JS Best Practices
전역 변수(global)를 지양하고, new를 지양하고, ==를 지양하고, eval()을 지양해야 한다.
Avoid Global Variables
전역 변수의 사용을 최소화 해야한다.
여기에는 모든 데이터 유형, 객체 및 함수를 포함한다.
전역 변수 및 함수는 다른 스크립트로 덮어쓸 수 있기 때문이다.
대신 지역 변수를 사용하고 클로저(closures)를 사용하는 방법을 배우자.
Always Declare Local Variables
함수에서 사용되는 모든 변수는 지역 변수로 선언되어야 한다.
지역 변수는 var 키워드, let 키워드 또는 const 키워드로 선언해야만 한다.
그렇지 않으면 전역 변수가 된다.
stirct mode는 선언되지 않은 변수를 허용하지 않는다.
Declarations on Top
모든 선언을 각 스크립트나 함수의 맨 위에 두는 것이 좋은 코딩 방법이다.
- 더욱 깔끔하게 코드 관리 가능
- 지역 변수를 찾을 수 있는 단일 장소 제공
- 원치 않는(암시된) 전역 변수를 쉽게 피할 수 있음
- 원치 않는 재선언의 가능성 감소
// Declare at the beginning
let firstName, lastName, price, discount, fullPrice;
// Use later
firstName = "John";
lastName = "Doe";
price = 19.90;
discount = 0.10;
fullPrice = price - discount;반복문 변수는 이렇게 선언할 수 도 있다.
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Initialize Variables
변수를 선언할 때 변수를 초기화하는 것은 좋은 코딩 방법이다.
- 더욱 깔끔하게 코드 관리 가능
- 변수를 초기화할 단일 장소 제공
- 정의되지 않은 값 피하기
// Declare and initiate at the beginning
let firstName = "",
let lastName = "",
let price = 0,
let discount = 0,
let fullPrice = 0,
const myArray = [],
const myObject = {};변수를 초기화하면 의도된 용도(및 의도된 데이터 유형)에 대한 아이디어를 얻을 수 있다.
Declare Objects with const
const로 객체를 선언하면 실수로 유형이 변경되는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
Example
let car = {type:"Fiat", model:"500", color:"white"}; car = "Fiat"; // Changes object to stringconst car = {type:"Fiat", model:"500", color:"white"}; car = "Fiat"; // Not possible
Declare Arrays with const
const로 배열을 선언하면 실수로 유형이 변경되는 것을 방지할 수 있다.
Example
let cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; cars = 3; // Changes array to numberconst cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; cars = 3; // Not possible
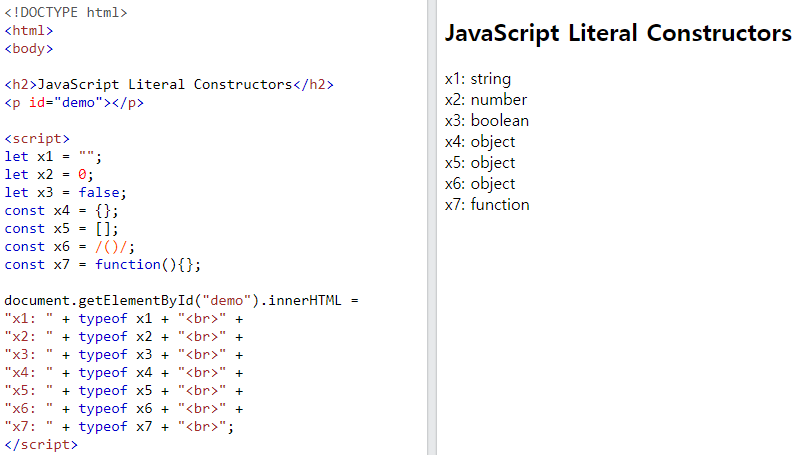
Don't Use new Object()
- Use
""instead ofnew String() - Use
0instead of newNumber() - Use
falseinstead ofnew Boolean() - Use
{}instead ofnew Object() - Use
[]instead ofnew Array() - Use
/()/instead ofnew RegExp() - Use
function (){}instead ofnew Function()
Example
let x1 = ""; // new primitive string let x2 = 0; // new primitive number let x3 = false; // new primitive boolean const x4 = {}; // new object const x5 = []; // new array object const x6 = /()/; // new regexp object const x7 = function(){}; // new function object
Beware of Automatic Type Conversions(자동 형변환에 주의)
JavaScript는 느슨하게(loosely) 입력된다.
변수는 모든 데이터 유형을 포함할 수 있다.
변수는 데이터 유형을 변경할 수 있다.
Example
let x = "Hello"; // typeof x is a string x = 5; // changes typeof x to a number
숫자는 실수로 문자열이나 NaN(숫자가 아님)으로 변환될 수 있다.
수학 연산을 수행할 때, 개발자의 실수로 JavaScript는 숫자를 문자열로 변환할 수 있다.
Example
let x = 5 + 7; // x.valueOf() is 12, typeof x is a number let x = 5 + "7"; // x.valueOf() is 57, typeof x is a string let x = "5" + 7; // x.valueOf() is 57, typeof x is a string let x = 5 - 7; // x.valueOf() is -2, typeof x is a number let x = 5 - "7"; // x.valueOf() is -2, typeof x is a number let x = "5" - 7; // x.valueOf() is -2, typeof x is a number let x = 5 - "x"; // x.valueOf() is NaN, typeof x is a number문자열에서 문자열을 빼면 오류가 발생하지 않지만
NaN(숫자가 아님)이 반환된다.
Example"Hello" - "Dolly" // returns NaN
Use === Comparison
== 비교 연산자는 비교 전에 항상 (일치하는 유형으로) 변환한다.
=== 연산자는 값과 유형을 강제로 비교합니다.
Example
0 == ""; // true 1 == "1"; // true 1 == true; // true 0 === ""; // false 1 === "1"; // false 1 === true; // false
Use Parameter Defaults
누락된 인수로 함수를 호출하면 누락된 인수의 값이 undefined로 설정된다.
정의되지 않은 값은 코드를 손상시킬 수 있다. 인수에 기본값을 할당하는 것은 좋은 습관이다.
Example
function myFunction(x, y) { if (y === undefined) { y = 0; } }
ECMAScript 2015는 함수 정의에서 기본 매개변수를 허용한다.
function (a=1, b=1) { /*function code*/ }
Function Parameters에서 함수 매개변수 및 인수에 대해 자세히 알아보자.
End Your Switches with Defaults
항상 기본값(default)으로 switch 문을 끝내야한다. 필요없다 하더라도!
Example
switch (new Date().getDay()) { case 0: day = "Sunday"; break; case 1: day = "Monday"; break; case 2: day = "Tuesday"; break; case 3: day = "Wednesday"; break; case 4: day = "Thursday"; break; case 5: day = "Friday"; break; case 6: day = "Saturday"; break; default: day = "Unknown"; }
Avoid Number, String, and Boolean as Objects
항상 숫자, 문자열 또는 부울(booleans)을 객체가 아닌 기본 값으로 취급해야한다.
이러한 유형을 객체로 선언하면 실행 속도가 느려지고 불쾌한 부작용이 발생한다.
Example
let x = "John"; let y = new String("John"); (x === y) // is false because x is a string and y is an object.
Or even worse:
Example
let x = new String("John"); let y = new String("John"); (x == y) // is false because you cannot compare objects.
Avoid Using eval()
eval() 함수는 텍스트를 코드로 실행하는 데 사용된다. 거의 모든 경우에 사용할 필요가 없다.
임의의 코드를 실행할 수 있기 때문에 보안 문제도 나타난다.