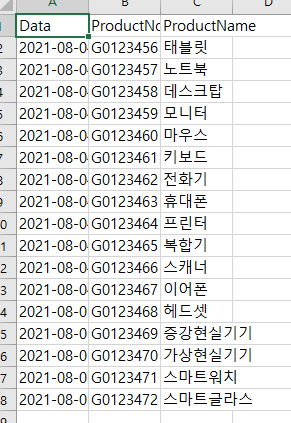
0. 결과
1. Nuget 패키지 설치
2. Excel File Import
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ImportExcelFileToGrid();
}
private void ImportExcelFileToGrid()
{
Thread thread = new Thread(ImportExcelFile);
thread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA);
thread.Start();
}
private void ImportExcelFile()
{
// excelRange.cells[].Value, excelRange.cells[].Value2의 차이점은 Value2가 Currency와 Date 데이터 타입을 사용하지 않는다는 것
// Value2는 Data/Currency의 데이터타입으로 포맷된 셀 값을 Doyble(배정도 부동 소수점 정수)형 데이터 타입으 사용하여 부동소수점 숫자로 반환
// Value2는 Value보다 약 15 ~ 20% 빠르기에 대용량의 데이터를 다룰 때 고려할 속성이다
string file = "";
DataTable dt = new DataTable(); // 엑셀 데이터를 위한 컨테이너
DataRow row;
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog = new OpenFileDialog();
if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
file = openFileDialog.FileName;
try
{
Excel.Application excelApp = new Excel.Application();
Excel.Workbook excelWorkbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(file);
Excel.Worksheet excelWorksheet = excelWorkbook.Sheets[1];
Excel.Range excelRange = excelWorksheet.UsedRange;
int rowCount = excelRange.Rows.Count;
int colCount = excelRange.Columns.Count;
// 열 이름인 Excel 파일의 첫 번째 열 가져오기
for (int i = 1; i <= rowCount; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= colCount; j++)
{
dt.Columns.Add(excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2.ToString());
}
break;
}
// Excel의 행 데이터 가져오기
int rowCounter; // 행 인덱스 번호
for (int i = 2; i < rowCount; i++) // 사용 가능한 Excel 데이터 행에 대한 반복문
{
row = dt.NewRow(); // DataTable에 새 행 할당
rowCounter = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= colCount; j++) // 사용 가능한 Excel 데이터 열에 대한 반복문
{
// 셀이 비어 있는지 확인
if (excelRange.Cells[i, j] != null && excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2 != null)
{
if (j == 1) // Value2로 Date값이 Double로 변형되어 DateTime으로 바꾸고 싶을 때
{
double date = excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2;
DateTime conv = DateTime.FromOADate(date);
row[rowCounter] = conv;
}
else
{
row[rowCounter] = excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2.ToString();
}
}
else
{
row[i] = "";
}
rowCounter++;
}
dt.Rows.Add(row); // 데이터 테이블에 행 추가
}
//dataGridView1.DataSource = dt; // assign DataTable as Datasource for datagridView
CrossThread(dataGridView1, dt);
//quit apps
excelWorkbook.Close();
excelApp.Quit();
// close and clean excel process
CleanProcess(new List<object> { excelRange, excelWorksheet, excelWorkbook, excelApp });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
}
public static void CrossThread(DataGridView item, DataTable dt)
{
// 컨트롤의Handle이 호출 스레드와 다른 스레드에서 만들어져 호출 메서드를 통해 해당 컨트롤을 호출해야 하는 경우 true이고, 그렇지 않으면 false입니다.
