- 소요시간 : 1시간
- 문제 사이트 : 백준
- 문제 수준 : 골드 2
- 문제 유형 : 구현, 그래프 이론, 그래프 탐색, 너비 우선 탐색, 시뮬레이션
- 다른 사람의 풀이를 참고 했는가 ? : X
- 문제 링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/19238
- 푼 날짜 : 2023.05.08
1. 사용한 자료구조 & 알고리즘
bfs, 구현, 시뮬레이션, 그래프 탐색, 그래프 이론
2. 사고과정
문제 자체는 크게 어렵지 않았기에, 어떻게 구현할지와 예외 를 잘 생각해주면 됐다.
1. 어떻게 구현할 것인가?
N이 20으로 매우 작았기에 BFS를 몇번이나 수행해도 상관없을 것으로 생각. 그래서 시작 택시 위치에서, 모든 맵으로 BFS를 통해서 그 거리를 구하고, 정렬한다. 정렬하면 가장 우선순위 높은 좌표를 알고 있으니, 그 좌표까지의 거리를 연료에서 뺀다.
그리고 그 좌표에서는 목적지가 정해져있다. 시작 위치와, 목적지의 위치가 정해져 있으니 bfs를 하면서 목적지의 위치에 도달한다면 그 거리만큼 연료를 뺀다. 그 후 조금전 사용한 연료의 2배를 더해준다.
2. 예외
(1) 손님까지 가는 중 벽에 막혀 태울 수 있는 손님이 없는 경우.
-> 손님을 만날 때마다 list에 손님의 좌표를 넣어주는데, bfs를 했는데 list의 크기가 0이면 손님을 태우지 못한 것. -1출력
(2) 손님을 태우고 목적지까지 가는데, bfs를 수행해도 목적지의 좌표로 이동하지 못하고 bfs가 끝난 것은 벽에 막혀 목적지까지 이동할 수 없는 것. -1출력
(3) 연료를 거리만큼 뺐는데 연료가 0 미만이 될 경우. 손님 혹은 목적지까지 이동할 수 없다고 판단. -1 출력
3. 풀이과정
- map에 벽과, 손님이 없다면 null, 손님이 있다면 목적지의 좌표를 저장
- 택시의 좌표에서 bfs를 수행하면서 손님의 위치 중 가장 가깝고, 행, 열이 작은 위치를 찾는다. 연료를 거리만큼 빼준다.
- 손님의 위치에서 해당 손님의 목적지까지 bfs를 수행한다. 연료는 거리만큼 뺴준다.
- (2~3)번에서 전에 말한 예외처리는 함께 처리한다.
4. 소스코드
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Taxi {
int wall;
Integer goal [];
Taxi(int wall,Integer goal[]) {
this.wall=wall;
this.goal=goal;
}
}
public class Main{
static Taxi map[][];
static int taxiY;
static int taxiX;
static int dy[] = {-1,1,0,0};
static int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st;
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int fuel = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map=new Taxi[N][N];
//해당 좌표의 벽과
//손님이 없다면 null
//손님이 있다면 목적지 좌표를 넣음
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int j=0;j<N;j++) {
map[i][j]=new Taxi(0,null);
map[i][j].wall = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
taxiY=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())-1;
taxiX=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())-1;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int personY=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int personX=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int goalY=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int goalX=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map[personY-1][personX-1].goal= new Integer[] {goalY-1,goalX-1};
}
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
///택시의 좌표에서 bfs수행
Integer temp[] = bfs1();
int personY=temp[0];
int personX=temp[1];
int distance1=temp[2];
int goalY=temp[3];
int goalX=temp[4];
fuel -= distance1;
//택시는 손님의 위치가 됨
taxiY=personY;
taxiX=personX;
//연료가 0미만이면 0출력
if(fuel<0) {
System.out.println(-1);
System.exit(0);
}
//손님의 위치에서, 손님의 목적지 까지 bfs
int distance2 = bfs2(personY,personX,goalY,goalX);
fuel-=distance2;
//연료가 0미만이면 0출력
if(fuel<0) {
System.out.println(-1);
System.exit(0);
}
//연료를 더해주고, 택시의 위치를 조정
fuel += (distance2*2);
taxiY=goalY;
taxiX=goalX;
}
//연료 출력
System.out.println(fuel);
}
//손님의 위치까지 가는 bfs.
