1. 프로젝트 테스트
- async project, web, lombok
- Package : controller, service
- Class : ApiController, AsyncService
01. 간단한 Async 처리
- Main AsyncApplication.java
- @EnableAsync
- 스프링의 Async 어노테이션을 감지하며 EJB 3.1javax.ejb.Asynchronous; 이 옵션으로 사용자 정의된 다른 어노테이션 또한 감지할 수 있다.
package com.example.async;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AsyncApplication.class, args);
}
}
- controller / ApiController.java
package com.example.async.controller;
import com.example.async.service.AsyncService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
final private AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
asyncService.hello();
log.info("method end");
return "hello";
}
}
- service / AsyncService.java
- @Async
- 비동기 처리를 위한 어노테이션, spring에서 제공하는 thread
- @Async 어노테이션을 빈bean에 넣으면 별도의 쓰레드에서 실행되도록 동작
- public method에만 적용가능
- @Service
- 서비스 레이어 클래스들에 사용되어지는 어노테이션으로 @Component를 사용해도 상관 없다
- @Service 어노테이션을 사용함으로써 해당 클래스가 서비스 레이어 클래스라는 것을 명확하게 할 수 있다
- @Service 어노테이션은 해당 클래스를 루트 컨테이너에 빈(Bean) 객체로 생성해주는 어노테이션
package com.example.async.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncService {
@Async
public void hello() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.info("thread sleep");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
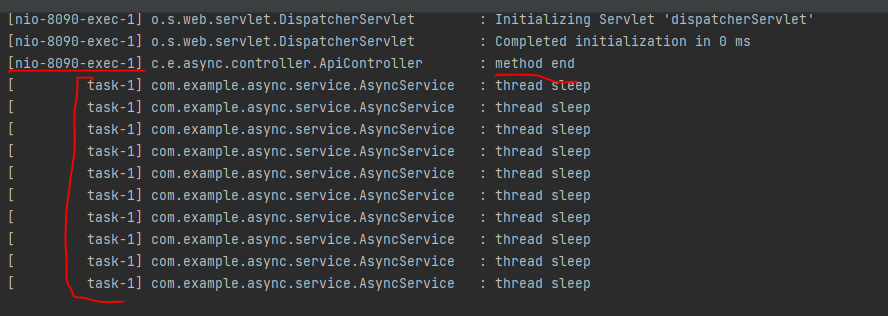
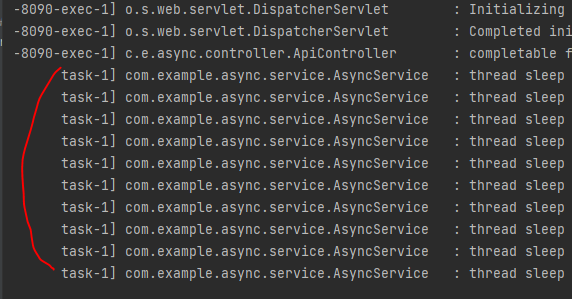
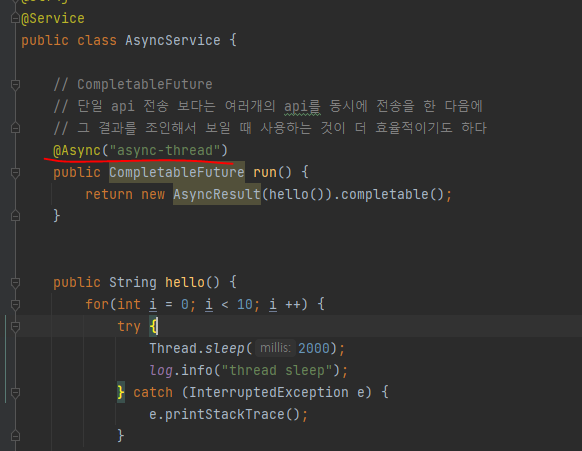
02. CompletableFuture 사용
- CompletableFuture
- @Async같은 비동기 메소드를 사용할 때, Void형태를 사용한다면 문제가 되지 않는다. 하지만 return이 존재한다면 기존에는 Future나 ListenableFuture를 이용하여 해결했지만 JAVA 8버전 부터는 CompletableFuture를 제공
- 단일 api 전송 보다는 여러개의 api를 동시에 전송을 한 다음에 그 결과를 조인해서 보일 때 사용하는 것이 더 효율적이기도 하다
- AsyncService.java
package com.example.async.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncService {
// CompletableFuture
// 단일 api 전송 보다는 여러개의 api를 동시에 전송을 한 다음에
// 그 결과를 조인해서 보일 때 사용하는 것이 더 효율적이기도 하다
@Async
