Data Structure and Algorithms (4)
1. 트리 (Tree)
-
구조 : 트리 node와 branch를 이용해 사이클을 이루지 않도록 구성한 데이터 구조
-
사용 : 이진트리 / 탐색(검색) 알고리즘 구현
-
용어
node,root node,level,parent node,child node,leaf node,sibling/brother node,depth -
종류
1) 이진트리 : branch가 최대 2개
2) 이진탐색트리(BST) : 이진트리이면서 동시에 왼쪽 노드와 오른쪽 노드가 부모노드보다 각각 작고 크다. -
시간복잡도
depth와 연관
O(h) = O(logn) -
단점
일렬로 나열된 트리의 경우 불필요한 탐색시간이 발생된다.
이를 해결하기 위해 트리정렬 알고리즘 필요 -
delete
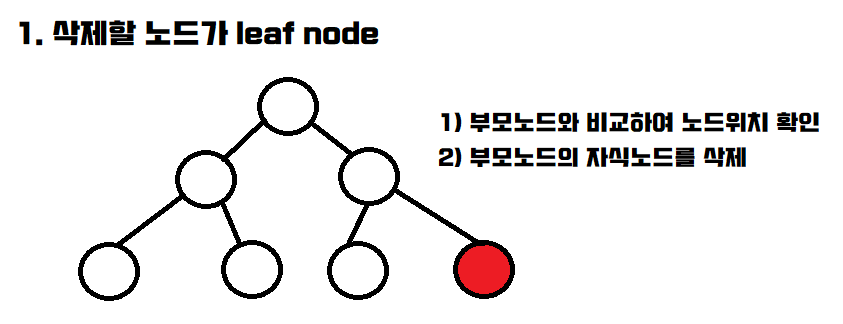
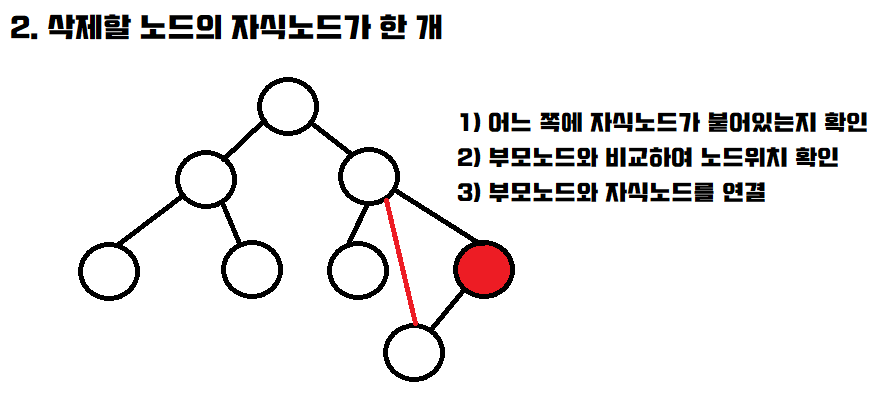

코드
class Node: def __init__(self, value): self.value = value self.left = None self.right = None ㅤ class NodeMgmt: def __init__(self, head): self.head = head ㅤ def insert(self, value): cur_node = self.head ㅤ while True: if value < cur_node.value: if cur_node.left != None: cur_node = cur_node.left else: cur_node.left = Node(value) break else: if cur_node.right != None: cur_node = cur_node.right else: cur_node.right = Node(value) break ㅤ def search(self, value): cur_node = self.head while cur_node: if cur_node.value == value: return True elif value < cur_node.value: cur_node = cur_node.left else: cur_node = cur_node.right return False ㅤ def delete(self, value): search = False cur_node = self.head ㅤ parent = self.head ㅤ # 해당 노드의 유무확인 및 삭제할 노드 업데이트 ㅤ while cur_node: if cur_node.value == value: search = True break elif value < cur_node.value: parent = cur_node cur_node = cur_node.left else: ㅤ parent = cur_node cur_node = cur_node.right ㅤ if search == False: return False ㅤ # case1 : 삭제할 노드가 leaf 노드인 경우 if cur_node.left == None and cur_node.right == None: if value < parent.value: parent.left = None else: parent.right = None ㅤ del cur_node ㅤ # case2 : 삭제할 노드의 자식노드가 한 개인 경우 elif cur_node.left != None and cur_node.right == None: if value < parent.value: parent.left = cur_node.left else: parent.right = cur_node.left elif cur_node.left == None and cur_node.right != None: if value < parent.value: parent.left = cur_node.right else: parent.right = cur_node.right ㅤ # case3 : 삭제할 노드의 자식노드가 두 개인 경우 elif cur_node.left != None and cur_node.right != None: # case3-1 : if value < parent.value: change_node = cur_node.right change_node_parent = cur_node.right while change_node.left != None: change_node_parent = change_node change_node = change_node.left if change_node.right != None: change_node_parent.left = change_node.right else: change_node_parent.left = None parent.left = change_node change_node.right = cur_node.right change_node.left = cur_node.left # case3-2 : else: ㅤ change_node = cur_node.right change_node_parent = cur_node.right while change_node.left != None: change_node_parent = change_node change_node = change_node.left if change_node.right != None: change_node_parent.left = change_node.right ㅤ else: change_node_parent.left = None ㅤ parent.right = change_node change_node.right = cur_node.right change_node.left = cur_node.left ㅤ -------------------------------------------------------------------- head = Node(1) BST = NodeMgmt(head) BST.insert(2) print(BST.search(2)) -------------------------------------------------------------------- import random ㅤ BST_num = set() while len(BST_num) != 100: ㅤ BST_num.add(random.randint(0, 999)) ㅤ head = Node(500) BST = NodeMgmt(head) for num in BST_num: if BST.search(num) == False: print('search failed') ㅤ delete_num = set() BST_num = list(BST_num) while len(delete_num) != 10: delete_num.add(BST_num[random.randint(0, 99)]) ㅤ for del_num in delete_num: if BST.delete(del_num) == False: print('delete failed', del_num)