if (item.InvokeRequired)
{
// BeginInvoke, 컨트롤의 내부 핸들이 작성된 스레드에서 대리자를 비동기식으로 실행합니다
item.BeginInvoke(new MethodInvoker(delegate ()
{
item.DataSource = dt;
}));
}
else
{
item.DataSource = dt;
}
}
private void CleanProcess(List<object> items)
{
GC.Collect();
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers();
foreach (object item in items)
{
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(item);
}
}3. Excel File Export
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool isExport = false;
// Creating a Excel object
Excel._Application excel = new Excel.Application();
Excel._Workbook workbook = excel.Workbooks.Add(Type.Missing);
Excel._Worksheet worksheet = null;
// DataGridView에 불러온 Data가 아무것도 없을 경우
if(dataGridView1.Rows.Count == 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("Data dose not exist", "Inform", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
try
{
worksheet = workbook.ActiveSheet;
int cellRowIndex = 1;
int cellColumnIndex = 1;
for(int col = 0; col < dataGridView1.Columns.Count; col++)
{
if(cellRowIndex == 1)
{
worksheet.Cells[cellRowIndex, cellColumnIndex++] = dataGridView1.Columns[col].HeaderText;
}
}
cellColumnIndex = 1;
cellRowIndex++;
for(int row = 0; row < dataGridView1.Rows.Count-1; row++)
{
for(int col = 0; col<dataGridView1.Columns.Count; col++)
{
worksheet.Cells[cellRowIndex, cellColumnIndex++] = dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col].Value.ToString();
}
cellColumnIndex = 1;
cellRowIndex++;
}
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = GetExcelSave();
if(saveFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
workbook.SaveAs(saveFileDialog.FileName);
MessageBox.Show("Export Successful!");
isExport = true;
}
// Close Excel Object after Export Success
if(isExport)
{
//quit apps
workbook.Close();
excel.Quit();
// close and clean excel process
CleanProcess(new List<object> { worksheet, workbook , excel });
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private SaveFileDialog GetExcelSave()
{
// Getting the location and file name of the excel to save from user
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog();
saveFileDialog.CheckPathExists = true;
saveFileDialog.AddExtension = true;
saveFileDialog.ValidateNames = true;
saveFileDialog.InitialDirectory = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop);
saveFileDialog.DefaultExt = ".xls";
saveFileDialog.Filter = "Microsoft Excel Workbook (*.xls)|*.xlsx";
saveFileDialog.FileName = "StudentData".ToString();
return saveFileDialog;
}4. 완성 코드
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
using Microsoft.Win32;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Threading;
namespace DataGridViewAndExcel
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
DataSet ds;
// BindingList<ViewModel> viewModel;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// https://www.freecodespot.com/blog/csharp-import-excel/
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ImportExcelFileToGrid();
}
private void ImportExcelFileToGrid()
{
Thread thread = new Thread(ImportExcelFile);
thread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA);
thread.Start();
}
private void ImportExcelFile()
{
// excelRange.cells[].Value, excelRange.cells[].Value2의 차이점은 Value2가 Currency와 Date 데이터 타입을 사용하지 않는다는 것
// Value2는 Data/Currency의 데이터타입으로 포맷된 셀 값을 Doyble(배정도 부동 소수점 정수)형 데이터 타입으 사용하여 부동소수점 숫자로 반환
// Value2는 Value보다 약 15 ~ 20% 빠르기에 대용량의 데이터를 다룰 때 고려할 속성이다
string file = "";
DataTable dt = new DataTable(); // 엑셀 데이터를 위한 컨테이너
DataRow row;
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog = new OpenFileDialog();
if (openFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
file = openFileDialog.FileName;
try
{
Excel.Application excelApp = new Excel.Application();
Excel.Workbook excelWorkbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(file);
Excel.Worksheet excelWorksheet = excelWorkbook.Sheets[1];
Excel.Range excelRange = excelWorksheet.UsedRange;
int rowCount = excelRange.Rows.Count;
int colCount = excelRange.Columns.Count;
// 열 이름인 Excel 파일의 첫 번째 열 가져오기
for (int i = 1; i <= rowCount; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= colCount; j++)
{
dt.Columns.Add(excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2.ToString());
}
break;
}
// Excel의 행 데이터 가져오기
int rowCounter; // 행 인덱스 번호
for (int i = 2; i < rowCount; i++) // 사용 가능한 Excel 데이터 행에 대한 반복문
{
row = dt.NewRow(); // DataTable에 새 행 할당
rowCounter = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= colCount; j++) // 사용 가능한 Excel 데이터 열에 대한 반복문
{
// 셀이 비어 있는지 확인
if (excelRange.Cells[i, j] != null && excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2 != null)
{
if (j == 1) // Value2로 Date값이 Double로 변형되어 DateTime으로 바꾸고 싶을 때
{
double date = excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2;
DateTime conv = DateTime.FromOADate(date);
row[rowCounter] = conv;
}
else
{
row[rowCounter] = excelRange.Cells[i, j].Value2.ToString();
}
}
else
{
row[i] = "";
}
rowCounter++;
}
dt.Rows.Add(row); // 데이터 테이블에 행 추가
}
//dataGridView1.DataSource = dt; // assign DataTable as Datasource for datagridView
CrossThread(dataGridView1, dt);
//quit apps
excelWorkbook.Close();
excelApp.Quit();
// close and clean excel process
CleanProcess(new List<object> { excelRange, excelWorksheet, excelWorkbook, excelApp });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
}
public static void CrossThread(DataGridView item, DataTable dt)
{
// 컨트롤의Handle이 호출 스레드와 다른 스레드에서 만들어져 호출 메서드를 통해 해당 컨트롤을 호출해야 하는 경우 true이고, 그렇지 않으면 false입니다.
