들어가며
정말 많이 쓰지만 내부동작을 정확히는 알지 못했던 HashMap 에 대해 알아보자.
put() 메소드에 대해 자세히 알아보자.
HashMap
HashMap 의 클래스를 보면 여러가지 주석이 적혀 있다.
그 중 중요한 문단 몇가지를 가져왔다.
An instance of HashMap has two parameters that affect its performance: initial capacity and load factor. The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the current capacity, the hash table is rehashed (that is, internal data structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the number of buckets.
용어정리
bucket
- 데이터를 담는공간
- HashMap 구현에서는 Node[] table 의 한칸을 의미한다.
- HashMap의 디폴트 버켓수는 16이다.
load factor
- 현재 bucket 이 가득찬 비율을 의미한다
- 이 수를 넘게 되면 버켓수가 2배가 되고, rehash 된다.
- 디폴트 값은 0.75 이다.
즉, 처음 버켓 개수는 16 개이고, 16*0.75 = 12 이므로 13개 째 버켓이 사용되려는 순간 사이즈가 2배가 되면서 버켓이 32개가 된다는 뜻이다.

그리고 해시테이블 구조는 hash collision 에 대한 대비가 되어 있어야 한다. HashMap 에서는 chaining 기법을 사용하고 있다. 다음 주석을 보자.
This map usually acts as a binned (bucketed) hash table, but
when bins get too large, they are transformed into bins of
TreeNodes, each structured similarly to those in
java.util.TreeMap. Most methods try to use normal bins, but
relay to TreeNode methods when applicable (simply by checking
instanceof a node). Bins of TreeNodes may be traversed and
used like any others, but additionally support faster lookup
when overpopulated. However, since the vast majority of bins in
normal use are not overpopulated, checking for existence of
tree bins may be delayed in the course of table methods.
디폴트로 linkedList 형태로 chaining을 하는데 bucket에 담은 수가 많아지면(collision 된 value 들이 많아지면) TreeNode 형태로 변신한다는 뜻이다.
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
전체 capacity 가 64 이상이고 collision 이 8개가 일어나면 linkedlist가 treeNode 형태로 변경하여, 탐색할때 O(logN)을 보장 해준다.
Node
HashMap 은 내부에 Node 클래스를 통해 Key, Value 를 저장하고 있다.
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
}우리가 주목해야 할점은, Node 클래스 내에 다음 Node 객체를 가르키는 포인터가 존재한다는 점이다. Node<K,V> next;
즉, Node 클래스는 링크드리스트 자료구조 형태를 지니게 된다.
그리고, HashMap은 Node 의 배열인 table 이라는 링크드리스트 배열을 이용해 실제로 Map 을 구현하고 있다.
transient Node<K,V>[] table;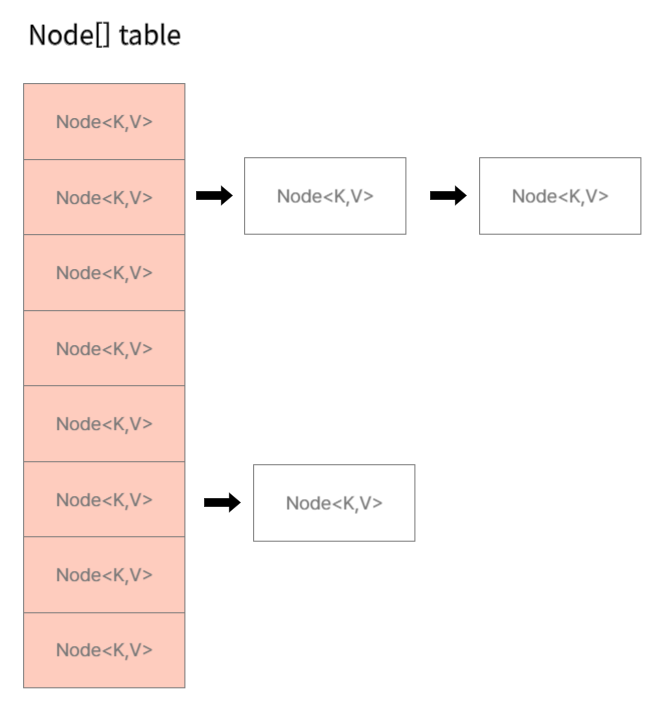
map.put()
put 메소드를 알아보자
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}putVal 메소드를 확인해보자
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//First
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//Second
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//Third
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//Fourth
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//Fifth
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//Sixth
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//Seventh
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//Eighth
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}먼저 //First 아래에 있는 2줄을 보자.
//First
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;HashMap 객체가 생성되고 처음 put 이 일어날때 실행된다.
HashMap이 막 선언된 경우 table 배열이 null 상태이므로 table 배열을 resize() 를 통해 배열을 생성해준다.
//Second 아래에 2줄을 보자.
//Second
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);put 을 진행할 bucket이 비어있었을 경우 이 if문을 실행하게 된다. 비어있는 배열에 새로운 Node 를 생성해 넣어주게 된다.
그렇다면, 그 아래 else 문에는 해당 bucket 이 비어있지 않은 경우 실행되는 코드들이다.
//Third 아래에 있는 코드
//Third
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;p 는 해당 버킷 제일 앞에있는 Node 라고 보면 된다.
이번에 put 한 key가 존재하고 있고, 그게 버킷의 맨 앞단에 있다면 해당코드가 실행되게 된다.
Node e = p 를 해준 이유는 조금 뒤에 나온다.
//Fourth 아래에 있는 코드
//Fourth
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);만약 해당 버킷이 collision 이 많아져서 tree 형태로 바뀐상황이라면 위의 코드가 실행된다.
//Fifth
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//Sixth
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//Seventh
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}//Fifth 에 들어오는 경우는 이번에 put 한 key가 속한 bucket이 비어있지 않고, 버킷의 첫번째 key 가 이번에 put 한 key와 다를 때의 경우다.
//Sixth 아래에는 해당 버킷에 이번에 put한 key가 없는 경우에 실행된다.
e = p.next 를 통해 링크드리스트의 다음 노드들을 탐색하면서 끝까지 탐색했을때까지 이번에 put한 key 가 없을 경우 제일 뒤에 이번에 추가한 Node를 달아주게 된다.
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);이 코드에서 보이듯이 해당 버킷에서 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD 수 보다 더 많은 Node 가 존재할경우 해당 버킷을 링크드리스트에서 트리형태로 바꿔주게 된다.
//Seventh 아래에는 해당 버킷에 이번에 put한 key가 있는 경우 실행된다.
//Eighth 아래 코드를 보자.
//Eighth
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}원래 버킷에 key가 존재했던 경우에 동작하는 코드이다. 이전 코드를 보면 기존에 존재하던 Node 를 e 에 담아두었었다. Node e 에 value 를 이번에 입력한 value로 업데이트 해주게된다.
if (++size > threshold)
resize();마지막으로 위의 코드를 보자. int threshold = 현재 capacity * LOAD_FACTOR 해준 값이 들어있다. 새로운 버킷이 사용되면 로드팩터를 고려해서 캐퍼시티를 늘릴지 말지를 결정 해주는 코드이다.