2. 힙 (Heap)
-
구조 : Max/Min Heap -> root에 최대값/최소값
-
목적 : 데이터에서 최소값과 최대값을 빠르게 구하기 위한 이진트리
-
힙을 사용하는 이유
1) 배열에 데이터를 넣고 최대값/최소값 찾기위해서
*배열에 데이터 넣고 찾으면 O(n) / 힙에 데이터 넣고 찾으면 O(logn)
2) 우선순위 큐와 같이 최대값 또는 최소값을 빠르게 찾아야하는 자료구조 및 알고리즘 구현에 활용 -
이진탐색트리 VS 힙
1) 공통점 : 이진트리
2) 차이점 : 이진탐색트리 - 왼쪽 오른쪽 크기비교 / 힙 - 최대값만 판별
코드
class Heap: def __init__(self, data): self.heap = list() self.heap.append(None) self.heap.append(data) ㅤㅤ def move_up(self, insert_idx): if insert_idx <= 1: return False parent_idx = insert_idx // 2 if self.heap[insert_idx] > self.heap[parent_idx]: return True else: return False ㅤㅤ def move_down(self, pop_idx): left_child_pop_idx = pop_idx * 2 right_child_pop_idx = pop_idx * 2 + 1 ㅤ # case1 왼쪽 자식노드 없을때 if left_child_pop_idx >= len(self.heap): return False ㅤ # case2 오른쪽 자식노드만 없을때 elif right_child_pop_idx >= len(self.heap): if self.heap[pop_idx] < self.heap[left_child_pop_idx]: #아직 max_heapify 이루어지지 않음 return True else: return False ㅤ # case3 오른쪽 왼쪽 다 있을때 else: if self.heap[left_child_pop_idx] > self.heap[right_child_pop_idx]: if self.heap[pop_idx] < self.heap[left_child_pop_idx]: return True else: return False else: if self.heap[pop_idx] < self.heap[right_child_pop_idx]: return True else: return False ㅤ def insert(self, data): if len(self.heap) == 0: self.heap.apppend(None) self.heap.append(data) return True ㅤ self.heap.append(data) ㅤ insert_idx = len(self.heap) - 1 ㅤ while self.move_up(insert_idx): parent_idx = insert_idx // 2 self.heap[insert_idx], self.heap[parent_idx] = \ self.heap[parent_idx], self.heap[insert_idx] insert_idx = parent_idx return True ㅤ def pop(self): if len(self.heap) <= 1: return None ㅤ return_data = self.heap[1] self.heap[1] = self.heap[-1] del self.heap[-1] poped_idx = 1 ㅤ while self.move_down(poped_idx): left_child_pop_idx = poped_idx * 2 right_child_pop_idx = poped_idx * 2 + 1 ㅤ # case2 오른쪽 자식노드만 없을때 if right_child_pop_idx >= len(self.heap): if self.heap[poped_idx] < self.heap[left_child_pop_idx]: self.heap[poped_idx], self.heap[left_child_pop_idx] = \ ㅤ self.heap[left_child_pop_idx], self.heap[poped_idx] poped_idx = left_child_pop_idx ㅤ # case3 오른쪽 왼쪽 다 있을때 else: if self.heap[left_child_pop_idx] > self.heap[right_child_pop_idx]: if self.heap[poped_idx] < self.heap[left_child_pop_idx]: self.heap[poped_idx], self.heap[left_child_pop_idx] = \ self.heap[left_child_pop_idx], self.heap[poped_idx] poped_idx = left_child_pop_idx else: if self.heap[poped_idx] < self.heap[right_child_pop_idx]: self.heap[poped_idx], self.heap[right_child_pop_idx] = \ self.heap[right_child_pop_idx], self.heap[poped_idx] poped_idx = right_child_pop_idx ㅤ return return_data ㅤ -------------------------------------------------------- heap = Heap(1) ㅤ for i in range(2,99): heap.insert((i)) ㅤ print(heap.heap) ㅤ for i in range(2,99): print(heap.pop()) print(heap.heap)
본 게시글은 fastcampus 이준희강사 수업을 듣고 개인적으로 정리한 내용임을 밝힘.