if (item.InvokeRequired)
{
// BeginInvoke, 컨트롤의 내부 핸들이 작성된 스레드에서 대리자를 비동기식으로 실행합니다
item.BeginInvoke(new MethodInvoker(delegate ()
{
item.DataSource = dt;
}));
}
else
{
item.DataSource = dt;
}
}
// https://afsdzvcx123.tistory.com/entry/C-%EC%9C%88%ED%8F%BCWindows-Form-DataGridView-%EC%9D%B4%EC%9A%A9%ED%95%98%EC%97%AC-Excel%EC%97%90-Export-%ED%95%98%EB%8A%94-%EB%B0%A9%EB%B2%95
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool isExport = false;
// Creating a Excel object
Excel._Application excel = new Excel.Application();
Excel._Workbook workbook = excel.Workbooks.Add(Type.Missing);
Excel._Worksheet worksheet = null;
// DataGridView에 불러온 Data가 아무것도 없을 경우
if(dataGridView1.Rows.Count == 0)
{
MessageBox.Show("Data dose not exist", "Inform", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
return;
}
try
{
worksheet = workbook.ActiveSheet;
int cellRowIndex = 1;
int cellColumnIndex = 1;
for(int col = 0; col < dataGridView1.Columns.Count; col++)
{
if(cellRowIndex == 1)
{
worksheet.Cells[cellRowIndex, cellColumnIndex++] = dataGridView1.Columns[col].HeaderText;
}
}
cellColumnIndex = 1;
cellRowIndex++;
for(int row = 0; row < dataGridView1.Rows.Count-1; row++)
{
for(int col = 0; col<dataGridView1.Columns.Count; col++)
{
worksheet.Cells[cellRowIndex, cellColumnIndex++] = dataGridView1.Rows[row].Cells[col].Value.ToString();
}
cellColumnIndex = 1;
cellRowIndex++;
}
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = GetExcelSave();
if(saveFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
workbook.SaveAs(saveFileDialog.FileName);
MessageBox.Show("Export Successful!");
isExport = true;
}
// Close Excel Object after Export Success
if(isExport)
{
//quit apps
workbook.Close();
excel.Quit();
// close and clean excel process
CleanProcess(new List<object> { worksheet, workbook , excel });
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
private SaveFileDialog GetExcelSave()
{
// Getting the location and file name of the excel to save from user
SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog();
saveFileDialog.CheckPathExists = true;
saveFileDialog.AddExtension = true;
saveFileDialog.ValidateNames = true;
saveFileDialog.InitialDirectory = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop);
saveFileDialog.DefaultExt = ".xls";
saveFileDialog.Filter = "Microsoft Excel Workbook (*.xls)|*.xlsx";
saveFileDialog.FileName = "StudentData".ToString();
return saveFileDialog;
}
private void CleanProcess(List<object> items)
{
GC.Collect();
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers();
foreach (object item in items)
{
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(item);
}
}
}
}4. 느낀점
- Export하는 자료는 찾기 쉬웠지만 Import는 생각보다 없어서 찾기 어려웠다
- 그리고 이번에 Value와 Vlaue2의 차이점도 같이 공부할 수 있게 되었고 Value2로 Date를 받았을 때 Datetime으로 바꾸는 공부도 같이 할 수 있는 기회였다
- 아직 미숙해서 좀 더 공부해서 효율적인 코드로 바꿔보자!