public CompletableFuture run() {
return new AsyncResult(hello()).completable();
}
public String hello() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.info("thread sleep");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return "async hello";
}
}
package com.example.async.controller;
import com.example.async.service.AsyncService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
final private AsyncService asyncService;
// CompletableFuture
// @Async같은 비동기 메소드를 사용할 때, Void형태를 사용한다면 문제가 되지 않는다. 하지만 return이 존재한다면 기존에는 Future나 ListenableFuture를 이용하여 해결했지만 JAVA 8버전 부터는 CompletableFuture를 제공
@GetMapping("/hello")
public CompletableFuture hello() {
log.info("completable future init");
return asyncService.run();
}
}
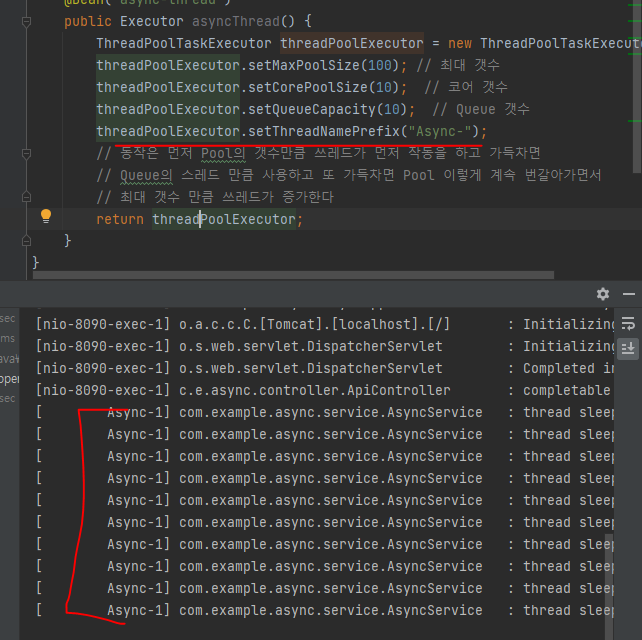
03. Thread 만들기
- Package : config
- Class : AppConfig
- AppConfig.java
package com.example.async.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean("async-thread")
public Executor asyncThread() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(100); // 최대 갯수
threadPoolExecutor.setCorePoolSize(10); // 코어 갯수
threadPoolExecutor.setQueueCapacity(10); // Queue 갯수
threadPoolExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix("Async-");
// 동작은 먼저 Pool의 갯수만큼 쓰레드가 먼저 작동을 하고 가득차면
// Queue의 스레드 만큼 사용하고 또 가득차면 Pool 이렇게 계속 번갈아가면서
// 최대 갯수 만큼 쓰레드가 증가한다
return threadPoolExecutor;
}
}
package com.example.async.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncService {
// CompletableFuture
// 단일 api 전송 보다는 여러개의 api를 동시에 전송을 한 다음에
// 그 결과를 조인해서 보일 때 사용하는 것이 더 효율적이기도 하다
@Async("async-thread")
public CompletableFuture run() {
return new AsyncResult(hello()).completable();
}
public String hello() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.info("thread sleep");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return "async hello";
}
}
- @Async 어노테이션에 @Bean으로 등록한 thread 호출