public static Integer[] bfs1() {
Queue<Integer[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new Integer[] {taxiY,taxiX,0});
boolean visited[][]=new boolean[map.length][map.length];
visited[taxiY][taxiX] = true;
ArrayList<Integer[]> list=new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer temp[]= queue.poll();
int nowY=temp[0];
int nowX=temp[1];
int count = temp[2];
//해당 좌표에 목적지가 있다면 list에 넣음
if(map[nowY][nowX].goal!=null)
list.add( new Integer[] {nowY,nowX,count});
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int nextY=nowY+dy[i];
int nextX=nowX+dx[i];
if(nextY<0||nextX<0||nextY>=map.length||nextX>=map.length)
continue;
if(map[nextY][nextX].wall==1||visited[nextY][nextX]==true)
continue;
visited[nextY][nextX] = true;
queue.add(new Integer[] {nextY,nextX,count+1});
}
}
//list size가 0이면 벽으로 가로막혀 손님의 위치까지 가지 못한 것. -1출력
if(list.size()==0) {
System.out.println(-1);
System.exit(0);
}
//손님들의 위치를 정렬
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator<>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer n1[],Integer n2[]) {
if(n1[2]>n2[2]) return 1;
else if(n1[2]==n2[2]) {
if(n1[0]>n2[0]) return 1;
else if(n1[0]==n2[0]) {
if(n1[1]>n2[1]) return 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
});
//손님의 위치, 손님의 목적지의 위치를 반환하고
//해당 좌표의 손님의 목적지를 null로 바꿈
int y=list.get(0)[0];
int x=list.get(0)[1];
int count = list.get(0)[2];
int goalY=map[y][x].goal[0];
int goalX=map[y][x].goal[1];
map[y][x].goal = null;
return new Integer[] {y,x,count,goalY,goalX};
}
//손님의 위치, 목적지의 위치가 주어졌을 때의 bfs
public static int bfs2(int nowY,int nowX,int goalY,int goalX) {
Queue<Integer[]> queue=new LinkedList<>();
boolean visited[][]=new boolean[map.length][map.length];
visited[nowY][nowX] = true;
queue.add(new Integer[] {nowY,nowX,0});
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer temp[]=queue.poll();
int Y=temp[0];
int X=temp[1];
int count = temp[2];
//목적지를 찾았다면 해당 좌표까지의 거리를 return
if(Y==goalY&&X==goalX)
return count;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++) {
int nextY=Y+dy[i];
int nextX=X+dx[i];
if(nextY<0||nextX<0||nextY>=map.length||nextX>=map.length)
continue;
if(map[nextY][nextX].wall==1||visited[nextY][nextX])
continue;
visited[nextY][nextX] = true;
queue.add(new Integer[] {nextY,nextX,count+1});
}
}
//queue가 다 비어도 목적지를 못찾았다면
//벽으로 가로막혀 목적지로 갈 수 없는 것임. -1출력
System.out.println(-1);
System.exit(0);
return 0;
}
}
5. 결과
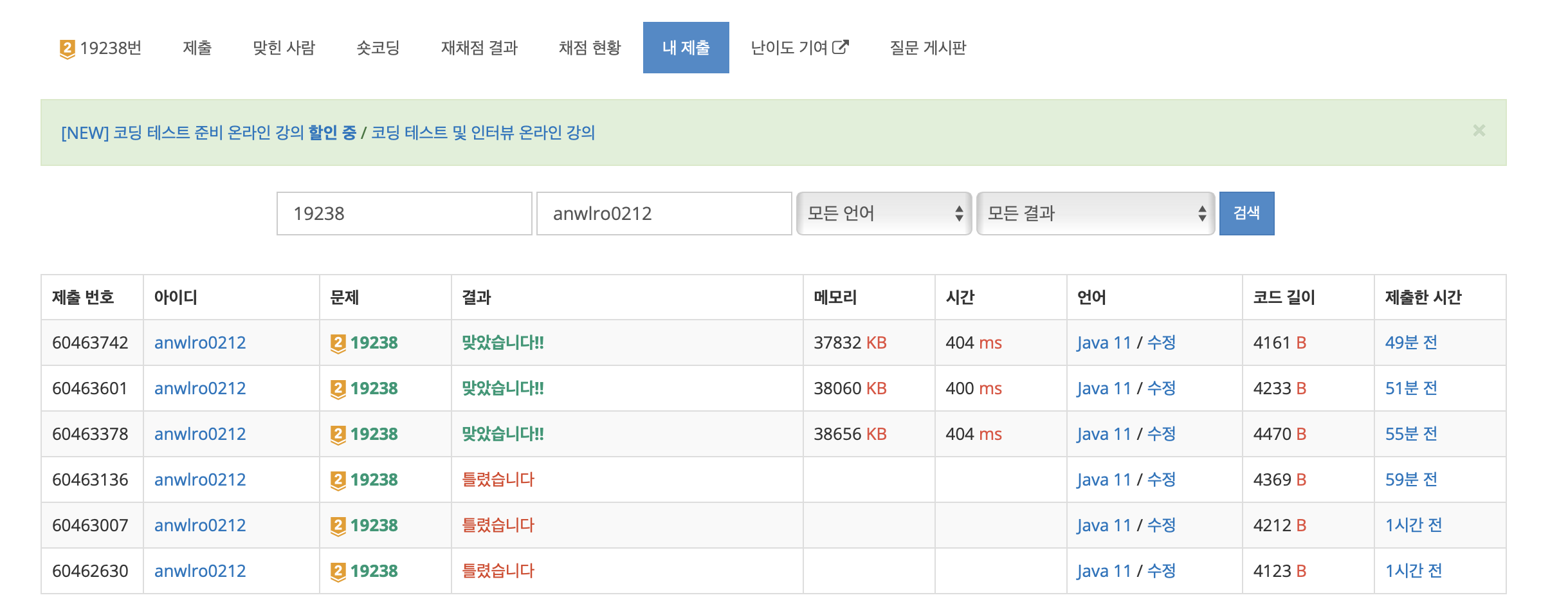
코드에서 visited를 true로 처리해 줄 때, 오타가 있었는데 그를 확인 못해서 3번 틀렸음.
6. 회고
이전까지 풀었던 문제들과 비교해 봤을 때 좀 쉬운 편이었다.
정답률도 20%가 나오는 것은 벽이 생겨서 이동 못하는 걸 고려하지 못해서 그런 게 아닐까 싶다.
나는 bfs 메소드가 2개인데, 이거를 1개로 통합해서 할 수는 없었을까...
하며 생각해 보고 있다.
하루에 백준 1문제 이상 푸는 것을 목표로 하고있다.
https://solved.ac/profile/anwlro0212
